
Hancock County is the southernmost county of the U.S. state of Mississippi and is named for Founding Father John Hancock. As of the 2020 census, the population was 46,053. Its county seat is Bay St. Louis.

Bayou Teche is a 125-mile-long (201 km) waterway in south central Louisiana in the United States. Bayou Teche was the Mississippi River's main course when it developed a delta about 2,800 to 4,500 years ago. Through a natural process known as deltaic switching, the river's deposits of silt and sediment cause the Mississippi to change its course every thousand years or so.
The first USS Arizona was an iron-hulled, side-wheel merchant steamship. Seized by the Confederate States of America in 1862 during the American Civil War, she was captured later the same year by the United States Navy.

The Atchafalaya River is a 137-mile-long (220 km) distributary of the Mississippi River and Red River in south central Louisiana in the United States. It flows south, just west of the Mississippi River, and is the fifth largest river in North America, by discharge. The name Atchafalaya comes from Choctaw for 'long river', from hachcha, 'river', and falaya, 'long'.

CSS Oregon was a wooden sidewheel steamer that served as a gunboat in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. Built in 1846 for the Mobile Mail Line, she transported mail between New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama, before the war. In 1861, she was seized by the Governor of Louisiana, Thomas Overton Moore, and served as a blockade runner before being selected for use by the Confederate Army. After transferring men and supplies to Ship Island, she was formally converted into a gunboat and armed with four cannon. Remaining behind on Lake Pontchartrain when many Confederate warships were transferred up the Mississippi River, Oregon served in the Mississippi Sound and Pass Christian areas. She took part in several minor actions involving USS New London, two of which resulted in the Confederates moving into shallow water to avoid close-range action, and the third ending when the Confederate ships abandoned the Pass Christian area. In April 1862, Union pressure confined her and other Confederate ships to Lake Pontchartrain. Later that month, with Union forces closing in on New Orleans, Oregon was sank as a blockship. Her wreck was removed and destroyed in the early 1870s.

The USS Queen of the West was a sidewheel steamer ram ship and the flagship of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. It was built at Cincinnati, Ohio in 1854. It served as a commercial steamer until purchased by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. in 1862 and converted for use as a ram ship. The ship operated in conjunction with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries during the American Civil War.
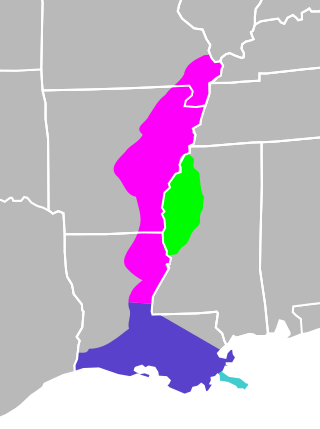
The Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois.

The Tensas River is a river in Louisiana in the United States. The river, known as Tensas Bayou in its upper reaches, begins in East Carroll Parish in the northeast corner of the state and runs roughly southwest for 177 miles (285 km) more or less in parallel with the Mississippi River. The Tensas River merges with the Ouachita River in Jonesville in Catahoula Parish to become the Black River, not to be confused with Black Lake in Natchitoches Parish in north central Louisiana.

The Atchafalaya Basin, or Atchafalaya Swamp, is the largest wetland and swamp in the United States. Located in south central Louisiana, it is a combination of wetlands and river delta area where the Atchafalaya River and the Gulf of Mexico converge. The river stretches from near Simmesport in the north through parts of eight parishes to the Morgan City southern area.
The Battle of Goodrich's Landing, Louisiana, was fought on June 29 and June 30, 1863, between Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. The Confederates attacked several Union regiments, who were composed mostly of black soldiers, in an attempt to disrupt the campaign at Vicksburg, Mississippi.
The Battle of Fort Bisland was fought in the American Civil War between Union Major General Nathaniel P. Banks against Confederate Major General Richard Taylor during Banks' operations against the Bayou Teche region in southern Louisiana.
Border irregularities of the United States, particularly panhandles and highway incursions into other jurisdictions, are shown here. Often they are a result of borders which do not conform to geological features such as changes in the course of a river that previously marked a border.
Berwick Bay is the section of the Lower Atchafalaya River in Louisiana from Morgan City north to Sixmile Lake. U.S. Route 90 crosses Berwick Bay connecting the town of Berwick on the west bank of the Atchafalaya to Morgan City on the east bank. There is also a Southern Pacific vertical lift bridge connecting the two municipalities. This stretch of water lends its name to Vessel Traffic Service Berwick Bay which manages the waters south of 29°45' N., west of 91°10' W., north of 29°37' N., and east of 91°18' W. These waters include the junction of the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway, the Port Allen-Morgan City Alternate Route and several tributary bayous. Narrow bridge openings and a swift river current require one-way traffic flow through the bridges. VTS Berwick Bay is unique among United States Coast Guard Vessel Traffic Services because it maintains direct control of vessel traffic.

USS Calhoun was a captured Confederate steamer and blockade runner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.
USS Ida was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used as a towboat and dispatch boat by the Navy, and she provided her services to ships in the blockade squadrons.

USS Kinsman, sometimes called USS Colonel Kinsman, was a sidewheel steamer captured by the Union Army during the American Civil War. She was used by the Army and then by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. On 23 February 1863, she hit a snag and sank.
Fort Adams is a small, river port community in Wilkinson County, Mississippi, United States, about 40 miles (64 km) south of Natchez. It is notable for having been the U.S. port of entry on the Mississippi River, before the acquisition of New Orleans; it was the site of an early fort by that name.

The Berwick Bay Bridge is a vertical lift bridge in the U.S. state of Louisiana which carries the BNSF Railway over the Atchafalaya River between Berwick and Morgan City. The bridge is primarily used for freight, but Amtrak runs the Sunset Limited three times weekely per direction over the line.
The A. B. Seger was acquired by the Confederate States Navy in 1861 for service as a gunboat in Berwick Bay, Louisiana. The steamer operated with the naval force of Flag Officer George N. Hollins, CSN, who was charged with the defence of the Mississippi River and Louisiana coast.

The Cypress Grove Plantation was a Southern plantation owned by President Zachary Taylor near Rodney, Mississippi. Later, it was also known as Buena Vista Plantation.












