
The economy of Alberta is the sum of all economic activity in Alberta, Canada's fourth largest province by population. Alberta's GDP in 2018 was CDN$338.2 billion.
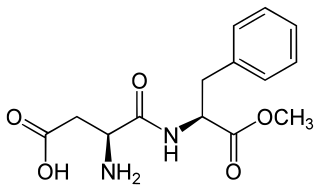
Aspartame is an artificial non-saccharide sweetener 200 times sweeter than sucrose and is commonly used as a sugar substitute in foods and beverages. It is a methyl ester of the aspartic acid/phenylalanine dipeptide with the trade names NutraSweet, Equal, and Canderel. First submitted for approval as a food ingredient in 1974, aspartame was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1981.

Stevia is a natural sweetener and sugar substitute derived from the leaves of the plant species Stevia rebaudiana, native to Paraguay and Brazil.

A sugar substitute is a food additive that provides a sweet taste like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie or low-calorie sweetener. Artificial sweeteners may be derived through manufacturing of plant extracts or processed by chemical synthesis. Sugar substitute products are commercially available in various forms, such as small pills, powders, and packets.

Corn syrup is a food syrup which is made from the starch of corn and contains varying amounts of sugars glucose, maltose and higher oligosaccharides, depending on the grade. Corn syrup is used in foods to soften texture, add volume, prevent crystallization of sugar, and enhance flavor. Corn syrup is distinct from high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), which is manufactured from corn syrup by converting a large proportion of its glucose into fructose using the enzyme D-xylose isomerase, thus producing a sweeter substance.

Edmonton is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".

The University of Alberta, also known as U of A or UAlberta, is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford, the first premier of Alberta, and Henry Marshall Tory, the university's first president. It was enabled through the Post-secondary Learning Act.

Chewing gum is a soft, cohesive substance designed to be chewed without being swallowed. Modern chewing gum is composed of gum base, sweeteners, softeners/plasticizers, flavors, colors, and, typically, a hard or powdered polyol coating. Its texture is reminiscent of rubber because of the physical-chemical properties of its polymer, plasticizer, and resin components, which contribute to its elastic-plastic, sticky, chewy characteristics.

Saccharin is an artificial sweetener with effectively no nutritional value. It is about 550 times as sweet as sucrose but has a bitter or metallic aftertaste, especially at high concentrations. Saccharin is used to sweeten products such as drinks, candies, cookies, and especially for masking bitter taste of some medicines.

Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing includes many forms of processing foods, from grinding grain to make raw flour to home cooking to complex industrial methods used to make convenience foods. Some food processing methods play important roles in reducing food waste and improving food preservation, thus reducing the total environmental impact of agriculture and improving food security.
Danisco A/S is a Danish bio-based company with activities in food production, enzymes and other bioproducts as well as a wide variety of pharmaceutical grade excipients. It was formed in 1989 from the largest Danish industrial merger ever of the two old C.F. Tietgen companies Danish Sugar, and Dansk Handels- og Industri Company.
Tate & Lyle PLC is a British-headquartered, global supplier of food and beverage ingredients to industrial markets. It was originally a sugar refining business, but from the 1970s it began to diversify, eventually divesting its sugar business in 2010. It specialises in turning raw materials such as corn and tapioca into ingredients that add taste, texture, and nutrients to food and beverages. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.

William Smith is a Canadian businessman, former politician, and former professional football player. Smith was a mayor of Edmonton, Alberta from 1995 until 2004. Smith was a Grey Cup champion with the Edmonton Eskimos.

High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzymes. To make HFCS, the corn syrup is further processed by D-xylose isomerase to convert some of its glucose into fructose. HFCS was first marketed in the early 1970s by the Clinton Corn Processing Company, together with the Japanese Agency of Industrial Science and Technology, where the enzyme was discovered in 1965.

The North Saskatchewan River is a glacier-fed river that flows from the Canadian Rockies continental divide east to central Saskatchewan, where it joins with the South Saskatchewan River to make up the Saskatchewan River. Its water flows eventually into the Hudson Bay.
Truvia is a brand of stevia-based sugar substitute developed jointly by The Coca-Cola Company and Cargill. It is distributed and marketed by Cargill as a tabletop sweetener as well as a food ingredient. Truvia is made of stevia leaf extract, erythritol, and natural flavors. Because it comes from the stevia plant, Cargill classifies Truvia as a natural sweetener in addition to being a non-nutritive sweetener, although Cargill has settled lawsuits alleging deceptive marketing of Truvia as "natural". Since its launch in 2008, Truvia natural sweetener has become the second best-selling sugar substitute in units in the U.S. behind Splenda, surpassing Equal and Sweet'n Low. Truvia competes with Stevia In The Raw, the #2 brand of stevia, owned by Cumberland Packaging who also makes Sweet 'n Low.

Ingredion Incorporated is an American multinational ingredient provider based in Westchester, Illinois, producing mainly starches, non-GMO sweeteners, stevia, and pea protein. The company turns corn, tapioca, potatoes, plant-based stevia, grains, fruits, gums and other vegetables into ingredients for the food, beverage, brewing, and pharmaceutical industries and numerous industrial sectors. It has about 12,000 employees in 44 locations, and customers in excess of 120 countries.
Bell Flavors & Fragrances is an American multinational manufacturer of flavors, fragrances, botanicals and ingredients. Bell is privately held by the Heinz family. Bell Flavors & Fragrances was founded in 1912 as the William M. Bell Company in Chicago, Illinois. The founder had been a flavor chemist with Kraft Foods in their confectionery and caramel division. In the early years, Bell sold his flavors to local shops and candy companies.
Isomaltooligosaccharide (IMO) is a mixture of short-chain carbohydrates which has a digestion-resistant property. IMO is found naturally in some foods, as well as being manufactured commercially. The raw material used for manufacturing IMO is starch, which is enzymatically converted into a mixture of isomaltooligosaccharides.
Safeway is a Canadian supermarket chain of 135 full service supermarket stores mostly operating in the western provinces in Canada. It was established in 1929 as a subsidiary of the American Safeway Inc., before being sold in 2013 to Canada's second-largest supermarket chain, Sobeys, a division of the conglomerate Empire Company. It is now independent from the American company but continues to use the same Safeway name and logo.













