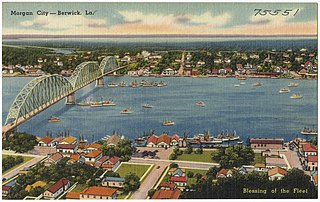The Mississippi River is the primary river, and second-longest river, of the largest drainage basin in the United States. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for 2,340 miles (3,766 km) to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is 1,151,000 sq mi (2,980,000 km2), of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.

The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by the Golden Gate Bridge. The entire shoreline and adjacent waters throughout the strait are managed by the Golden Gate National Recreation Area.

The North Sea Canal is a Dutch ship canal from Amsterdam to the North Sea at IJmuiden, constructed between 1865 and 1876 to enable seafaring vessels to reach the port of Amsterdam. This man-made channel terminates at Amsterdam in the closed-off IJ Bay, which in turn connects to the Amsterdam-Rhine Canal.

The James River is a river in Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows 348 miles (560 km) to the Chesapeake Bay. The river length extends to 444 miles (715 km) if the Jackson River is included, the longer of its two headwaters. It is the longest river in Virginia. Jamestown and Williamsburg, Virginia's first colonial capitals, and Richmond, Virginia's current capital, lie on the James River.

The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway (GIWW) is the portion of the Intracoastal Waterway located along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It is a navigable inland waterway running approximately 1,300 mi (2,100 km) from Saint Marks, Florida, to Brownsville, Texas.
The first USS Arizona was an iron-hulled, side-wheel merchant steamship. Seized by the Confederate States of America in 1862 during the American Civil War, she was captured later the same year by the United States Navy.

The Atchafalaya River is a 137-mile-long (220 km) distributary of the Mississippi River and Red River in south central Louisiana in the United States. It flows south, just west of the Mississippi River, and is the fifth largest river in North America, by discharge. The name Atchafalaya comes from Choctaw for 'long river', from hachcha, 'river', and falaya, 'long'.
Highway 17 is a provincial highway in British Columbia, Canada. It comprises two separate sections connected by a ferry link. The Vancouver Island section is known as the Patricia Bay Highway and connects Victoria to the Swartz Bay ferry terminal in North Saanich. The Lower Mainland section is known as the South Fraser Perimeter Road and connects the Tsawwassen ferry terminal to Delta and Surrey, terminating at an interchange with Highway 1 in the Fraser Valley.

The Tāmaki River or Tāmaki Estuary is mostly an estuarial arm and harbour of the Hauraki Gulf, within the city of Auckland in New Zealand. It extends south for 15 kilometres (9 mi) from its mouth between the suburb of Saint Heliers and the long thin peninsula of Bucklands Beach, which reaches its end at Musick Point. The inlet extends past the suburbs of Glendowie, Wai o Taiki Bay, Point England, Glen Innes, Tāmaki, Panmure, and Ōtāhuhu to the west, and Bucklands Beach, Half Moon Bay, Farm Cove, Sunnyhills and Pakuranga to the east.

Eastchester Bay is a sound between City Island and the mainland Bronx in New York City, New York. Technically, it is not a bay, since it is open to larger bodies of water at both ends. The northern end connects via a narrow channel to Pelham Bay. The Hutchinson River empties into Eastchester Bay near the northern end. The lower portion of the bay opens onto the East River, Little Neck Bay, and Long Island Sound. Eastchester Bay is designated an Essential Fish Habitat by the National Marine Fisheries Service.
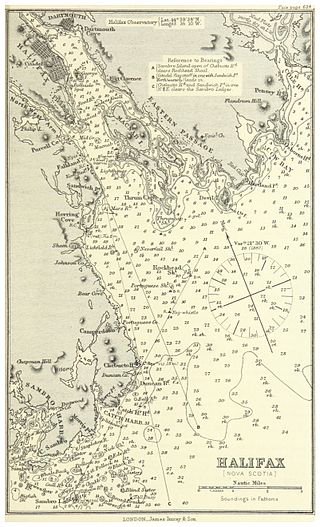
Halifax Harbour is a large natural harbour on the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada, located in the Halifax Regional Municipality. Halifax largely owes its existence to the harbour, being one of the largest and deepest ice-free natural harbours in the world. Before Confederation it was one of the most important commercial ports on the Atlantic seaboard. In 1917, it was the site of the world's largest man-made accidental explosion, when the SS Mont-Blanc blew up in the Halifax Explosion of December 6.

