
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time. A major risk factor for glaucoma is increased pressure within the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). It is associated with old age, a family history of glaucoma, and certain medical conditions or the use of some medications. The word glaucoma comes from the Ancient Greek word γλαυκός, meaning 'gleaming, blue-green, gray'.

The pleural cavity, or pleural space, is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient.
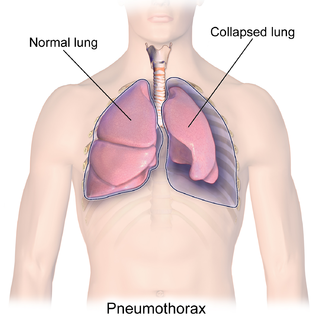
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed by an area of damaged tissue, and the amount of air in the space between chest wall and lungs increases; this is called a tension pneumothorax. This can cause a steadily worsening oxygen shortage and low blood pressure. This leads to a type of shock called obstructive shock, which can be fatal unless reversed. Very rarely, both lungs may be affected by a pneumothorax. It is often called a "collapsed lung", although that term may also refer to atelectasis.

Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever, or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause.
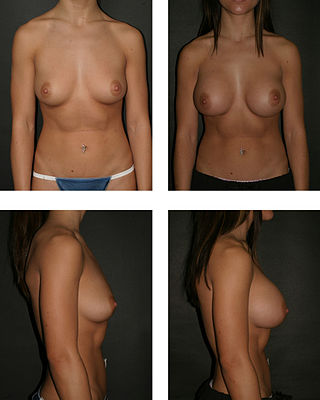
Breast augmentation and augmentation mammoplasty is a cosmetic surgery procedure, which uses breast-implants and/ or fat-graft mammoplasty technique to increase the size, change the shape, and alter the texture of the breasts. Although in some cases augmentation mammoplasty is applied to correct congenital defects of the breasts and the chest wall in other cases it is performed purely for cosmetic reasons.

Pleurodesis is a medical procedure in which part of the pleural space is artificially obliterated. It involves the adhesion of the visceral and the costal pleura. The mediastinal pleura is spared.
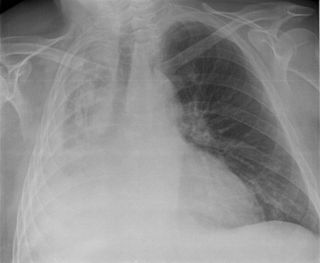
Atelectasis is the partial collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absence in gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation, in which they are filled with liquid. It is often referred to informally as a collapsed lung, although more accurately it usually involves only a partial collapse, and that ambiguous term is also informally used for a fully collapsed lung caused by a pneumothorax.

A hemothorax is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may include reduced breath sounds on the affected side and a rapid heart rate. Hemothoraces are usually caused by an injury, but they may occur spontaneously due to cancer invading the pleural cavity, as a result of a blood clotting disorder, as an unusual manifestation of endometriosis, in response to pneumothorax, or rarely in association with other conditions.

A glaucoma valve is a medical shunt used in the treatment of glaucoma to reduce the eye's intraocular pressure (IOP).

Catamenial pneumothorax is a spontaneous pneumothorax that recurs during menstruation, within 72 hours before or after the onset of a cycle. It usually involves the right side of the chest and right lung, and is associated with thoracic endometriosis. A third to a half of patients have pelvic endometriosis as well. Despite this association, CP is still considered to be misunderstood as is endometriosis considered to be underdiagnosed. The lack of a clear cause means that diagnosis and treatment is difficult. The disease is believed to be largely undiagnosed or misdiagnosed, leaving the true frequency unknown in the general population.

Trabeculectomy is a surgical procedure used in the treatment of glaucoma to relieve intraocular pressure by removing part of the eye's trabecular meshwork and adjacent structures. It is the most common glaucoma surgery performed and allows drainage of aqueous humor from within the eye to underneath the conjunctiva where it is absorbed. This outpatient procedure was most commonly performed under monitored anesthesia care using a retrobulbar block or peribulbar block or a combination of topical and subtenon anesthesia. Due to the higher risks associated with bulbar blocks, topical analgesia with mild sedation is becoming more common. Rarely general anesthesia will be used, in patients with an inability to cooperate during surgery.

