
Zulu people are a native people of Southern Africa of the Nguni. The Zulu people are the largest ethnic group and nation in South Africa, living mainly in the province of KwaZulu-Natal.

The Thembu are a Xhosa Nation who inhabited the Kingdom of Thembuland. They were established around the 16th century as one of the Xhosa federations in the Transkeian territories. The federation was later annexed by British Empire shortly after the death of King Sarhili.

The Natalia Republic was a short-lived Boer republic founded in 1839 after a Voortrekker victory against the Zulus at the Battle of Blood River. The area was previously named Natália by Portuguese sailors, due to its discovery on Christmas. The republic came to an end in 1843 when British forces annexed it to form the Colony of Natal. After the British annexation of the Natalia Republic, most local Voortrekkers trekked northwest into Transorangia, later known as the Orange Free State, and the South African Republic.

The amaMfengu were a group of Xhosa clans whose ancestors were refugees that fled from the Mfecane in the early-mid 19th century to seek land and protection from the Xhosa. These refugees were assimilated into the Xhosa nation and were officially recognized by the then king, Hintsa.

The Mpondo People, or simply Ama-Mpondo, is a kingdom in what is now the Eastern Cape. It was established in 1226. The Ama-Mpondo Nation was first ruled by its founder who was King Mpondo kaNjanya who lived around and later the 'Ama-Nyawuza' clan, by nationality referred to themselves as 'Ama-Mpondo'. They are related to other Aba-Mbo kingdoms and chiefdoms in South Africa.
Mnguni was the leader of the Nguni nation who reached Southern Africa migrating from the North. Additionally, he was the father of King Xhosa. The Xhosa people, today considered a sub-nation of the Nguni nation, were historically referred to as AbeNguni. Mnguni's name derives from the word Nguni, the name for the major ethnicity in South Africa. It now includes the Zulus, Xhosas, Ndebeles and Swazis among others.
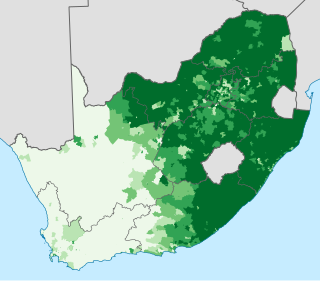
Blacks are the majority ethno-racial group in South Africa, belonging to various Bantu ethnic groups. They are descendants of Southern Bantu-speaking peoples who settled in South Africa during the Bantu expansion.

King Sarhili Ka-Hintsa was the King of Xhosa nation from 1835 until his death in 1892 at Sholora, Bomvanaland. He was also known as "Kreli", and led the Xhosa armies in a series of frontier wars.

The Nguni people are a linguistic cultural group of Bantu cattle herders who migrated from central Africa into Southern Africa, made up of ethnic groups formed from iron age and proto-agrarians, with offshoots in neighboring colonially-created countries in Southern Africa. Swazi people live in both South Africa and Eswatini, while Ndebele people live in both South Africa and Zimbabwe.

Pondoland or Mpondoland, is a natural region on the South African shores of the Indian Ocean. It is located in the coastal belt of the Eastern Cape province. Its territory is the former Mpondo Kingdom of the Mpondo people.

The Bhaca people, or amaBhaca, are an Nguni ethnic group in South Africa.

The Wild Coast is a section of the coast of the Eastern Cape, a province of South Africa. The region stretches from East London in the south to the border of KwaZulu-Natal in the north. It is the traditional home of the Xhosa, Thembu people, and the Mpondo people, and the birthplace of many prominent South Africans, including Nelson Mandela, Winnie Mandela, Zwelonke Sigcawu, Xolilizwe Sigcawu, Thabo Mbeki.

The Hlubi people or AmaHlubi are an AmaMbo ethnic group native to Southern Africa, with the majority of population found in Gauteng, Mpumalanga, KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa.

The Xhosa people( KAW-sə, KOH-sə; Xhosa pronunciation:[kǁʰɔ́ːsa] ) are a Bantu ethnic group and nation native to South Africa. They are the second largest ethnic group in South Africa and are native speakers of the isiXhosa language.

Maputaland is a natural region of Southern Africa. It is located in the northern part of the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa between Eswatini and the coast. In a wider sense it may also include the southernmost region of Mozambique. The bird routes and coral reefs off the coast are major tourist attractions.

The Gcaleka House is the Great house of the Xhosa Kingdom in what is now the Eastern Cape. Its royal palace is in the former Transkei and its counterpart in the former Ciskei is the Rharhabe, which is the right hand house of Phalo.

Langalibalele (isiHlubi: meaning 'The blazing sun', also known as Mthethwa, Mdingi, was king of the amaHlubi, a Bantu tribe in what is the modern-day province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.

Thembuland, Afrikaans: Temboeland, is a natural region in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. Its territory is the traditional region of the abaThembu.

Matiwane ka Masumpa, son of Masumpa, was the king of an independent Nguni-speaking nation, the amaNgwane, a people named after Matiwane's ancestor Ngwane ka Kgwadi. The amaNgwane lived at the headwaters of the White Umfolozi, in what is now Vryheid in northern KwaZulu-Natal. The cunning of Matiwane would keep the amaNgwane one step ahead of the ravages of the rising Zulu kingdom, but their actions also set the Mfecane in motion. After his nation was ousted from their homeland by Zwide with Shaka, Matiwane and his armies clashed with neighboring nations as he attempted to nourish his people. Eventually he fled South into lands occupied by abaThembu, amaMpondo and the neighboring Xhosa nations, which ultimately teamed up with the British and got his nation dismantled and scattered as smaller splinters at the Battle of Mbholompo in what is today Mthatha in the Eastern Cape. In his exodus from Mthatha, Matiwane and the biggest of the amaNgwane splinters was sheltered by baSotho but eventually had to return to his country, Ntenjwa, which he had settled briefly upon fleeing from his old country on uMfolozi omhlophe. Being back at Ntenjwa put a very much weakened amaNgwane and the king, Matiwane, within easy reach of the Zulu nation he had fled from. Matiwane had to then go make peace with the Zulu king, now Dingane, successor to Shaka. This despotic ruler put Matiwane to death shortly after Matiwane sought peace with the amaZulu.

The Mpondomise people, also called Ama-Mpondomise, are a Xhosa-speaking people. Their traditional homeland has been in the contemporary era Eastern Cape province of South Africa, and during apartheid they were located both in the Ciskei and Transkei region. Like other separate Xhosa-speaking kingdoms such as Aba-Thembu and Ama-Mpondo, they speak Xhosa and are at times considered as part of the Xhosa people.




















