Related Research Articles

AppImage is a format for distributing portable software on Linux without needing superuser permissions to install the application. It tries also to allow Linux distribution-agnostic binary software deployment for application developers, also called upstream packaging. Released first in 2004 under the name klik, it was continuously developed, then renamed in 2011 to PortableLinuxApps and later in 2013 to AppImage.
This is a comparison of notable free and open-source configuration management software, suitable for tasks like server configuration, orchestration and infrastructure as code typically performed by a system administrator.
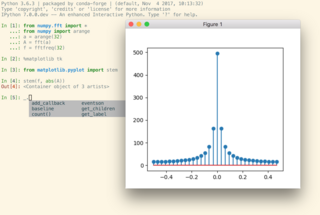
IPython is a command shell for interactive computing in multiple programming languages, originally developed for the Python programming language, that offers introspection, rich media, shell syntax, tab completion, and history. IPython provides the following features:

Cython is a superset of the programming language Python, which allows developers to write Python code that yields performance comparable to that of C.
FriCAS is a general purpose computer algebra system with a strong focus on mathematical research and development of new algorithms. It comprises an interpreter, a compiler and a still-growing library of more than 1,000 domains and categories.

Node.js is a cross-platform, open-source server environment that can run on Windows, Linux, Unix, macOS, and more. Node.js is a back-end JavaScript runtime environment, runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, and executes JavaScript code outside a web browser.
Dart is a programming language designed by Lars Bak and Kasper Lund and developed by Google. The programming language can be used to develop web and mobile apps as well as server and desktop applications.
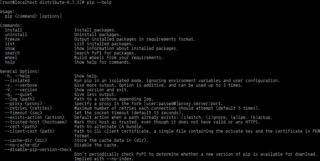
pip is a package-management system written in Python and is used to install and manage software packages. The Python Software Foundation recommends using pip for installing Python applications and its dependencies during deployment. Pip connects to an online repository of public packages, called the Python Package Index. Pip can be configured to connect to other package repositories, provided that they comply to Python Enhancement Proposal 503.

Julia is a high-level, general-purpose dynamic programming language. Its features are well suited for numerical analysis and computational science.
Docker is a set of platform as a service (PaaS) products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. The service has both free and premium tiers. The software that hosts the containers is called Docker Engine. It was first released in 2013 and is developed by Docker, Inc.

Anaconda is a distribution of the Python and R programming languages for scientific computing, that aims to simplify package management and deployment. The distribution includes data-science packages suitable for Windows, Linux, and macOS. It is developed and maintained by Anaconda, Inc., which was founded by Peter Wang and Travis Oliphant in 2012. As an Anaconda, Inc. product, it is also known as Anaconda Distribution or Anaconda Individual Edition, while other products from the company are Anaconda Team Edition and Anaconda Enterprise Edition, neither of which are free.
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management. Originally designed by Google, the project is now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation.

WebAssembly defines a portable binary-code format and a corresponding text format for executable programs as well as software interfaces for facilitating interactions between such programs and their host environment.

American fuzzy lop (AFL), stylized in lowercase as american fuzzy lop, is a free software fuzzer that employs genetic algorithms in order to efficiently increase code coverage of the test cases. So far it has detected dozens of significant software bugs in major free software projects, including X.Org Server, PHP, OpenSSL, pngcrush, bash, Firefox, BIND, Qt, and SQLite.

Eclipse Che is an open-source, Java-based developer workspace server and Online IDE. It includes a multi-user remote development platform. The workspace server comes with a flexible RESTful webservice. It also contains a SDK for creating plug-ins for languages, frameworks or tools. Eclipse Che is an Eclipse Cloud Development (ECD) top-level project, allowing contributions from the user community.

A notebook interface or computational notebook is a virtual notebook environment used for literate programming, a method of writing computer programs. Some notebooks are WYSIWYG environments including executable calculations embedded in formatted documents; others separate calculations and text into separate sections. Notebooks share some goals and features with spreadsheets and word processors but go beyond their limited data models.

Searx is a free and open-source metasearch engine, available under the GNU Affero General Public License version 3, with the aim of protecting the privacy of its users. To this end, Searx does not share users' IP addresses or search history with the search engines from which it gathers results. Tracking cookies served by the search engines are blocked, preventing user-profiling-based results modification. By default, Searx queries are submitted via HTTP POST, to prevent users' query keywords from appearing in webserver logs. Searx was inspired by the Seeks project, though it does not implement Seeks' peer-to-peer user-sourced results ranking.

Project Jupyter is a project to develop open-source software, open standards, and services for interactive computing across multiple programming languages. It was spun off from IPython in 2014 by Fernando Pérez and Brian Granger. Project Jupyter's name is a reference to the three core programming languages supported by Jupyter, which are Julia, Python and R. Its name and logo are an homage to Galileo's discovery of the moons of Jupiter, as documented in notebooks attributed to Galileo. Project Jupyter has developed and supported the interactive computing products Jupyter Notebook, JupyterHub, and JupyterLab. Jupyter is financially sponsored by NumFOCUS.
Container Linux is a discontinued open-source lightweight operating system based on the Linux kernel and designed for providing infrastructure to clustered deployments, while focusing on automation, ease of application deployment, security, reliability and scalability. As an operating system, Container Linux provided only the minimal functionality required for deploying applications inside software containers, together with built-in mechanisms for service discovery and configuration sharing.

MkDocs is static site generator designed for building project documentation. It is written in Python, and also used in other environments.
References
- ↑ "Getting started with Binder — Binder 0.1b documentation". mybinder.readthedocs.io. Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ↑ "Toward versatile JupyterHub deployments, with the Binder and JupyterHub convergence". opendreamkit.org. Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ↑ Holdgraf, Chris (2017-11-30). "Binder 2.0, a Tech Guide". Medium. Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ↑ "The Binder Project". mybinder.org. Retrieved 2019-11-22.
- ↑ "The BinderHub Federation — BinderHub 0.1.0 documentation". binderhub.readthedocs.io. Retrieved 2019-11-22.