Related Research Articles

A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (~109 to 1011 T, ~1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays and gamma rays.

A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of magnetic field and accompanying plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established.
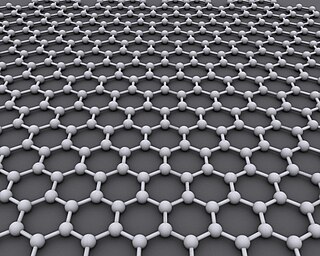
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a honeycomb nanostructure. The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the graphite allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds.
In astrophysics, chemically peculiar stars are stars with distinctly unusual metal abundances, at least in their surface layers.
Multiferroics are defined as materials that exhibit more than one of the primary ferroic properties in the same phase:

A Majorana fermion, also referred to as a Majorana particle, is a fermion that is its own antiparticle. They were hypothesised by Ettore Majorana in 1937. The term is sometimes used in opposition to a Dirac fermion, which describes fermions that are not their own antiparticles.
The magnetospheric eternally collapsing object (MECO) is an alternative model for black holes initially proposed by Indian scientist Abhas Mitra in 1998 and later generalized by American researchers Darryl J. Leiter and Stanley L. Robertson. A proposed observable difference between MECOs and black holes is that a MECO can produce its own intrinsic magnetic field. An uncharged black hole cannot produce its own magnetic field, though its accretion disk can.
Quantum cloning is a process that takes an arbitrary, unknown quantum state and makes an exact copy without altering the original state in any way. Quantum cloning is forbidden by the laws of quantum mechanics as shown by the no cloning theorem, which states that there is no operation for cloning any arbitrary state perfectly. In Dirac notation, the process of quantum cloning is described by:

Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface.

Radio relics are diffuse synchrotron radio sources found in the peripheral regions of galaxy clusters. As in the case of radio halos, they do not have any obvious galaxy counterpart, but their shapes are much more elongated and irregular compared to those of radio halos. Their energy distribution is steep, with hints of a distribution of different ages for the emitting electrons across the whole dimension of the emitting region.

The nitrogen-vacancy center is one of numerous photoluminescent point defects in diamond. Its most explored and useful properties include its spin-dependent photoluminescence, and its relatively long (millisecond) spin coherence at room temperature. The NV center energy levels are modified by magnetic fields, electric fields, temperature, and strain, which allow it to serve as a sensor of a variety of physical phenomena. Its atomic size and spin properties can form the basis for useful quantum sensors. It has also been explored for applications in quantum computing, quantum simulation, and spintronics.
Within quantum technology, a quantum sensor utilizes properties of quantum mechanics, such as quantum entanglement, quantum interference, and quantum state squeezing, which have optimized precision and beat current limits in sensor technology. The field of quantum sensing deals with the design and engineering of quantum sources and quantum measurements that are able to beat the performance of any classical strategy in a number of technological applications. This can be done with photonic systems or solid state systems.
In chemistry, oxypnictides are a class of materials composed of oxygen, a pnictogen and one or more other elements. Although this group of compounds has been recognized since 1995, interest in these compounds increased dramatically after the publication of the superconducting properties of LaOFeP and LaOFeAs which were discovered in 2006 and 2008. In these experiments the oxide was partly replaced by fluoride.

A comet tail and coma are visible features of a comet when they are illuminated by the Sun and may become visible from Earth when a comet passes through the inner Solar System. As a comet approaches the inner Solar System, solar radiation causes the volatile materials within the comet to vaporize and stream out of the nucleus, carrying dust away with them.
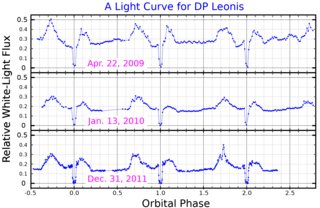
DP Leonis is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Leo. It is a variable star that ranges in apparent visual magnitude from 17.5 down to 19. The system is located at a distance of approximately 990 light-years from the Sun based on parallax. It is a cataclysmic variable star of the AM Herculis-type also known as polars. The system comprises an eclipsing white dwarf and red dwarf in tight orbit and an extrasolar planet. This eclipsing variable was discovered by P. Biermann and associates in 1982 as the optical counterpart to the EINSTEIN X-ray source E1114+182.
In condensed matter physics, a quantum spin liquid is a phase of matter that can be formed by interacting quantum spins in certain magnetic materials. Quantum spin liquids (QSL) are generally characterized by their long-range quantum entanglement, fractionalized excitations, and absence of ordinary magnetic order.

Hughes–Drever experiments are spectroscopic tests of the isotropy of mass and space. Although originally conceived of as a test of Mach's principle, they are now understood to be an important test of Lorentz invariance. As in Michelson–Morley experiments, the existence of a preferred frame of reference or other deviations from Lorentz invariance can be tested, which also affects the validity of the equivalence principle. Thus these experiments concern fundamental aspects of both special and general relativity. Unlike Michelson–Morley type experiments, Hughes–Drever experiments test the isotropy of the interactions of matter itself, that is, of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The accuracy achieved makes this kind of experiment one of the most accurate confirmations of relativity.

Supra-arcade downflows (SADs) are sunward-traveling plasma voids that are sometimes observed in the Sun's outer atmosphere, or corona, during solar flares. In solar physics, arcade refers to a bundle of coronal loops, and the prefix supra indicates that the downflows appear above flare arcades. They were first described in 1999 using the Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT) on board the Yohkoh satellite. SADs are byproducts of the magnetic reconnection process that drives solar flares, but their precise cause remains unknown.

BP Tauri is a young T Tauri star in the constellation of Taurus about 416 light years away, belonging to the Taurus Molecular Cloud.

Magnetic switchbacks are sudden reversals in the magnetic field of the solar wind. They can also be described as traveling disturbances in the solar wind that caused the magnetic field to bend back on itself. They were first observed by the NASA-ESA mission Ulysses, the first spacecraft to fly over the Sun's poles. NASA's Parker Solar Probe and NASA/ESA Solar Orbiter both observed switchbacks.
References
- ↑ Xu, Hao; O'Shea, Brian W.; Collins, David C.; Norman, Michael L.; Li, Hui; Li, Shengtai (2008). "The Biermann Battery in Cosmological MHD Simulations of Population III Star Formation". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 688 (2): L57. arXiv: 0807.2647 . Bibcode:2008ApJ...688L..57X. doi:10.1086/595617. S2CID 118321017.
- ↑ Biermann, L. "Uber den Ursprung der Magnetfelder auf Sternen und im interstellaren Raum (mit einem Anhang von A. Schluter)". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung. 5: 65.
- ↑ Khanna, Ramon (1998). "Generation of magnetic fields by a gravitomagnetic plasma battery". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 295 (1): L6–L10. arXiv: astro-ph/9803240 . Bibcode:1998MNRAS.295L...6K. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.29511447.x . S2CID 15612364.