
Bursfelde Abbey is a former Benedictine monastery located in Bursfelde, a hamlet which for administrative purposes is included in the municipality of nearby Hannoversch Münden in Lower Saxony, Germany. Today the abbey church and its estate cover a site of approximately 300 hectares which is administered by the Klosterkammer Hannover, a body that operates under the auspices of the Lower Saxony Ministry for Arts and the Sciences to look after reassigned or disused ecclesiastical buildings and other heritage properties in the region. The legal owner of the Bursfelde Monastery Complex is the Evangelical-Lutheran Church of Hanover.
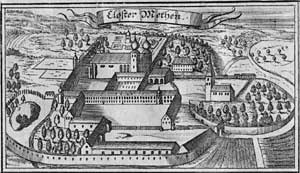
Metten Abbey, or St. Michael's Abbey at Metten is a house of the Benedictine Order in Metten near Deggendorf, situated between the fringes of the Bavarian Forest and the valley of the Danube, in Bavaria in Germany.

Saint Emmeram's Abbey was a Benedictine monastery founded around 739 at Regensburg in Bavaria at the grave of the itinerant Frankish bishop Saint Emmeram. The original abbey church is now a parish church named St. Emmeram's Basilica. The other buildings on the site form a large complex known as Schloss Thurn und Taxis or Schloss St. Emmeram, which has served as the main residence of the Thurn und Taxis princely family since the early 19th century.

Tegernsee Abbey is a former Benedictine monastery in the town and district of Tegernsee in Bavaria. Both the abbey and the town that grew up around it are named after the Tegernsee, the lake on the shores of which they are located. The name is from the Old High German tegarin seo, meaning great lake.

Scheyern Abbey, formerly also Scheyern Priory, is a house of the Benedictine Order in Scheyern in Bavaria.

Niederaltaich Abbey is a house of the Benedictine Order founded in 741, situated in the village of Niederalteich on the Danube in Bavaria.

Oberalteich Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Bogen, Bavaria, Germany.

Scharnitz Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Mittenwald in Bavaria, Germany.

Beuerberg Abbey, formerly a monastery of the Augustinian Canons, is now the Monastery of the Visitation, Beuerberg, a community of the Visitandines in Eurasburg in Bavaria, Germany.

Plankstetten Abbey is a monastery of the Benedictines located between Berching and Beilngries in Bavaria, Germany. It is a member of the Bavarian Congregation of the Benedictine Confederation.

Seeon Abbey is a former Benedictine monastery in the municipality of Seeon-Seebruck in the rural district of Traunstein in Bavaria, Germany.

Wettenhausen Abbey was an Imperial Abbey of Augustinian Canons until its secularization in 1802–1803. Being one of the 40-odd self-ruling Imperial Abbeys of the Holy Roman Empire, Wettenhaussen Abbey was a virtually independent state. Its abbot had seat and voice in the Imperial Diet, where he sat on the Bench of the Prelates of Swabia. At the time of secularization, the Abbey's territory covered 56 square kilometers and it had about 5,400 subjects.

Ellwangen Abbey was the earliest Benedictine monastery established in the Duchy of Swabia, at the present-day town of Ellwangen an der Jagst, Baden-Württemberg, about 100 km (60 mi) north-east of Stuttgart.

Elchingen Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Oberelchingen in Bavaria, Germany, in the diocese of Augsburg.

Aldersbach Abbey is a former Cistercian monastery in the community of Aldersbach in the district of Passau in the valley of the Vils, Lower Bavaria, Germany.
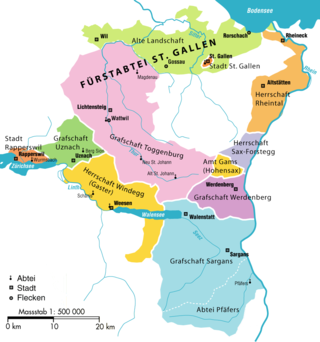
Pfäfers Abbey, also known as St. Pirminsberg from its position on a mountain, was a Benedictine monastery in Pfäfers near Bad Ragaz, in the canton of St. Gallen, Switzerland.

St. George's Abbey in the Black Forest was a Benedictine monastery in St. Georgen im Schwarzwald in the southern Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.

Banz Abbey, now known as Banz Castle, is a former Benedictine monastery, since 1978 a part of the town of Bad Staffelstein north of Bamberg, Bavaria, southern Germany.

Fürstenfeld Abbey is a former Cistercian monastery in Fürstenfeldbruck, Bavaria, Germany.
Roggenburg Abbey is a Premonstratensian canonry in Roggenburg near Neu-Ulm, Bavaria, in operation between 1126 and 1802, and again from its re-foundation in 1986. Since 1992 it has been a dependent priory of Windberg Abbey in Lower Bavaria. The monastery manages a training centre and a museum, and is widely known for its almost unchanged Baroque building and the organ concerts that are held in the church.


















