
The binnenvestgracht was a system of canals that formed part of the fortifications of the Dutch city of Leiden in the early modern period. [1] [2]

The binnenvestgracht was a system of canals that formed part of the fortifications of the Dutch city of Leiden in the early modern period. [1] [2]
Leiden expanded to the north in 1611 and to the east in 1659 and with it completed its bastion fort structure. On the outside was the moat, a semicircular ring of water, with a name and function much the same as the Singel in Amsterdam. Within that were the city's walls, ramparts and gates. To the inside of those the 'binnenvestgracht' was dug, as an extra obstacle. It enclosed most of the city and comprised seven larger parts.
In the nineteenth century city fortifications had lost their use and in Leiden most were demolished. Waste materials were used for narrowing the 'singels' and for filling in the 'binnenvestgracht'. Most stretches of the latter were done between 1867 and 1900. [3] Four segments were filled in as late as 1930 and 1937, two of which have been reopened in 1983.
As of 2018 a few segments of the ring remain, most notably on the north east side of the former bastion fort. Five streets in Leiden are named Binnenvestgracht (1st to 5th) in places where the canals used to be. Only the fifth has water in it, but it is not the original segment of the 'binnenvestgracht' in the south west corner of Leiden. That stretch was filled in at the end of the sixteenth century, to make room for what is now the Hortus Botanicus Leiden.

A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates for access to the city. From ancient to modern times, they were used to enclose settlements. Generally, these are referred to as city walls or town walls, although there were also walls, such as the Great Wall of China, Walls of Benin, Hadrian's Wall, Anastasian Wall, and the Atlantic Wall, which extended far beyond the borders of a city and were used to enclose regions or mark territorial boundaries. In mountainous terrain, defensive walls such as letzis were used in combination with castles to seal valleys from potential attack. Beyond their defensive utility, many walls also had important symbolic functions – representing the status and independence of the communities they embraced.

A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive water defences, including natural or artificial lakes, dams and sluices. In older fortifications, such as hillforts, they are usually referred to simply as ditches, although the function is similar. In later periods, moats or water defences may be largely ornamental. They could also act as a sewer.

A fortification is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin fortis ("strong") and facere.

Hoofddorp is the main town of the municipality of Haarlemmermeer, in the province of North Holland, the Netherlands. In 2021, the population was 77,885. The town was founded in 1853, immediately after the Haarlemmermeer had been drained.

Tilbury Fort, also known historically as the Thermitage Bulwark and the West Tilbury Blockhouse, is an artillery fort on the north bank of the River Thames in England. The earliest version of the fort, comprising a small blockhouse with artillery covering the river, was constructed by King Henry VIII to protect London against attack from France as part of his Device programme. It was reinforced during the 1588 Spanish Armada invasion scare, after which it was reinforced with earthwork bastion, and Parliamentary forces used it to help secure the capital during the English Civil War of the 1640s. Following naval raids during the Anglo-Dutch Wars, the fort was enlarged by Sir Bernard de Gomme from 1670 onwards to form a star-shaped defensive work, with angular bastions, water-filled moats and two lines of guns facing onto the river.

Christianshavn is a neighbourhood in Copenhagen, Denmark. Part of the Indre By District, it is located on several artificial islands between the islands of Zealand and Amager and separated from the rest of the city centre by the Inner Harbour. It was founded in the early 17th century by Christian IV as part of his extension of the fortifications of Copenhagen. Originally, it was laid out as an independent privileged merchant's town with inspiration from Dutch cities but it was soon incorporated into Copenhagen proper. Dominated by canals, it is the part of Copenhagen with the most nautical atmosphere.

The Singel is one of the canals of Amsterdam. The Singel encircled Amsterdam in the Middle Ages, serving as a moat around the city until 1585, when Amsterdam expanded beyond the Singel. The canal runs from the IJ bay, near the Central Station, to the Muntplein square, where it meets the Amstel river. It is now the inner-most canal in Amsterdam's semicircular ring of canals.

Bratislava fortifications usually refers to the medieval city fortifications of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia, of which one gate and two sections of walls remain today. The Bratislava Castle was also heavily fortified. Other fortification systems were built in the following centuries, including a World War I artillery fortification system and World War I shelters, system of bunkers and fortifications built by the First Czechoslovak Republic between the World Wars, World War II aircraft raid shelters, fortifications built by the Nazi Germany in the city during World War II and finally Cold War-era city defenses including a system of 8,602 air raid and nuclear shelters capable of holding over 760,000 citizens, far more than the number of inhabitants. The pinnacle of the communist era city defense was a military rocket base located on the Devínska Kobyla hill, the highest point in the city.

