Related Research Articles

The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by President Franklin Pierce. Douglas introduced the bill intending to open up new lands to develop and facilitate the construction of a transcontinental railroad. However, the Kansas–Nebraska Act effectively repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820, stoking national tensions over slavery and contributing to a series of armed conflicts known as "Bleeding Kansas."
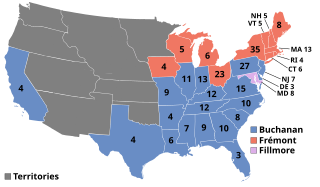
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 4, 1856. Democratic nominee James Buchanan defeated Republican nominee John C. Frémont and Know Nothing/Whig nominee Millard Fillmore. The main issue was the expansion of slavery as facilitated by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854. Buchanan defeated President Franklin Pierce at the 1856 Democratic National Convention for the nomination. Pierce had become widely unpopular in the North because of his support for the pro-slavery faction in the ongoing civil war in territorial Kansas, and Buchanan, a former Secretary of State, had avoided the divisive debates over the Kansas–Nebraska Act by being in Europe as the Ambassador to the United Kingdom.

The Free Soil Party, also called the Free Democratic Party or the Free Democracy, was a political party in the United States from 1848 to 1854, when it merged into the Republican Party. The party was focused on opposing the expansion of slavery into the western territories of the United States. The 1848 presidential election took place in the aftermath of the Mexican–American War and debates over the extension of slavery into the Mexican Cession. After the Whig Party and the Democratic Party nominated presidential candidates who were unwilling to rule out the extension of slavery into the Mexican Cession, anti-slavery Democrats and Whigs joined with members of the Liberty Party to form the new Free Soil Party. Running as the Free Soil presidential candidate, former President Martin Van Buren won 10.1 percent of the popular vote, the strongest popular vote performance by a third party up to that point in U.S. history.

The Constitutional Union Party was a political party which stood in the 1860 United States elections. It mostly consisted of conservative former Whigs from the Southern United States who wanted to avoid secession over slavery and refused to join either the Republican Party or Democratic Party. The Constitutional Union Party campaigned on a simple platform "to recognize no political principle other than the Constitution of the country, the Union of the states, and the Enforcement of the Laws".

William Hayden English was an American politician. He served as a U.S. Representative from Indiana from 1853 to 1861 and was the Democratic Party's nominee for Vice President of the United States in 1880.

Lyman Trumbull was an American lawyer, judge, and politician who represented the state of Illinois in the United States Senate from 1855 to 1873. Trumbull was a leading abolitionist attorney and key political ally to Abraham Lincoln and authored several landmark pieces of reform as chair of the Judiciary Committee during the American Civil War and Reconstruction era, including the Confiscation Acts, which created the legal basis for the Emancipation Proclamation; the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which abolished chattel slavery; and the Civil Rights Act of 1866, which led to the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.

William Alexander Richardson was a prominent Illinois Democratic politician before and during the American Civil War. A protege of Stephen Douglas, Richardson was an ardent proponent of Jacksonian democracy, popular sovereignty, and strict constructionism. During the American Civil War, he switched from supporting the conflict to join the Copperhead wing of the Democratic party and bitterly criticize President Abraham Lincoln.

The 1856 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met from June 17 to June 19, 1856, at Musical Fund Hall at 808 Locust Street in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was the first national nominating convention of the Republican Party, founded two years earlier in 1854. It was held to nominate the party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1856 election. The convention selected John C. Frémont, a former United States Senator from California, for president, and former Senator William L. Dayton of New Jersey for vice president. The convention also appointed members of the newly established Republican National Committee.

The presidency of Franklin Pierce began on March 4, 1853, when Franklin Pierce was inaugurated as the 14th President of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1857. Pierce, a Democrat from New Hampshire, took office after defeating Whig Party nominee Winfield Scott in the 1852 presidential election. Seen by fellow Democrats as pleasant and accommodating to all the party's factions, Pierce, then a little-known politician, won the presidential nomination on the 49th ballot of the 1852 Democratic National Convention. His hopes for reelection ended after losing the Democratic nomination at the 1856 Democratic National Convention, and was succeeded by Democrat James Buchanan.

