
New Zealand is an island country located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, near the centre of the water hemisphere. It consists of a large number of islands, estimated around 700, mainly remnants of a larger landmass now beneath the sea. The land masses by size are the South Island and the North Island, separated by the Cook Strait. The third-largest is Stewart Island / Rakiura, located 30 kilometres off the tip of the South Island across Foveaux Strait. Other islands are significantly smaller in area. The three largest islands stretch 1,600 kilometres across latitudes 35° to 47° south. New Zealand is the sixth-largest island country in the world, with a land size of 268,680 km2 (103,740 sq mi).

Oceania is a geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, at the centre of the water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about 9,000,000 square kilometres (3,500,000 sq mi) and a population of around 44.4 million as of 2022. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the second-least populated after Antarctica.

Tokelau is a dependent territory of New Zealand in the southern Pacific Ocean. It consists of three tropical coral atolls: Atafu, Nukunonu, and Fakaofo. They have a combined land area of 10 km2 (4 sq mi). In addition to these three, Swains Island, which forms part of the same archipelago, is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute; it is currently administered by the United States as part of American Samoa. Tokelau lies north of the Samoan Islands, east of Tuvalu, south of the Phoenix Islands, southwest of the more distant Line Islands, and northwest of the Cook Islands.

Zealand is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper at 7,031 km2. Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020, comprising 40% of the country's population.
Aotearoa is the Māori-language name for New Zealand. The name was originally used by Māori in reference only to the North Island, with the whole country being referred to as Aotearoa me Te Waipounamu – where Te Ika-a-Māui means North Island, and Te Waipounamu means South Island. In the pre-European era, Māori did not have a collective name for the two islands.

The North Island is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but less populous South Island by Cook Strait. With an area of 113,729 km2 (43,911 sq mi), it is the world's 14th-largest island, constituting 43% of New Zealand's land area. It has a population of 4,077,800, which is 76% of New Zealand's residents, making it the most populous island in Polynesia and the 28th-most-populous island in the world.

The South Island is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island and sparsely populated Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers 150,437 square kilometres (58,084 sq mi), making it the world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate. The major centres are Christchurch, with a metropolitan population of 521,881, and the smaller Dunedin. The economy relies on agriculture, fishing, tourism, and general manufacturing and services.

Moa are an extinct group of flightless birds formerly endemic to New Zealand. During the Late Pleistocene-Holocene, there were nine species. The two largest species, Dinornis robustus and Dinornis novaezelandiae, reached about 3.6 metres (12 ft) in height with neck outstretched, and weighed about 230 kilograms (510 lb) while the smallest, the bush moa, was around the size of a turkey. Estimates of the moa population when Polynesians settled New Zealand circa 1300 vary between 58,000 and approximately 2.5 million.

The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about 2,000 km (1,200 mi) across and about 2,800 km (1,700 mi) from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 was the first known person to cross it. British explorer Lieutenant James Cook later extensively navigated the Tasman Sea in the 1770s during his three voyages of exploration.

The Chatham Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about 800 km (430 nmi) east of New Zealand's South Island, administered as part of New Zealand, and consisting of about 10 islands within an approximate 60 km (30 nmi) radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island (Rangiauria). They include New Zealand's easternmost point, the Forty-Fours. Some of the islands, formerly cleared for farming, are now preserved as nature reserves to conserve some of the unique flora and fauna.

The Southern Hemisphere is the half (hemisphere) of Earth that is south of the Equator. It contains all or parts of five continents and four oceans, as well as New Zealand and most of the Pacific Islands in Oceania. Its surface is 80.9% water, compared with 60.7% water in the Northern Hemisphere, and it contains 32.7% of Earth's land.

The Bay of Islands is an area on the east coast of the Far North District of the North Island of New Zealand. It is one of the most popular fishing, sailing and tourist destinations in the country, and has been renowned internationally for its big-game fishing since American author Zane Grey publicised it in the 1930s. It is 60 km (37 mi) north-west of the city of Whangārei. Cape Reinga, at the northern tip of the country, is about 210 km (130 mi) by road further to the north-west.

The Northland Region is the northernmost of New Zealand's 16 local government regions. New Zealanders sometimes refer to it as the Winterless North because of its mild climate all throughout the year. The major population centre is the city of Whangārei, and the largest town is Kerikeri. At the 2018 New Zealand census, Northland recorded a population growth spurt of 18.1% since the previous 2013 census, placing it as the fastest growing region in New Zealand, ahead of other strong growth regions such as the Bay of Plenty Region and Waikato.

The Kermadec Islands are a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean 800–1,000 km (500–620 mi) northeast of New Zealand's North Island, and a similar distance southwest of Tonga. The islands are part of New Zealand. They are 33.6 km2 (13.0 sq mi) in total area and uninhabited, except for the permanently staffed Raoul Island Station, the northernmost outpost of New Zealand.

The Realm of New Zealand is the area over which the monarch of New Zealand is head of state. The realm is not a federation but is a collection of states and territories united under its monarch. New Zealand is an independent and sovereign state that has one territorial claim in Antarctica, one dependent territory (Tokelau), and two associated states. The Realm of New Zealand encompasses the three autonomous jurisdictions of New Zealand, the Cook Islands, and Niue.

New Zealand is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island and the South Island —and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland.

Auckland is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of about 1,531,400. It is located in the greater Auckland Region, the area governed by Auckland Council, which includes outlying rural areas and the islands of the Hauraki Gulf, and which has a total population of 1,798,300 as of June 2024. It is the most populous city of New Zealand and the fifth largest city in Oceania. While Europeans continue to make up the plurality of Auckland's population, the city became multicultural and cosmopolitan in the late-20th century, with Asians accounting for 34.9% of the city's population in 2023. Auckland has the fourth largest foreign-born population in the world, with 39% of its residents born overseas. With its sizable population of Pasifika New Zealanders, the city is also home to the largest ethnic Polynesian population in the world. The Māori-language name for Auckland is Tāmaki Makaurau, meaning "Tāmaki desired by many", in reference to the desirability of its natural resources and geography.
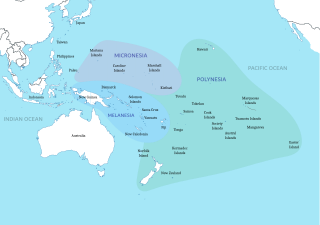
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including linguistic relations, cultural practices, and traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night.
Mark Fredrick Noble is a New Zealand chess and lawn bowls player. He was awarded the title of International Correspondence Chess Grandmaster (GM) in 2010, the first New Zealand player to be awarded this title.

