Glaucoma is a group of diseases affecting the optic nerve that results in vision loss and is frequently characterized by raised intraocular pressure (IOP). There are many glaucoma surgeries, and variations or combinations of those surgeries, that facilitate the escape of excess aqueous humor from the eye to lower intraocular pressure, and a few that lower IOP by decreasing the production of aqueous humor.

Fibrothorax is a medical condition characterised by severe scarring (fibrosis) and fusion of the layers of the pleural space surrounding the lungs resulting in decreased movement of the lung and ribcage. The main symptom of fibrothorax is shortness of breath. There also may be recurrent fluid collections surrounding the lungs. Fibrothorax may occur as a complication of many diseases, including infection of the pleural space known as an empyema or bleeding into the pleural space known as a haemothorax.

Canine glaucoma refers to a group of diseases in dogs that affect the optic nerve and involve a loss of retinal ganglion cells in a characteristic pattern. An intraocular pressure greater than 22 mmHg (2.9 kPa) is a significant risk factor for the development of glaucoma. Untreated glaucoma in dogs leads to permanent damage of the optic nerve and resultant visual field loss, which can progress to blindness.
Tumor-like disorders of the lung pleura are a group of conditions that on initial radiological studies might be confused with malignant lesions. Radiologists must be aware of these conditions in order to avoid misdiagnosing patients. Examples of such lesions are: pleural plaques, thoracic splenosis, catamenial pneumothorax, pleural pseudotumor, diffuse pleural thickening, diffuse pulmonary lymphangiomatosis and Erdheim–Chester disease.

Emphysema is any air-filled enlargement in the body's tissues. Most commonly emphysema refers to the permanent enlargement of air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs, and is also known as pulmonary emphysema.

A blocked milk duct is a blockage of one or more ducts carrying milk to the nipple for the purpose of breastfeeding an infant that can cause mastitis. The symptoms are a tender, localised lump in one breast, with redness in the skin over the lump. The cause of a blocked milk duct is the failure to remove milk from part of the breast. This may be due to infrequent breastfeeding, poor attachment, tight clothing or trauma to the breast. Sometimes the duct to one part of the breast is blocked by thickened milk. A blocked milk duct can be managed by improving the removal of milk and correcting the underlying cause.

A nipple bleb is a blister on the nipple that can be filled with serous or other fluid. It may be pink or light yellow. It is thin-walled and may appear as a small blister, more than 5 mm in diameter. It can also be referred to as a bulla. Some clinicians may also include milk blisters as a type of bleb. In addition, a blocked Montgomery gland may also be called a nipple bleb though its cause is different than a milk or serous-filled bleb on the nipple. In some cases the bleb may be associated with an adjacent blocked sebaceous cyst.
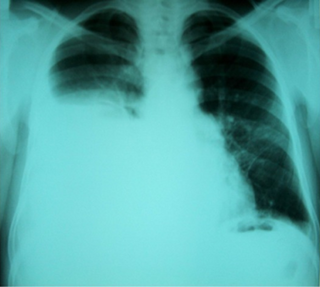
Hepatic hydrothorax is a rare form of pleural effusion that occurs in people with liver cirrhosis. It is defined as an effusion of over 500 mL in people with liver cirrhosis that is not caused by heart, lung, or pleural disease. It is found in 5–10% of people with liver cirrhosis and 2–3% of people with pleural effusions. In cases of decompensated liver cirrhosis, prevalence rises significantly up to 90%. Over 85% of cases occurring on the right, 13% on the left, and 2% on both. Although it is most common in people with severe ascites, it can also occur in people with mild or no ascites. Symptoms are not specific and mostly involve the respiratory system.

Lung surgery is a type of thoracic surgery involving the repair or removal of lung tissue, and can be used to treat a variety of conditions ranging from lung cancer to pulmonary hypertension. Common operations include anatomic and nonanatomic resections, pleurodesis and lung transplants. Though records of lung surgery date back to the Classical Age, new techniques such as VATS continue to be developed.


















