
Chinese checkers (US) or Chinese chequers (UK), known as Sternhalma in German, is a strategy board game of German origin that can be played by two, three, four, or six people, playing individually or with partners. The game is a modern and simplified variation of the game Halma.
Mak-yek is a two-player abstract strategy board game played in Thailand and Myanmar. Players move their pieces as in the rook in chess and attempt to capture their opponent's pieces through custodian and intervention capture. The game may have been first described in literature by Captain James Low a writing contributor in the 1839 work Asiatic Researches; or, Transactions of the Society, Instituted in Bengal, For Inquiring into The History, The Antiquities, The Arts and Sciences, and Literature of Asian, Second Part of the Twentieth Volume in which he wrote chapter X On Siamese Literature and documented the game as Maak yék. Another early description of the game is by H.J.R. Murray in his 1913 work A History of Chess, and the game was written as Maak-yek.

Ludus latrunculorum, latrunculi, or simply latrones was a two-player strategy board game played throughout the Roman Empire. It is said to resemble chess or draughts, as it is generally accepted to be a game of military tactics. Because of the scarcity of sources, reconstruction of the game's rules and basic structure is difficult, and therefore there are multiple interpretations of the available evidence.

Hasami shogi is a variant of shogi. The game has two main variants, and all Hasami variants, unlike other shogi variants, use only one type of piece, and the winning objective is not checkmate. One main variant involves capturing all but one of the opponent's men; the other involves building an unbroken vertical or horizontal chain of five-in-a-row.
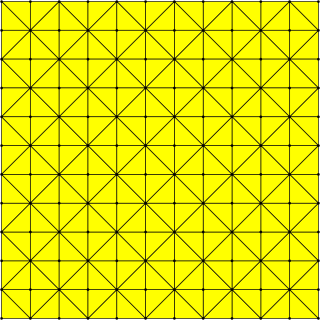
In geometry, the tetrakis square tiling is a tiling of the Euclidean plane. It is a square tiling with each square divided into four isosceles right triangles from the center point, forming an infinite arrangement of lines. It can also be formed by subdividing each square of a grid into two triangles by a diagonal, with the diagonals alternating in direction, or by overlaying two square grids, one rotated by 45 degrees from the other and scaled by a factor of √2.

PÜNCT is a two-player strategy board game. It is the sixth release in the GIPF project of seven abstract strategy games, although it is considered the fifth game in the project. It was released in 2005. PÜNCT won the Games Magazine Best Abstract Strategy game for 2007.
Sannin shōgi, or in full kokusai sannin shōgi, is a three-person shogi variant invented circa 1930 by Tanigasaki Jisuke and recently revived. It is played on a hexagonal grid of border length 7 with 127 cells. Standard shogi pieces may be used, and the rules for capture, promotion, drops, etc. are mostly similar to standard shogi. While piece movement differs somewhat from standard shogi, especially in the case of the powerful promoted king, the main difference in play is due to the rules for voluntary and mandatory alliance between two of the three players.
Three-player chess is a family of chess variants specially designed for three players. Many variations of three-player chess have been devised. They usually use a non-standard board, for example, a hexagonal or three-sided board that connects the center cells in a special way. The three armies are differentiated usually by color, with White, Black, and Red serving as the most common color combination.
Ming mang is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Tibet. Ming mang is also a general term for the word "boardgame" in Tibet. The correct name and spelling of the game may actually be Mig mang(s), but pronounced Ming mang or Mi Mang. The term mig mang is also applied to Tibetan go with both games using exactly the same board which is a 17 x 17 square board, and black and white pieces. Mig is in reference to the chart of the board, and Mangs refers to the notion that the more charts are used on the board, the more pieces are needed to play the game, but some state that it means "many eyes". The game may also be known as Gundru. The game was popular among some Tibetan monks before the Chinese invasion of Tibet in 1950, and the uprising in 1959, and among aristocratic families.
Pasang is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Brunei. The game is often referred to as Pasang Emas which is actually a software implementation of the traditional board game. The object of this game is to acquire the most points by capturing black and white tokens on the board. Black tokens are worth 1 point, and white tokens are worth 2 points. The board is initially laid out with all 120 black and white tokens in one of over 30 traditional patterns. Players choose a piece called a "ka" which is used to capture the tokens on the board. Each player's "ka" moves around the board capturing as many tokens as possible As a note, the "kas" are the only mobile pieces in the game. The other pieces are stationary, and are captured by the "kas". Players must capture token(s) during their turn, or lose the game. When all tokens have been captured from the board, the player with the most points is the winner. However, if there are any tokens left on the board, and none can be captured on a player's turn, then that player loses the game, and the other player is the winner.
Jul-gonu is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Korea. It is one of many gonu games. The game has a relatively small board, and yet offers a challenge at different levels. The game could be played on a larger board, however, it tends to be tiresome. Jul means "lines", and the lines of the board are often drawn on the ground. The game is also referred to as "ne-jul-gonu", i.e. "four-lines gonu", referring to the four lines in each direction.
Brax is a two-player abstract strategy board game. It was invented in 1889 in America by Frederic B. Denham of New York City. The board design is unique. The players move their pieces along paths on the square board; each path is one of two colors. A piece can move one or two spaces in a turn depending upon whether it matches the color of the path. Players attempt to capture each other's pieces.
Terhüchü is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Nagaland in Northeast India and is played by the Angami Naga ethnic group.
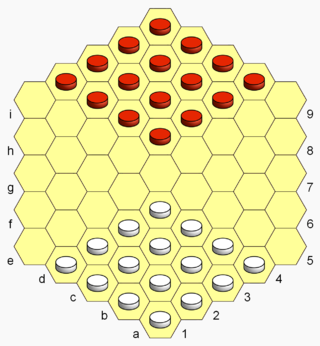
Hexdame is a strategy board game for two players invented by Christian Freeling in 1979. The game is a literal adaptation of the game international draughts to a hexagonal gameboard.

Chesquerque is a chess variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board composed of four Alquerque boards combined into a square. Like Alquerque, pieces are positioned on points of intersection and make their moves along marked lines ; as such, the board comprises a 9×9 grid with 81 positions (points) that pieces can move to.
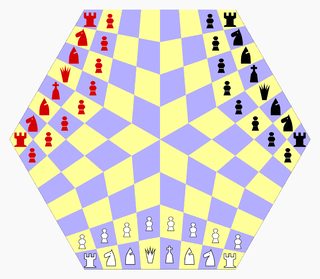
Three-man chess is a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1984. The game is played on a hexagonal board comprising 96 quadrilateral cells. Each player controls a standard army of chess pieces.

Diplomat chess is a chess variant invented by Carlos Martín-Fuertes in 2003 as a contribution to a contest to design a chess variant on 43 squares, organised by The Chess Variant Pages. It is played on a circular board with 43 cells, including the center circle which is considered orthogonal and diagonal to every adjacent cell. The game includes a fairy piece called the 'diplomat' which instead of capturing can suborn enemy pieces.
This glossary of board games explains commonly used terms in board games, in alphabetical order. For a list of board games, see List of board games; for terms specific to chess, see Glossary of chess; for terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems.

Diamond is a two-player abstract strategy board game invented by Larry Back. The invention was inspired by the game Kensington, which uses a similar board pattern and game objective. Rules for Diamond were conceived in 1985 and finalized in 1994. Diamond introduces a new board geometry and neutral pieces, with the aim of enhancing the game dynamic and lowering the potential for draws.










