Bioelectrochemistry is a branch of electrochemistry and biophysical chemistry concerned with electrophysiological topics like cell electron-proton transport, cell membrane potentials and electrode reactions of redox enzymes.
The beginnings of bioelectrochemistry, as well as those of electrochemistry, are closely related to physiology through the works of Luigi Galvani and then Alessandro Volta. The first modern work in this field is considered that of the German physiologist Julius Bernstein (1902) concerning the source of biopotentials due to different ion concentration through the cell's membrane. [1] The domain of bioelectrochemistry has grown considerably over the past century, maintaining the close connections to various medical and biological and engineering disciplines like electrophysiology, biomedical engineering, and enzyme kinetics. The achievements in this field have been awarded several Nobel prizes for Physiology or Medicine. [2] Among prominent electrochemists who have contributed to this field one could mention John Bockris.
Cell biology is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of the structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as cancer, and other diseases. Research in cell biology is interconnected to other fields such as genetics, molecular genetics, molecular biology, medical microbiology, immunology, and cytochemistry.

A lysosome is a single membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that digest many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in cell processes of secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism.

Electroporation, or electropermeabilization, is a technique in which an electrical field is applied to cells in order to increase the permeability of the cell membrane. This may allow chemicals, drugs, electrode arrays or DNA to be introduced into the cell.
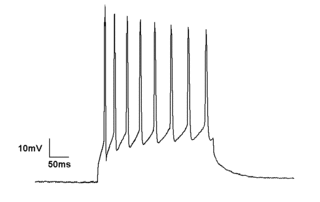
Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring.

Membrane potential is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. It equals the interior potential minus the exterior potential. This is the energy per charge which is required to move a positive charge at constant velocity across the cell membrane from the exterior to the interior.

Valinomycin is a naturally occurring dodecadepsipeptide used in the transport of potassium and as an antibiotic. Valinomycin is obtained from the cells of several Streptomyces species, S. fulvissimus being a notable one.
The Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz voltage equation, sometimes called the Goldman equation, is used in cell membrane physiology to determine the Resting potential across a cell's membrane, taking into account all of the ions that are permeant through that membrane.
Articles related specifically to biomedical engineering include:
Cell physiology is the biological study of the activities that take place in a cell to keep it alive. The term physiology refers to normal functions in a living organism. Animal cells, plant cells and microorganism cells show similarities in their functions even though they vary in structure.
Biomolecular engineering is the application of engineering principles and practices to the purposeful manipulation of molecules of biological origin. Biomolecular engineers integrate knowledge of biological processes with the core knowledge of chemical engineering in order to focus on molecular level solutions to issues and problems in the life sciences related to the environment, agriculture, energy, industry, food production, biotechnology and medicine.

A biointerface is the region of contact between a biomolecule, cell, biological tissue or living organism or organic material considered living with another biomaterial or inorganic/organic material. The motivation for biointerface science stems from the urgent need to increase the understanding of interactions between biomolecules and surfaces. The behavior of complex macromolecular systems at materials interfaces are important in the fields of biology, biotechnology, diagnostics, and medicine. Biointerface science is a multidisciplinary field in which biochemists who synthesize novel classes of biomolecules cooperate with scientists who have developed the tools to position biomolecules with molecular precision, scientists who have developed new spectroscopic techniques to interrogate these molecules at the solid-liquid interface, and people who integrate these into functional devices. Well-designed biointerfaces would facilitate desirable interactions by providing optimized surfaces where biological matter can interact with other inorganic or organic materials, such as by promoting cell and tissue adhesion onto a surface.
An enzymatic biofuel cell is a specific type of fuel cell that uses enzymes as a catalyst to oxidize its fuel, rather than precious metals. Enzymatic biofuel cells, while currently confined to research facilities, are widely prized for the promise they hold in terms of their relatively inexpensive components and fuels, as well as a potential power source for bionic implants.
Bioelectronics is a field of research in the convergence of biology and electronics.
A Bioelectrochemical reactor is a type of bioreactor where bioelectrochemical processes are used to degrade/produce organic materials using microorganisms. This bioreactor has two compartments: The anode, where the oxidation reaction takes place; And the cathode, where the reduction occurs. At these sites, electrons are passed to and from microbes to power reduction of protons, breakdown of organic waste, or other desired processes. They are used in microbial electrosynthesis, environmental remediation, and electrochemical energy conversion. Examples of bioelectrochemical reactors include microbial electrolysis cells, microbial fuel cells, enzymatic biofuel cells, electrolysis cells, microbial electrosynthesis cells, and biobatteries.
Isotope electrochemistry is a field within electrochemistry concerned with various topics like electrochemical separation of isotopes, electrochemical estimation of isotopic exchange equilibrium constants, electrochemical kinetic isotope effect, electrochemical isotope sensors, etc.
Hugh Allen Oliver Hill FRSC FRS, usually known as Allen Hill, was Professor, and later Emeritus Professor, of Bioinorganic Chemistry at the University of Oxford and Honorary Fellow of The Queen's College, Oxford, and Wadham College, Oxford. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1990 and was awarded the 2010 Royal Medal of the Royal Society "for his pioneering work on protein electrochemistry, which revolutionised the diagnostic testing of glucose and many other bioelectrochemical assays.".
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions from sub-disciplines and related fields, see Glossary of cell biology, Glossary of genetics, Glossary of evolutionary biology, Glossary of ecology, Glossary of environmental science and Glossary of scientific naming, or any of the organism-specific glossaries in Category:Glossaries of biology.
Shelley D. Minteer is an American academic and chemistry professor at the University of Utah. Minteer field of study focuses on the interface between biocatalysts and enzyme-based electrodes for biofuel cells and sensors.
Microbial electrochemical technologies (METs) use microorganisms as electrochemical catalyst, merging the microbial metabolism with electrochemical processes for the production of bioelectricity, biofuels, H2 and other valuable chemicals. Microbial fuel cells (MFC) and microbial electrolysis cells (MEC) are prominent examples of METs. While MFC is used to generate electricity from organic matter typically associated with wastewater treatment, MEC use electricity to drive chemical reactions such as the production of H2 or methane. Recently, microbial electrosynthesis cells (MES) have also emerged as a promising MET, where valuable chemicals can be produced in the cathode compartment. Other MET applications include microbial remediation cell, microbial desalination cell, microbial solar cell, microbial chemical cell, etc.,.