The Atchafalaya Basin, or Atchafalaya Swamp, is the largest wetland and swamp in the United States. Located in south central Louisiana, it is a combination of wetlands and river delta area where the Atchafalaya River and the Gulf of Mexico converge. The river stretches from near Simmesport in the north through parts of eight parishes to the Morgan City southern area.

The Acushnet River is the largest river, 8.6 miles (13.8 km) long, flowing into Buzzards Bay in southeastern Massachusetts, in the United States. The name "Acushnet" comes from the Wampanoag or Algonquian word, "Cushnea", meaning "as far as the waters", a word that was used by the original owners of the land in describing the extent of the parcel they intended to sell to the English settlers from the nearby Plimouth colony. Quite naturally, the English mistook "Cushnea" for a fixed placename or the name of a specific river.
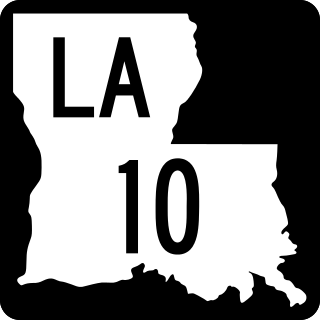
Louisiana Highway 10 (LA 10) is a state highway located in southern Louisiana. It runs 255.51 miles (411.20 km) in an east–west direction from U.S. Highway 171 (US 171) south of Leesville to the Mississippi state line east of Bogalusa.

Victoria Harbour is a harbour, seaport, and seaplane airport in the Canadian city of Victoria, British Columbia. It serves as a cruise ship and ferry destination for tourists and visitors to the city and Vancouver Island. It is both a port of entry and an airport of entry for general aviation. Historically it was a shipbuilding and commercial fishing centre. While the Inner Harbour is fully within the City of Victoria, separating the city's downtown on its east side from the Victoria West neighbourhood, the Upper Harbour serves as the boundary between the City of Victoria and the district municipality of Esquimalt. The inner reaches are also bordered by the district of Saanich and the town of View Royal. Victoria is a federal "public harbour" as defined by Transport Canada. Several port facilities in the harbour are overseen and developed by the Greater Victoria Harbour Authority, however the harbour master's position is with Transport Canada.
The E. J. "Lionel" Grizzaffi Bridge is a cantilever bridge in the U.S. state of Louisiana which carries US 90 over the Atchafalaya River between Berwick and Morgan City.
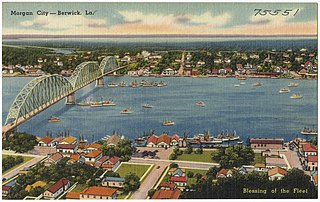
The Long–Allen Bridge is a truss bridge in the U.S. state of Louisiana which carries LA 182 over the Atchafalaya River between Berwick and Morgan City.

The York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway (YN&BR) was an English railway company formed in 1847 by the amalgamation of the York and Newcastle Railway and the Newcastle and Berwick Railway. Both companies were part of the group of business interests controlled by George Hudson, the so-called Railway King. In collaboration with the York and North Midland Railway and other lines he controlled, he planned that the YN&BR would form the major part of a continuous railway between London and Edinburgh. At this stage the London terminal was Euston Square and the route was through Normanton. This was the genesis of the East Coast Main Line, but much remained to be done before the present-day route was formed, and the London terminus was altered to King's Cross.
St. Georges Bay is a bay with shore on the Nova Scotia peninsula and Cape Breton Island, Canada, thus comprising a sub-basin of the Gulf of St. Lawrence.

The West Atchafalaya Floodway is a flood control structure of the Mississippi River and Tributaries Project located in the Lower Atchafalaya Basin in south-central Louisiana. It has a project design flood flow capacity of 250,000 cu ft/s (7,100 m3/s).