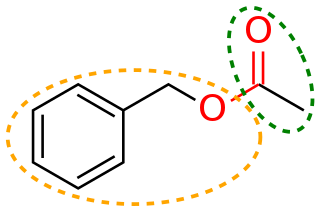
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.
In chemistry, a zwitterion, also called an inner salt, is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively- and negatively-charged functional groups. With amino acids, for example, in solution a chemical equilibrium will be established between the "parent" molecule and the zwitterion.
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate, is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule. The first known racemic mixture was racemic acid, which Louis Pasteur found to be a mixture of the two enantiomeric isomers of tartaric acid. A sample with only a single enantiomer is an enantiomerically pure or enantiopure compound.
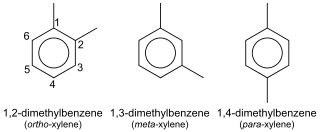
Xylene (from Greek ξύλον xylon, "wood"), xylol or dimethylbenzene is any one of three isomers of dimethylbenzene, or a combination thereof. With the formula (CH3)2C6H4, in each of the three compounds a benzene ring is substituted by two methyl groups. They are all colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquids. They are of great industrial value. The mixture is referred to as both xylene and, more precisely, xylenes. Mixed xylenes refers to a mixture of the xylenes plus ethylbenzene. The four compounds have identical empirical formulas C8H10. Typically the four compounds are produced together by various catalytic reforming and pyrolysis methods.

A meso compound or meso isomer is a non-optically active member of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. This means that despite containing two or more stereogenic centers, the molecule is not chiral. A meso compound is "superposable" on its mirror image. Two objects can be superposed if all aspects of the objects coincide and it does not produce a "(+)" or "(-)" reading when analyzed with a polarimeter.
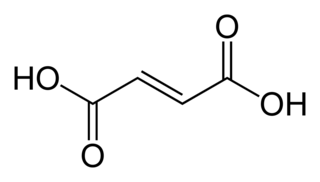
Fumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297. The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C
4H
2O2−
4 ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer.
Dihydroxybenzenes are organic chemical compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three isomer: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.
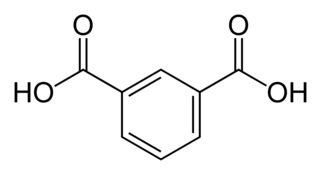
Isophthalic acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO2H)2. This colorless solid is an isomer of phthalic acid and terephthalic acid. The main industrial uses of purified isophthalic acid (PIA) are for the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resin and for the production of unsaturated polyester resin (UPR) and other types of coating resins.
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Pyridinecarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are monocarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinecarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.

Hydroxybutyric acid is a group of four-carbon organic compounds that have both hydroxyl and carboxylic acid functional groups. They can be viewed as derivatives of butyric acid. The carboxylate anion and the esters of hydroxybutyric acids are known as hydroxybutyrates. β-hydroxybutyric acid is relevant to human health as it is a member of a class of products of fatty acid oxidation referred to as ketone bodies.

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical elements may or may not be included in the definition, depending on expert viewpoint.
Dichlorophenols (DCPs) are any of several chemical compounds which are derivatives of phenol containing two chlorine atoms. There are six isomers:

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulas — that is, same number of atoms of each element — but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.

An octadecatrienoic acid is a chemical compounds with formula C
18H
30O
2, a fatty acid with whose molecule has an 18-carbon unbranched backbone with three double bonds.

Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, nonsteroidal, orally active estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, the levorotatory isomer of which is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone.

Benzenetricarboxylic acid is a group of chemical compounds which are tricarboxylic derivatives of benzene. Benzenetricarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:

Pyridinedicarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are dicarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinedicarboxylic acid comes in several isomers:
Pyridinetricarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are tricarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinetricarboxylic acid comes in several isomers:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.















