
The cervix or cervix uteri is the lower part of the uterus in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during pregnancy. The narrow, central cervical canal runs along its entire length, connecting the uterine cavity and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os, and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix, bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago.

The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer; the functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, and the elephant shrew. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus. The speculated presence of an endometrial microbiota has been argued against.

Menstruation, also known as a period or monthly, is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. However, periods may occasionally start as young as eight years old and still be considered normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world, and earlier in the developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women, and 21 to 31 days in adults. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days. Menstruation stops occurring after menopause, which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Periods also stop during pregnancy and typically do not resume during the initial months of breastfeeding.
Dysmenorrhea, also known as painful periods, or menstrual cramps, is pain during menstruation. Its usual onset occurs around the time that menstruation begins. Symptoms typically last less than three days. The pain is usually in the pelvis or lower abdomen. Other symptoms may include back pain, diarrhea, or nausea.
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is vaginal bleeding from the uterus that is abnormally frequent, last excessively long, is more than normal, or is irregular. Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is excluded. Iron deficiency anemia may occur and quality of life may be negatively effected.

Adenomyosis is a gynecologic medical condition characterized by the abnormal presence of endometrial tissue within the myometrium. When endometrial tissue is present abnormally entirely outside the uterus, it is considered to be a similar but distinct medical condition, endometriosis. The two conditions are found together in many cases, but often occur separately. Before being recognized as a distinct condition, adenomyosis was called endometriosis interna. The less-commonly-used term "adenomyometritis" is a more specific name for the condition, specifying involvement of the uterus.
Vaginal bleeding is any bleeding through the vagina, including bleeding from the vaginal wall itself, as well as bleeding from another location of the female reproductive system, often the uterus. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductive system, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Vaginal bleeding may occur at any age, but always needs investigation when encountered in children or in postmenopausal women. Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy may indicate a possible pregnancy complication that needs to be medically addressed.

Pregnancy, also known as gestation, is the time during which one or more offspring develops inside a woman. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy can occur by sexual intercourse or assisted reproductive technology. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the last menstrual period (LMP). This is just over nine months, where each month averages 31 days. When measured from fertilization it is about 38 weeks. An embryo is the developing offspring during the first eight weeks following fertilization, after which, the term fetus is used until birth. Symptoms of early pregnancy may include missed periods, tender breasts, nausea and vomiting, hunger, and frequent urination. Pregnancy may be confirmed with a pregnancy test.

Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Most women have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bladder causing a frequent need to urinate. They may also cause pain during sex or lower back pain.A woman can have one uterine fibroid or many. Occasionally, fibroids may make it difficult to become pregnant, although this is uncommon.
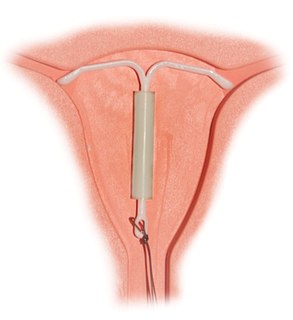
Intrauterine device (IUD) with progestogen, sold under the brand name Mirena among others, is a intrauterine device that releases the hormone levonorgestrel. It is used for birth control, heavy menstrual periods, and to prevent excessive build of the lining of the uterus in those on estrogen replacement therapy. It is one of the most effective forms of birth control with a one-year failure rate around 0.2%. The device is placed in the uterus and lasts three to five years. Following removal fertility returns quickly.

Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a procedure where an interventional radiologist uses a catheter to deliver small particles that block the blood supply to the uterine body. The procedure is done for the treatment of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis. Given that this minimally invasive procedure is commonly used in the treatment of uterine fibroids it is also called uterine fibroid embolization (UFE).
Adenomyoma is a tumor (-oma) including components derived from glands (adeno-) and muscle (-my-). It is a type of complex and mixed tumor.

Endometrial ablation is an outpatient medical procedure that is used to remove (ablate) or destroy the endometrial lining of the uterus in women who have heavy menstrual bleeding. Endometrial ablation should never be performed on women who wish to have children.
A menstrual disorder is an abnormal condition in a woman's menstrual cycle.

The uterine appendages are the structures most closely related structurally and functionally to the uterus.
Parametritis is an inflammation of the parametrium.

The fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, or salpinges are uterine appendages, lined from inside with ciliated simple columnar epithelium, leading from the ovaries of female mammals into the uterus, via the uterotubal junction. They enable the passage of egg cells from the ovaries to the uterus. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the equivalent structures are just called oviducts.









