Related Research Articles
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse and Lazarus contain the necessary compiler, interpreter or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and NetBeans, do not.
Turbo Pascal is a software development system that includes a compiler and an integrated development environment (IDE) for the programming language Pascal running on the operating systems CP/M, CP/M-86, and MS-DOS. It was originally developed by Anders Hejlsberg at Borland, and was notable for its very fast compiling. Turbo Pascal, and the later but similar Turbo C, made Borland a leader in PC-based development tools.
In typography, a serif is a small line or stroke regularly attached to the end of a larger stroke in a letter or symbol within a particular font or family of fonts. A typeface or "font family" making use of serifs is called a serif typeface, and a typeface that does not include them is sans-serif. Some typography sources refer to sans-serif typefaces as "grotesque" or "Gothic" and serif typefaces as "roman".
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.

Photographic paper is a paper coated with a light-sensitive chemical, used for making photographic prints. When photographic paper is exposed to light, it captures a latent image that is then developed to form a visible image; with most papers the image density from exposure can be sufficient to not require further development, aside from fixing and clearing, though latent exposure is also usually present. The light-sensitive layer of the paper is called the emulsion, and functions similarly to photographic film. The most common chemistry used is gelatin silver, but other alternatives have also been used.

Bodoni is the name given to the serif typefaces first designed by Giambattista Bodoni (1740–1813) in the late eighteenth century and frequently revived since. Bodoni's typefaces are classified as Didone or modern. Bodoni followed the ideas of John Baskerville, as found in the printing type Baskerville—increased stroke contrast reflecting developing printing technology and a more vertical axis—but he took them to a more extreme conclusion. Bodoni had a long career and his designs changed and varied, ending with a typeface of a slightly condensed underlying structure with flat, unbracketed serifs, extreme contrast between thick and thin strokes, and an overall geometric construction.

Adrian Johann Frutiger was a Swiss typeface designer who influenced the direction of type design in the second half of the 20th century. His career spanned the hot metal, phototypesetting and digital typesetting eras. Until his death, he lived in Bremgarten bei Bern.

In the processing of photographic films, plates or papers, the photographic developer is one or more chemicals that convert the latent image to a visible image. Developing agents achieve this conversion by reducing the silver halides, which are pale-colored, into silver metal, which is black when in the form of fine particles. The conversion occurs within the gelatine matrix. The special feature of photography is that the developer acts more quickly on those particles of silver halide that have been exposed to light. When left in developer, all the silver halides will eventually be reduced and turn black. Generally, the longer a developer is allowed to work, the darker the image.

Stop bath is an acidic solution used for processing black-and-white photographic films, plates, and paper. It is used to neutralize the alkaline developer, thus halting development.
C-41 is a chromogenic color print film developing process introduced by Kodak in 1972, superseding the C-22 process. C-41, also known as CN-16 by Fuji, CNK-4 by Konica, and AP-70 by AGFA, is the most popular film process in use, with most, if not all photofinishing labs devoting at least one machine to this development process.

Catechol, also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4(OH)2. It is the ortho isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Small amounts of catechol occur in fruits and vegetables.
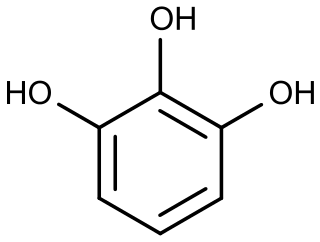
Pyrogallol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a water-soluble, white solid although samples are typically brownish because of its sensitivity toward oxygen. It is one of three isomers of benzenetriols.

Jonathan Hoefler is an American type designer. Hoefler founded the Hoefler Type Foundry in 1989, a type foundry in New York.

Didone is a genre of serif typeface that emerged in the late 18th century and was the standard style of general-purpose printing during the 19th century. It is characterized by:
Fogging in photography is the deterioration in the quality of the image or the negative caused either by extraneous light, other electromagnetic radiation, radioactivity or the effects of a processing chemical. It is seen either as deposition of silver or dyes across all or part of the image unrelated to the original exposure. It can be confused with chemical staining that can be produced from poorly compounded developer, contamination of processing baths or poor washing after processing.

Bell is the name given to a serif typeface designed and cut in 1788 by the punchcutter Richard Austin for the British Letter Foundry, operated by publisher John Bell, and revived several times since.
Prestige refers to a good reputation or high esteem; in earlier usage, prestige meant "showiness".

Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast, and resolution of the film. Film is typically segmented in frames, that give rise to separate photographs.

Bean dip is a type of dipping sauce made using beans or refried beans as a primary ingredient. It is typically served with tortilla chips, and can also be served with other foods such as crackers and crudités. Various types of beans are used, and fresh-cooked, canned or flaked beans can be used. Various additional ingredients are used in its preparation, such as onion, garlic, chili peppers and spices, and it is sometimes garnished with some ingredients. Bean dip can be served cold, at room temperature, or hot. Bean dip is sometimes used as an ingredient in the preparation of other dishes such as burritos and quesadillas.

Mordançage is an alternative photographic process that alters silver gelatin prints to give them a degraded effect. The mordançage solution works in two ways: it chemically bleaches the print so that it can be redeveloped, and it lifts the black areas of the emulsion away from the paper, giving the appearance of veils. Once the emulsion is lifted, it can then be removed or manipulated depending on the desired outcome. Areas where the emulsion was removed appear to be in relief. These prints can become oxidized during their creation, further altering the tonality of the image.
References
- ↑ Troop, Bill and Anchell, Steve (1998) "The Film Developing Cookbook". Focal Press/Reed Elsevier, ISBN 0-240-80277-2.
- ↑ Routledge, ISBN 1138204870
- ↑ "La Bible du développement de films noir et blanc", Éditions First, ISBN 2412061335
- ↑ Richard J. Henry, 1987 "Controls in Black and White Photography", 2nd edition, Focal Press, ISBN 978-0240517889.
- 1 2 Hutchings, Gordon (1992) "The Book of Pyro". Bitter Dog Press, ISBN B0006P3UEW.
- ↑ Troop, Bill (1993) "Silicon Valley IDE mirror card: safety in numbers". PC Magazine, Volume 12 Issue 12, June 29, 1993. Ziff-Davis Publishing Co.
- ↑ US Patent nos. 6,772,108 and 8,073,675
- 1 2 Home Cooks Pull the Plug On Kitchen Appliances
- ↑ Collins, Ian, 2007. "Tell me the truth about an animal attraction," Eastern Daily Press, 27 December 2007.