
Frederick I of Ansbach and Bayreuth was born at Ansbach as the eldest son of Albert III, Margrave of Brandenburg by his second wife Anna, daughter of Frederick II, Elector of Saxony. His elder half-brother was the Elector John Cicero of Brandenburg. Friedrich succeeded his father as Margrave of Ansbach in 1486 and his younger brother Siegmund as Margrave of Bayreuth in 1495.

Charles Frederick was Margrave, Elector and later Grand Duke of Baden from 1738 until his death.

The Margraviate of Baden was a historical territory of the Holy Roman Empire. Spread along the right banks of the Upper Rhine in south-western Germany, it was named a margraviate in 1112 and existed until 1535, when it was split into the two margraviates of Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden. The two parts were reunited in 1771 under Margrave Charles Frederick, even if the three parts of the state maintained their distinct seats to the Reichstag. The restored Margraviate of Baden was elevated to the status of electorate in 1803. In 1806, the Electorate of Baden, receiving territorial additions, became the Grand Duchy of Baden. The rulers of Baden, known as the House of Baden, were a cadet line of the Swabian House of Zähringen.

Archduchess Maria of Austria was the daughter of Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor from the House of Habsburg and Anna of Bohemia and Hungary.

William of Jülich-Cleves-Berge was a Duke of Jülich-Cleves-Berg (1539–1592). William was born in and died in Düsseldorf. He was the only son of John III, Duke of Jülich-Cleves-Berg, and Maria, Duchess of Jülich-Berg. William took over rule of his father's estates upon his death in 1539. Despite his mother having lived until 1543, William also became the Duke of Berg and Jülich and the Count of Ravensberg.

Charles II, Margrave of Baden-Durlach, nicknamed Charles with the bag, governed the Margravate of Baden-Durlach from 1552 to 1577. On 1 June 1556 Charles issued a new Church Order, which made Lutheranism the official religion in Baden-Durlach.

George Frederick of Baden-Durlach was Margrave of Baden-Durlach from 1604 until his abdication in 1622. He also ruled Baden-Baden.
The Second Margrave War was a conflict in the Holy Roman Empire between 1552 and 1555. Instigated by Albert Alcibiades, Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach and Brandenburg-Bayreuth, who was attempting to form a Duchy of Franconia under his rule, the war resulted in widespread devastation in Franconia, while also affecting the Rhineland and Lower Saxony.

Christopher I of Baden was the Margrave of Baden from 1475 to 1515.

Charles III William was Margrave of Baden-Durlach between 1709 and 1738. He was the son of Margrave Frederick Magnus of Baden-Durlach and Augusta Maria of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp. In 1715, he established Karlsruhe, where he built his residence. Karlsruhe has since grown to a large city. With the consolidation of public finances and the creation of a reliable administration, he laid the foundations for the reform policies of his grandson, Charles Frederick.

The Margraviate of Baden-Durlach was an early modern territory of the Holy Roman Empire, in the upper Rhine valley, which existed from 1535 to 1771. It was formed when the Margraviate of Baden was split between the sons of Margrave Christopher I and was named for its capital, Durlach. The other half of the territory became the Margraviate of Baden-Baden, located between the two halves of Baden-Durlach. Baden-Durlach became Lutheran during the Protestant Reformation, unlike Baden-Baden, which remained Catholic. Baden-Durlach occupied Baden-Baden from 1594 to 1622, but was driven out after being defeated at the Battle of Wimpfen, during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). The territory was ravaged during the Nine Years' War (1688–1697). Following the extinction of the Baden-Baden line in 1771, the Baden-Durlach inherited their territories and reunited the Margraviate of Baden. The reunified territory was caught up in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, emerging in 1806 as the Grand Duchy of Baden.

Countess Palatine Christina Magdalena of Kleeburg of the House of Wittelsbach, Margravine of Baden-Durlach, was a Swedish princess, daughter of John Casimir, Count Palatine of Kleeburg and Princess Catherine of Sweden. Christina Magdalena belonged to Swedish royalty as a sister of King Charles X of Sweden, and grew up in Sweden.

Margrave Philip I of Baden took over the administration of his father's possessions Baden (Baden-Baden), Durlach, Pforzheim and Altensteig and parts of Eberstein, Lahr and Mahlberg in 1515 and ruled as governor until he inherited the territories in 1527. From 1524 till 1527, he also acted as an imperial governor in the second Imperial Government.
His official title was Margrave of Baden-Sponheim.
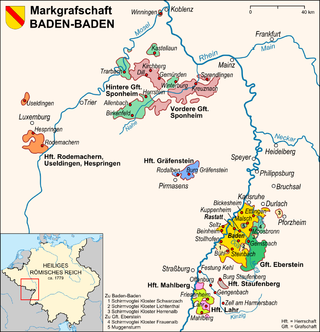
The Margraviate of Baden-Baden was an early modern southwest German territory within the Holy Roman Empire. It was created in 1535 along with the Margraviate of Baden-Durlach as a result of the division of the Margraviate of Baden. Its territory consisted of a core area on the middle stretch of the Upper Rhine around the capital city of Baden, as well as lordships on the Moselle and Nahe.

Margrave Ernest I of Baden-Durlach was the founder of the so-called "Ernestine" line of the House of Baden, the line from which the later Grand Dukes descended. He was the ruling Margrave of Baden-Pforzheim from 1533 and resided in Pforzheim from 1537. In 1565, his son Charles II moved the capital to Durlach and thereby changed the name of his country to Baden-Durlach. He had to deal with the upcoming Reformation and the frequent Ottoman wars in Europe. In this turbulent time, he tried to maintain a neutral position between the Protestants and Catholics. He did not participate in the Schmalkaldic War.
Kunigunde of Brandenburg-Kulmbach was a princess of Brandenburg-Kulmbach by birth and by marriage Margravine of Baden-Durlach.
Bad Rotenfels is a district in the city of Gaggenau, district of Rastatt, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located some 8 km northeast of Baden-Baden.

Ernest Frederick of Baden-Durlach ruled the northern part of the Margraviate of Baden-Durlach. He came to power when he came of age in 1584. He founded the first Gymnasium Illustre in the margraviate. Ernst Friedrich, who had a strict Lutheran upbringing, started a reconciliation between Lutheranism and Calvinism with the publication of the Staffort Book in 1599 His occupation of Upper Baden caused serious conflicts – even with the Emperor – the consequences of which damaged Lower Baden and ultimately also led to losses of territory.

Margrave James III of Baden-Hachberg was margrave of Baden-Hachberg from 1584 to 1590 and resided at Emmendingen. He converted, in 1590, from Lutheranism to the Roman Catholic confession, causing some political turmoil.

Barbara of Württemberg was margravine of the historical German territory of Baden-Durlach. The daughter of Frederick I, Duke of Württemberg and his wife, Sibylla of Anhalt, she was born a Duchess of Württemberg and became margravine after marrying Frederick V, Margrave of Baden-Durlach, in 1616. She is depicted as Saint Barbara in a posthumous miniature portrait.

















