
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period. The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude, which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude.

In telecommunications, a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code is a binary code in which ones are represented by one significant condition, usually a positive voltage, while zeros are represented by some other significant condition, usually a negative voltage, with no other neutral or rest condition.
In telecommunications, a ternary signal is a signal that can assume, at any given instant, one of three states or significant conditions, such as power level, phase position, pulse duration, or frequency.

In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal amplitude or power at the output port to the amplitude or power at the input port. It is often expressed using the logarithmic decibel (dB) units. A gain greater than one, that is, amplification, is the defining property of an active component or circuit, while a passive circuit will have a gain of less than one.

Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) is a form of signal modulation where the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a series of signal pulses. It is an analog pulse modulation scheme in which the amplitudes of a train of carrier pulses are varied according to the sample value of the message signal. Demodulation is performed by detecting the amplitude level of the carrier at every single period.
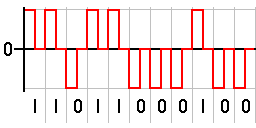
Return-to-zero describes a line code used in telecommunications signals in which the signal drops (returns) to zero between pulses. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0s or 1s occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking. This means that a separate clock does not need to be sent alongside the signal, but suffers from using twice the bandwidth to achieve the same data-rate as compared to non-return-to-zero format.

In electronics, a buffer amplifier is a unity gain amplifier that copies a signal from one circuit to another while transforming its electrical impedance to provide a more ideal source. This "buffers" the signal source in the first circuit against being affected by currents from the electrical load of the second circuit and may simply be called a buffer or follower when context is clear.

Power electronics is the application of electronics to the control and conversion of electric power.
Linear electronic oscillator circuits, which generate a sinusoidal output signal, are composed of an amplifier and a frequency selective element, a filter. A linear oscillator circuit which uses an RC network, a combination of resistors and capacitors, for its frequency selective part is called an RC oscillator.
Unipolar encoding is a line code. A positive voltage represents a binary 1, and zero volts indicates a binary 0. It is the simplest line code, directly encoding the bitstream, and is analogous to on-off keying in modulation.
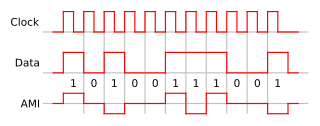
In telecommunication, bipolar encoding is a type of return-to-zero (RZ) line code, where two nonzero values are used, so that the three values are +, −, and zero. Such a signal is called a duobinary signal. Standard bipolar encodings are designed to be DC-balanced, spending equal amounts of time in the + and − states.
In signal processing, when describing a periodic function in the time domain, the DC bias, DC component, DC offset, or DC coefficient is the mean value of the waveform. A waveform with zero mean or no DC bias is known as a DC balanced or DC free waveform.
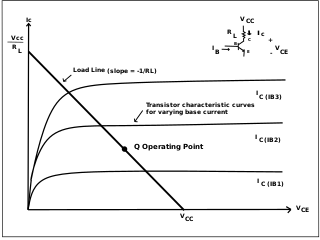
In electronics, biasing is the setting of DC operating conditions of an electronic component that processes time-varying signals. Many electronic devices, such as diodes, transistors and vacuum tubes, whose function is processing time-varying (AC) signals, also require a steady (DC) current or voltage at their terminals to operate correctly. This current or voltage is called bias. The AC signal applied to them is superposed on this DC bias current or voltage.

A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values.
Noise-based logic (NBL) is a class of multivalued deterministic logic schemes, developed in the twenty-first century, where the logic values and bits are represented by different realizations of a stochastic process. The concept of noise-based logic and its name was created by Laszlo B. Kish. In its foundation paper it is noted that the idea was inspired by the stochasticity of brain signals and by the unconventional noise-based communication schemes, such as the Kish cypher.
Pulse-density modulation, or PDM, is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with a binary signal. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into codewords of pulses of different weight as they would be in pulse-code modulation (PCM); rather, the relative density of the pulses corresponds to the analog signal's amplitude. The output of a 1-bit DAC is the same as the PDM encoding of the signal.
In electronics, faithful amplification is the amplification of a signal, particularly a weak one, by a triode or a transistor such that the signal changes in amplitude but not in shape. In order to achieve this with a bipolar transistor, the transistor is biased. Faithful amplification can only occur on transistors with a forward biased emitter-base junction, a reverse biased collector-base junction, and proper zero signal collector current. Without the correct bias, the transistor will not operate efficiently and cause its output to distort.










