Related Research Articles
An analog signal or analogue signal is any continuous-time signal representing some other quantity, i.e., analogous to another quantity. For example, in an analog audio signal, the instantaneous signal voltage varies continuously with the pressure of the sound waves.
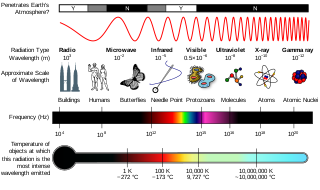
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications.

High fidelity is the high-quality reproduction of sound. It is popular with audiophiles and home audio enthusiasts. Ideally, high-fidelity equipment has inaudible noise and distortion, and a flat frequency response within the human hearing range.

Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.
The early history of radio is the history of technology that produces and uses radio instruments that use radio waves. Within the timeline of radio, many people contributed theory and inventions in what became radio. Radio development began as "wireless telegraphy". Later radio history increasingly involves matters of broadcasting.
A communications system or communication system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. The components of a communications system serve a common purpose, are technically compatible, use common procedures, respond to controls, and operate in union.

In telecommunications, especially radio communication, spread spectrum are techniques by which a signal generated with a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain over a wider frequency band. Spread-spectrum techniques are used for the establishment of secure communications, increasing resistance to natural interference, noise, and jamming, to prevent detection, to limit power flux density, and to enable multiple-access communications.

Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths greater than 1 millimeter, about the diameter of a grain of rice. Radio waves with frequencies above about 1 GHz and wavelengths shorter than 30 centimeters are called microwaves. Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a slightly lower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects.

Robert Llewellyn is a British actor, comedian, presenter and writer. He plays the mechanoid Kryten in the sci-fi television sitcom Red Dwarf and formerly presented the engineering gameshow Scrapheap Challenge. He has also founded and hosts a YouTube series, Fully Charged, which has grown into a company that puts on EV and "Everything Electric" conventions in the UK, USA, Canada, Australia and Europe.
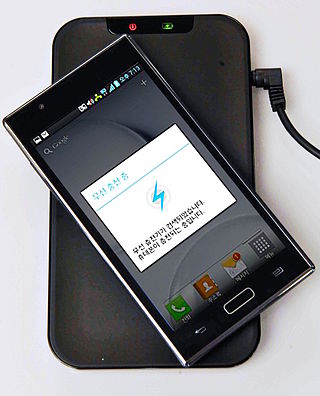
Wireless power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system, an electrically powered transmitter device generates a time-varying electromagnetic field that transmits power across space to a receiver device; the receiver device extracts power from the field and supplies it to an electrical load. The technology of wireless power transmission can eliminate the use of the wires and batteries, thereby increasing the mobility, convenience, and safety of an electronic device for all users. Wireless power transfer is useful to power electrical devices where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or are not possible.
The radio spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequencies from 3 Hz to 3,000 GHz (3 THz). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range, called radio waves, are widely used in modern technology, particularly in telecommunication. To prevent interference between different users, the generation and transmission of radio waves is strictly regulated by national laws, coordinated by an international body, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Diathermy is electrically induced heat or the use of high-frequency electromagnetic currents as a form of physical therapy and in surgical procedures. The earliest observations on the reactions of the human organism to high-frequency electromagnetic currents were made by Jacques Arsene d'Arsonval. The field was pioneered in 1907 by German physician Karl Franz Nagelschmidt, who coined the term diathermy from the Greek words διά dia and θέρμη thermē, literally meaning "heating through".

The invention of radio communication was preceded by many decades of establishing theoretical underpinnings, discovery and experimental investigation of radio waves, and engineering and technical developments related to their transmission and detection. These developments allowed Guglielmo Marconi to turn radio waves into a wireless communication system.
Hyperland is a 50-minute-long documentary film about hypertext and surrounding technologies. It was written by Douglas Adams and produced and directed by Max Whitby for BBC Two in 1990. It stars Douglas Adams as a computer user and Tom Baker, with whom Adams had already worked on Doctor Who, as a personification of a software agent.
The timeline of radio lists within the history of radio, the technology and events that produced instruments that use radio waves and activities that people undertook. Later, the history is dominated by programming and contents, which is closer to general history.

Nikola Tesla is portrayed in many forms of popular culture. The Serbian-American engineer has particularly been depicted in science fiction, a genre which is well suited to address his inventions; while often exaggerated, the fictionalized variants build mostly upon his own alleged claims or ideas. A popular, growing fixation among science fiction, comic book, and speculative history storytellers is to portray Tesla as a member of a secret society, along with other luminaries of science. The impacts of the technologies invented by Nikola Tesla are a recurring theme in the steampunk genre of alternate technology science-fiction.
Helena Bulaja is a Croatian multimedia artist, film director, scriptwriter, designer and film producer.
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also referred to as a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is a brief burst of electromagnetic energy. The origin of an EMP can be natural or artificial, and can occur as an electromagnetic field, as an electric field, as a magnetic field, or as a conducted electric current. The electromagnetic interference caused by an EMP can disrupt communications and damage electronic equipment. An EMP such as a lightning strike can physically damage objects such as buildings and aircraft. The management of EMP effects is a branch of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) engineering.
Medical applications of radio frequency (RF) energy, in the form of electromagnetic waves or electrical currents, have existed for over 125 years, and now include diathermy, hyperthermy treatment of cancer, electrosurgery scalpels used to cut and cauterize in operations, and radiofrequency ablation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses radio frequency waves to generate images of the human body.
Bioelectromagnetic medicine deals with the phenomenon of resonance signaling and discusses how specific frequencies modulate cellular function to restore or maintain health. Such electromagnetic (EM) signals are then called medical information, which are used in health informatics.
References
- ↑ "Timeless Places". TV Guide.
- ↑ "The Search For Ancient Wisdom". Cambrix. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- ↑ "Skulls from Ica, Peru and Merida, Mexico". UFO Disclosure.
- ↑ "Dynamic Media". Creative Pro Magazine.
- ↑ "Creating Interactive Rich Media PDFs with Adobe InDesign and More!". Layers Magazine. 5 November 2006.
- ↑ "Dynamic Rich-Media PDFs". How Design Conference. Archived from the original on 10 December 2013. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- ↑ "The history of magnetic field therapy". Mediconsult. Archived from the original on 11 December 2013. Retrieved 7 December 2013.