
Artificial neural networks are a branch of machine learning models that are built using principles of neuronal organization discovered by connectionism in the biological neural networks constituting animal brains.
In computational intelligence (CI), an evolutionary algorithm (EA) is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses mechanisms inspired by biological evolution, such as reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection. Candidate solutions to the optimization problem play the role of individuals in a population, and the fitness function determines the quality of the solutions. Evolution of the population then takes place after the repeated application of the above operators.
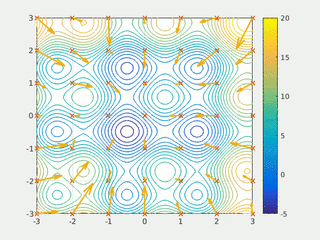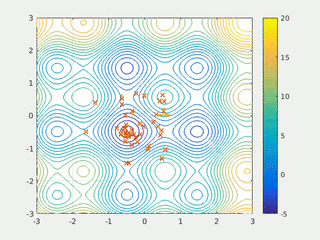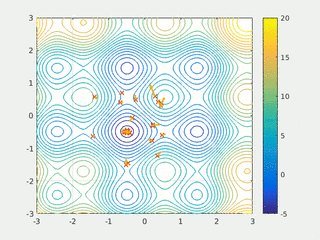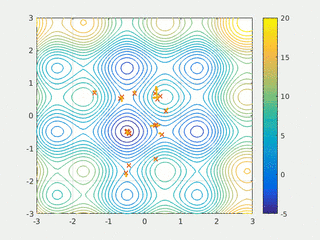
In computational science, particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a computational method that optimizes a problem by iteratively trying to improve a candidate solution with regard to a given measure of quality. It solves a problem by having a population of candidate solutions, here dubbed particles, and moving these particles around in the search-space according to simple mathematical formula over the particle's position and velocity. Each particle's movement is influenced by its local best known position, but is also guided toward the best known positions in the search-space, which are updated as better positions are found by other particles. This is expected to move the swarm toward the best solutions.
Neuroevolution, or neuro-evolution, is a form of artificial intelligence that uses evolutionary algorithms to generate artificial neural networks (ANN), parameters, and rules. It is most commonly applied in artificial life, general game playing and evolutionary robotics. The main benefit is that neuroevolution can be applied more widely than supervised learning algorithms, which require a syllabus of correct input-output pairs. In contrast, neuroevolution requires only a measure of a network's performance at a task. For example, the outcome of a game can be easily measured without providing labeled examples of desired strategies. Neuroevolution is commonly used as part of the reinforcement learning paradigm, and it can be contrasted with conventional deep learning techniques that use gradient descent on a neural network with a fixed topology.
The expression computational intelligence (CI) usually refers to the ability of a computer to learn a specific task from data or experimental observation. Even though it is commonly considered a synonym of soft computing, there is still no commonly accepted definition of computational intelligence.
Search-based software engineering (SBSE) applies metaheuristic search techniques such as genetic algorithms, simulated annealing and tabu search to software engineering problems. Many activities in software engineering can be stated as optimization problems. Optimization techniques of operations research such as linear programming or dynamic programming are often impractical for large scale software engineering problems because of their computational complexity or their assumptions on the problem structure. Researchers and practitioners use metaheuristic search techniques, which impose little assumptions on the problem structure, to find near-optimal or "good-enough" solutions.
In artificial immune systems, clonal selection algorithms are a class of algorithms inspired by the clonal selection theory of acquired immunity that explains how B and T lymphocytes improve their response to antigens over time called affinity maturation. These algorithms focus on the Darwinian attributes of the theory where selection is inspired by the affinity of antigen-antibody interactions, reproduction is inspired by cell division, and variation is inspired by somatic hypermutation. Clonal selection algorithms are most commonly applied to optimization and pattern recognition domains, some of which resemble parallel hill climbing and the genetic algorithm without the recombination operator.

In numerical optimization, meta-optimization is the use of one optimization method to tune another optimization method. Meta-optimization is reported to have been used as early as in the late 1970s by Mercer and Sampson for finding optimal parameter settings of a genetic algorithm.
Zbigniew Michalewicz is an entrepreneur, author and professor in the fields of mathematical optimisation and new technologies. He is the author of over 250 articles and 25 books which have been widely cited. He is the co-founder of NuTech Solutions, SolveIT Software, and Complexica where he currently serves as the Chief Scientific Officer.

The MNIST database is a large database of handwritten digits that is commonly used for training various image processing systems. The database is also widely used for training and testing in the field of machine learning. It was created by "re-mixing" the samples from NIST's original datasets. The creators felt that since NIST's training dataset was taken from American Census Bureau employees, while the testing dataset was taken from American high school students, it was not well-suited for machine learning experiments. Furthermore, the black and white images from NIST were normalized to fit into a 28x28 pixel bounding box and anti-aliased, which introduced grayscale levels.
Convolutional neural network (CNN) is a regularized type of feed-forward neural network that learns feature engineering by itself via filters optimization. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by using regularized weights over fewer connections. For example, for each neuron in the fully-connected layer 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded convolution kernels, only 25 neurons are required to process 5x5-sized tiles. Higher-layer features are extracted from wider context windows, compared to lower-layer features.

Symbolic regression (SR) is a type of regression analysis that searches the space of mathematical expressions to find the model that best fits a given dataset, both in terms of accuracy and simplicity.
A recursive neural network is a kind of deep neural network created by applying the same set of weights recursively over a structured input, to produce a structured prediction over variable-size input structures, or a scalar prediction on it, by traversing a given structure in topological order. Recursive neural networks, sometimes abbreviated as RvNNs, have been successful, for instance, in learning sequence and tree structures in natural language processing, mainly phrase and sentence continuous representations based on word embedding. RvNNs have first been introduced to learn distributed representations of structure, such as logical terms. Models and general frameworks have been developed in further works since the 1990s.

Neural architecture search (NAS) is a technique for automating the design of artificial neural networks (ANN), a widely used model in the field of machine learning. NAS has been used to design networks that are on par or outperform hand-designed architectures. Methods for NAS can be categorized according to the search space, search strategy and performance estimation strategy used:
Multi-task optimization is a paradigm in the optimization literature that focuses on solving multiple self-contained tasks simultaneously. The paradigm has been inspired by the well-established concepts of transfer learning and multi-task learning in predictive analytics.
This is a chronological table of metaheuristic algorithms that only contains fundamental algorithms. Hybrid algorithms and multi-objective algorithms are not listed in the table below.

Spatial embedding is one of feature learning techniques used in spatial analysis where points, lines, polygons or other spatial data types. representing geographic locations are mapped to vectors of real numbers. Conceptually it involves a mathematical embedding from a space with many dimensions per geographic object to a continuous vector space with a much lower dimension.
Yixin Chen is a computer scientist, academic, and author. He is a professor of computer science and engineering at Washington University in St. Louis.
Wang Gang, also known as Michael Wang, is an electrical and computer engineer and academic specializing in Artificial Intelligence and its application in autonomous driving. Wang has authored or co-authored more than 100 publications, cited over 28,000 times. His h-index is computed to be 72.






