
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. This contrasts with structural isomers, which share the same molecular formula, but the bond connections or their order differs. By definition, molecules that are stereoisomers of each other represent the same structural isomer.
In chemistry, a zwitterion, also called an inner salt, is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively- and negatively-charged functional groups. With amino acids, for example, in solution a chemical equilibrium will be established between the "parent" molecule and the zwitterion.
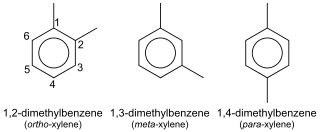
Xylene (from Greek ξύλον xylon, "wood"), xylol or dimethylbenzene is any one of three isomers of dimethylbenzene, or a combination thereof. With the formula (CH3)2C6H4, in each of the three compounds a benzene ring is substituted by two methyl groups. They are all colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquids. They are of great industrial value. The mixture is referred to as both xylene and, more precisely, xylenes. Mixed xylenes refers to a mixture of the xylenes plus ethylbenzene. The four compounds have identical empirical formulas C8H10. Typically the four compounds are produced together by various catalytic reforming and pyrolysis methods.

A meso compound or meso isomer is a non-optically active member of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. This means that despite containing two or more stereogenic centers, the molecule is not chiral. A meso compound is "superposable" on its mirror image. Two objects can be superposed if all aspects of the objects coincide and it does not produce a "(+)" or "(-)" reading when analyzed with a polarimeter.

Pentane is an organic compound with the formula C5H12—that is, an alkane with five carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of three structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, pentane means exclusively the n-pentane isomer; the other two are called isopentane (methylbutane) and neopentane (dimethylpropane). Cyclopentane is not an isomer of pentane because it has only 10 hydrogen atoms where pentane has 12.
Dihydroxybenzenes are organic chemical compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three isomer: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Pyridinecarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are monocarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinecarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.

Hydroxybutyric acid is a group of four-carbon organic compounds that have both hydroxyl and carboxylic acid functional groups. They can be viewed as derivatives of butyric acid. The carboxylate anion and the esters of hydroxybutyric acids are known as hydroxybutyrates. β-hydroxybutyric acid is relevant to human health as it is a member of a class of products of fatty acid oxidation referred to as ketone bodies.

Trimesic acid, also known as benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid, is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(CO2H)3. It is one of three isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid. A colorless solid, trimesic acid has some commercial value as a precursor to some plasticizers.
A trichlorophenol is any organochloride of phenol that contains three covalently bonded chlorine atoms. Trichlorophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine. Different isomers of trichlorophenol exist according to which ring positions on the phenol contain chlorine atoms. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, for example, has two chlorine atoms in the ortho positions and one chlorine atom in the para position.
Dichlorophenols (DCPs) are any of several chemical compounds which are derivatives of phenol containing two chlorine atoms. There are six isomers:

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulas — that is, same number of atoms of each element — but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.

An octadecatrienoic acid is a chemical compounds with formula C
18H
30O
2, a fatty acid with whose molecule has an 18-carbon unbranched backbone with three double bonds.
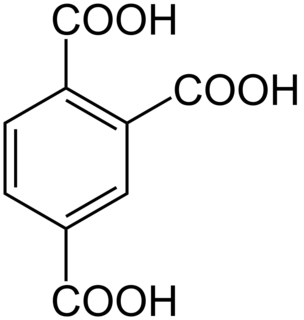
Trimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H3(СООН)3. Like the other isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid, trimellitic acid is a colorless solid. It is prepared by oxidation of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene.

Benzenedicarboxylic acid is a group of chemical compounds which are dicarboxylic derivatives of benzene. Benzenedicarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:

Pyridinedicarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are dicarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinedicarboxylic acid comes in several isomers:
Pyridinetricarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are tricarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinetricarboxylic acid comes in several isomers:

Hemimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H3(СО2Н)3. Like the other isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid, hemimellitic acid is a colorless solid. It is prepared by oxidation of 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.