The 1856 United States presidential election in California took place on November 4, 1856, as part of the 1856 United States presidential election. Voters chose four representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president. California voted for the Democratic nominee, former Secretary of State James Buchanan, over the American Party nominee, former Whig President Millard Fillmore, and the Republican nominee, former U.S. Senator and Military Governor of California John C. Frémont.

Archibald Williams was a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the District of Kansas. Williams was a friend and political ally of President Abraham Lincoln.

Stephen Arnold Douglas was an American politician and lawyer from Illinois. A U.S. Senator, he was one of two nominees of the badly split Democratic Party to run for president in the 1860 presidential election, which was won by Republican candidate Abraham Lincoln. Douglas had previously defeated Lincoln in the 1858 United States Senate election in Illinois, known for the pivotal Lincoln–Douglas debates. He was one of the brokers of the Compromise of 1850, which sought to avert a sectional crisis; to further deal with the volatile issue of extending slavery into the territories, Douglas became the foremost advocate of popular sovereignty, which held that each territory should be allowed to determine whether to permit slavery within its borders. This attempt to address the issue was rejected by both pro-slavery and anti-slavery advocates. Douglas was nicknamed the "Little Giant" because he was short in physical stature but a forceful and dominant figure in politics.

The 1864 National Union National Convention was the United States presidential nominating convention of the National Union Party, which was a name adopted by the main faction of the Republican Party in a coalition with many, if not most, War Democrats after some Republicans and War Democrats nominated John C. Frémont over Lincoln. During the Convention, the party officially called for the end of the ongoing Civil War, the eradication of slavery and the adoption of the Emancipation Proclamation.

George Schneider was a German American journalist and banker who served as editor-in-chief of the Illinois Staats-Zeitung. He was appointed by President Abraham Lincoln as the United States Consul in Elsinore, Denmark, at the outbreak of the American Civil War and later served as Collector of Internal Revenue for the 1st District of Illinois. He was a German refugee, one of the Forty-Eighters.

The 1856 Illinois gubernatorial election was the eleventh election for this office. Democratic governor Joel Aldrich Matteson did not seek re-election. Former Democratic Congressman William Henry Bissell was nominated by the newly formed Republican Party at the Bloomington Convention. Former Whig Mayor of Chicago Buckner S. Morris was nominated on the Know-Nothing Party ticket.
The Northern Democratic Party was a leg of the Democratic Party during the 1860 presidential election, when the party split in two factions because of disagreements over slavery. They held two conventions before the election, in Charleston and Baltimore, where they established their platform. Democratic Candidate Stephen A. Douglas was the nominee and lost to Republican Candidate Abraham Lincoln, whose victory prompted the secession of 11 Southern states and the formation of the Confederate States of America.
The Opposition Party was a party identification under which Northern anti-slavery politicians, formerly members of the Democratic and the Whig Parties, briefly ran in the 1850s in response to the expansion of slavery into the new territories. It was one of the movements that arose from the political chaos in the decade before the American Civil War in the wake of the Compromise of 1850. The movement had arisen before and was quickly subsumed by the coalescence of the Republican Party in 1856.
This article documents the political career of Abraham Lincoln from the end of his term in the United States House of Representatives in March 1849 to the beginning of his first term as President of the United States in March 1861.
The history of the United States Whig Party lasted from the establishment of the Whig Party early in President Andrew Jackson's second term (1833–1837) to the collapse of the party during the term of President Franklin Pierce (1853–1857). This article covers the party in national politics. For state politics see Whig Party.

The 1854 Massachusetts gubernatorial election was held on November 15. American Party candidate Henry J. Gardner was elected to his first term as governor, defeating incumbent Whig governor Emory Washburn.