Related Research Articles

Beta-secretase 2 is an enzyme that cleaves Glu-Val-Asn-Leu!Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe in the Swedish variant of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein. BACE2 is a close homolog of BACE1.

Amyloid beta denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP), which is cleaved by beta secretase and gamma secretase to yield Aβ in a cholesterol-dependent process and substrate presentation. Aβ molecules can aggregate to form flexible soluble oligomers which may exist in several forms. It is now believed that certain misfolded oligomers can induce other Aβ molecules to also take the misfolded oligomeric form, leading to a chain reaction akin to a prion infection. The oligomers are toxic to nerve cells. The other protein implicated in Alzheimer's disease, tau protein, also forms such prion-like misfolded oligomers, and there is some evidence that misfolded Aβ can induce tau to misfold.

Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) is an integral membrane protein expressed in many tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons. It functions as a cell surface receptor and has been implicated as a regulator of synapse formation, neural plasticity, antimicrobial activity, and iron export. It is coded for by the gene APP and regulated by substrate presentation. APP is best known as the precursor molecule whose proteolysis generates amyloid beta (Aβ), a polypeptide containing 37 to 49 amino acid residues, whose amyloid fibrillar form is the primary component of amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients.

Secretases are enzymes that "snip" pieces off a longer protein that is embedded in the cell membrane.

Beta-secretase 1, also known as beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1, beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), membrane-associated aspartic protease 2, memapsin-2, aspartyl protease 2, and ASP2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BACE1 gene. Expression of BACE1 is observed mainly in neurons.
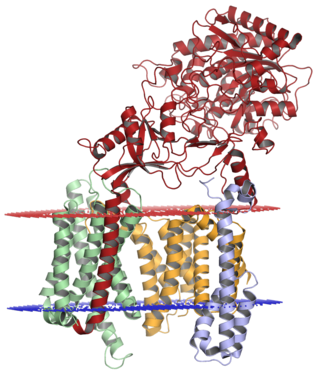
Gamma secretase is a multi-subunit protease complex, itself an integral membrane protein, that cleaves single-pass transmembrane proteins at residues within the transmembrane domain. Proteases of this type are known as intramembrane proteases. The most well-known substrate of gamma secretase is amyloid precursor protein, a large integral membrane protein that, when cleaved by both gamma and beta secretase, produces a short 37-43 amino acid peptide called amyloid beta whose abnormally folded fibrillar form is the primary component of amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Gamma secretase is also critical in the related processing of several other type I integral membrane proteins, such as Notch, ErbB4, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, ephrin-B2, or CD44.

Presenilins are a family of related multi-pass transmembrane proteins which constitute the catalytic subunits of the gamma-secretase intramembrane protease protein complex. They were first identified in screens for mutations causing early onset forms of familial Alzheimer's disease by Peter St George-Hyslop. Vertebrates have two presenilin genes, called PSEN1 that codes for presenilin 1 (PS-1) and PSEN2 that codes for presenilin 2 (PS-2). Both genes show conservation between species, with little difference between rat and human presenilins. The nematode worm C. elegans has two genes that resemble the presenilins and appear to be functionally similar, sel-12 and hop-1.
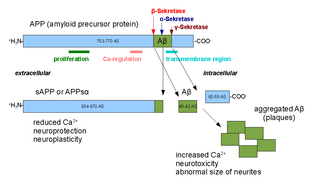
Alpha secretases are a family of proteolytic enzymes that cleave amyloid precursor protein (APP) in its transmembrane region. Specifically, alpha secretases cleave within the fragment that gives rise to the Alzheimer's disease-associated peptide amyloid beta when APP is instead processed by beta secretase and gamma secretase. The alpha-secretase pathway is the predominant APP processing pathway. Thus, alpha-secretase cleavage precludes amyloid beta formation and is considered to be part of the non-amyloidogenic pathway in APP processing. Alpha secretases are members of the ADAM family, which are expressed on the surfaces of cells and anchored in the cell membrane. Several such proteins, notably ADAM10, have been identified as possessing alpha-secretase activity. Upon cleavage by alpha secretases, APP releases its extracellular domain - a fragment known as APPsα - into the extracellular environment in a process known as ectodomain shedding.