Amsterdam, capital of the Netherlands, has more than 100 kilometers (62 mi) of grachten (canals), about 90 islands and 1,500 bridges. The three main canals, dug in the 17th century during the Dutch Golden Age, form concentric belts around the city, known as the Grachtengordel. Alongside the main canals are 1550 monumental buildings. The 17th-century canal ring area, including the Prinsengracht, Keizersgracht, Herengracht and Jordaan, were listed as UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2010, contributing to Amsterdam's fame as the "Venice of the North".

Poznań Fortress, known in German as Festung Posen was a set of fortifications in the city of Poznań in western Poland, built under Prussian rule in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It represents the third largest system of its kind in Europe.

The fortifications of Copenhagen is the broad name for the rings of fortifications surrounding the city of Copenhagen. They can be classified historically as follows:
Gracht is a Dutch word for a canal within a city. Grachten often have a round shape, and form a circle around the city cores in the Netherlands, Belgium, and northern Germany. Outside the Netherlands, the word grachten mostly refers to the city canals of Amsterdam and also Utrecht, Leiden and The Hague. The Koninginnegracht in The Hague was conceived by King Willem I for the promotion of tourism in the early 19th century. Since 2009 the Willemsvaart once more offers tours over this gracht, to Scheveningen, known as "StrandRelax" or "BeachRelax", a unique stretch of sand between The Hague and the sea.

Galle Fort, in the Bay of Galle on the southwest coast of Sri Lanka, was built first in 1588 by the Portuguese, then extensively fortified by the Dutch during the 17th century from 1649 onwards. It is a historical, archaeological and architectural heritage monument, which even after more than 432 years maintains a polished appearance, due to extensive reconstruction work done by Archaeological Department of Sri Lanka.

The walls of Amsterdam were built in the Middle Ages to protect the city against attack. The Medieval walls were replaced with a series of bastions in the 17th century. In the 19th century, the walls were torn down and replaced with the Defence Line of Amsterdam, a fortification line which encircled Amsterdam at a distance from the city.

Oudeschans is a small village with a population of around 100 in the municipality of Westerwolde in the province of Groningen in the Netherlands. The 16th-century fortification is now a state protected village area with several national heritage sites, among which a 17th-century garrison church, and the Vestingmuseum Oudeschans.

Antwerp was developed as a fortified city, but very little remains of the 10th century enceinte. Only some remains of the first city wall can be seen near the Vleeshuis museum at the corner of Bloedberg and Burchtgracht, and a replica of a burg (castle) named Steen has been partly rebuilt near the Scheldt-quais during the 19th century. Parts of the canals that protected the city between the 12th and 16th century have been covered and used as a sewage system. Both the 16th century city walls and the 19th century fortifications have been covered up by major infrastructure works during the 19th and 20th century.

The fortifications of Valletta are a series of defensive walls and other fortifications which surround Valletta, the capital city of Malta. The first fortification to be built was Fort Saint Elmo in 1552, but the fortifications of the city proper began to be built in 1566 when it was founded by Grand Master Jean de Valette. Modifications were made throughout the following centuries, with the last major addition being Fort Lascaris which was completed in 1856. Most of the fortifications remain largely intact today.
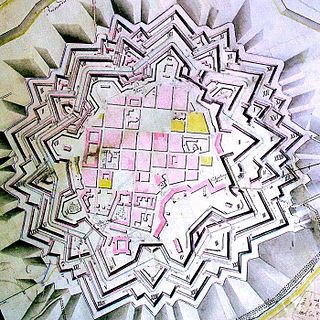
Timișoara Fortress is a historical fortress in western Romania around which the town of Timișoara was built.

The Spuistraat in downtown Amsterdam connects the Hekelveld to the Spui. It runs roughly north to south, parallel to the Singel and the Nieuwezijds Voorburgwal. At the Royal Palace of Amsterdam, the Spuistraat crosses the Raadhuisstraat and Paleisstraat. Originally the Spuistraat was a canal, the Nieuwezijds Achterburgwal. The canal was filled in in 1867, and the street renamed then.