Nicastrin, also known as NCSTN, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCSTN gene.
APH-1 is a protein gene product originally identified in the Notch signaling pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans as a regulator of the cell-surface localization of nicastrin. APH-1 homologs in other organisms, including humans, have since been identified as components of the gamma secretase complex along with the catalytic subunit presenilin and the regulatory subunits nicastrin and PEN-2. The gamma-secretase complex is a multimeric protease responsible for the intramembrane proteolysis of transmembrane proteins such as the Notch protein and amyloid precursor protein (APP). Gamma-secretase cleavage of APP is one of two proteolytic steps required to generate the peptide known as amyloid beta, whose misfolded form is implicated in the causation of Alzheimer's disease. All of the components of the gamma-secretase complex undergo extensive post-translational modification, especially proteolytic activation; APH-1 and PEN-2 are regarded as regulators of the maturation process of the catalytic component presenilin. APH-1 contains a conserved alpha helix interaction motif glycine-X-X-X-glycine (GXXXG) that is essential to both assembly of the gamma secretase complex and to the maturation of the components.

PSENEN, formally PEN-2, is a protein that is a regulatory component of the gamma secretase complex, a protease complex responsible for proteolysis of transmembrane proteins such as the Notch protein and amyloid precursor protein (APP). The gamma secretase complex consists of PEN-2, APH-1, nicastrin, and the catalytic subunit presenilin. PEN-2 is a 101-amino acid integral membrane protein likely with a topology such that both the N-terminus and the C-terminus face first the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum and later the extracellular environment. Biochemical studies have shown that a conserved sequence motif D-Y-L-S-F at the C-terminus, as well as the overall length of the C-terminal tail, is required for the formation of an active gamma secretase complex.

Presenilin-1(PS-1) is a presenilin protein that in humans is encoded by the PSEN1 gene. Presenilin-1 is one of the four core proteins in the gamma secretase complex, which is considered to play an important role in generation of amyloid beta (Aβ) from amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP). Accumulation of amyloid beta is associated with the onset of Alzheimer's disease.

Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRP1B gene.
C99 is a past version of the C programming language standard.
Early-onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD), also called younger-onset Alzheimer's disease (YOAD), is Alzheimer's disease diagnosed before the age of 65. It is an uncommon form of Alzheimer's, accounting for only 5–10% of all Alzheimer's cases. About 60% have a positive family history of Alzheimer's and 13% of them are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Most cases of early-onset Alzheimer's share the same traits as the "late-onset" form and are not caused by known genetic mutations. Little is understood about how it starts.

Protein pigeon homolog also known as gamma-secretase activating protein (GSAP) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PION gene.
The Alzheimer's disease biomarkers are neurochemical indicators used to assess the risk or presence of the disease. The biomarkers can be used to diagnose Alzheimer's disease (AD) in a very early stage, but they also provide objective and reliable measures of disease progress. It is imperative to diagnose AD disease as soon as possible, because neuropathologic changes of AD precede the symptoms by years. It is well known that amyloid beta (Aβ) is a good indicator of AD disease, which has facilitated doctors to accurately pre-diagnose cases of AD. When Aβ peptide is released by proteolytic cleavage of amyloid-beta precursor protein, some Aβ peptides that are solubilized are detected in CSF and blood plasma which makes AB peptides a promising candidate for biological markers. It has been shown that the amyloid beta biomarker shows 80% or above sensitivity and specificity, in distinguishing AD from dementia. It is believed that amyloid beta as a biomarker will provide a future for diagnosis of AD and eventually treatment of AD.
Gamma subunit may refer to:
The Swedish mutation, or familial Alzheimer's disease genetic mutation, is one of the most well known genetic variations that causes early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease.

DAPT is a chemical compound used in the study of the Notch signaling pathway. DAPT is a γ-secretase inhibitor. It indirectly inhibits Notch, which is a substrate for γ-secretase.
References
- ↑ Tallon C, Farah MH (October 2017). "Beta secretase activity in peripheral nerve regeneration". Neural Regeneration Research. 12 (10): 1565–1574. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.217319 . PMC 5696827 . PMID 29171411.