
Gabon, officially the Gabonese Republic, is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of 270,000 square kilometres (100,000 sq mi) and a population of 2.3 million. There are coastal plains, mountains, and a savanna in the east. Libreville is the country's capital and the largest city.

Washington Township is a township in Cambria County, Pennsylvania, United States. As of the 2010 census, the township population was 875. It is part of the Johnstown, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area.
A massif is a principal mountain mass, such as a compact portion of a mountain range, containing one or more summits. In mountaineering literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain.

The Gwa'Sala-Nakwaxda'xw Nations are a union of two Kwakwaka'wakw peoples in a band government based on northern Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada, whose main reserve community is near the town of Port Hardy in the Queen Charlotte Strait region of the Central Coast region of British Columbia, Canada. The band government is a member of the Kwakiutl District Council and, for treaty negotiation purposes, the Winalagalis Treaty Group which includes three other members of the Kwakiutl District Council.

Bahr al-Arab is a river which flows approximately 800 kilometres (500 mi) through the southwest of Sudan and marks part of its international border with South Sudan. It is part of the Nile river system, being a tributary of Bahr el Ghazal, which is a tributary of the White Nile.

ALSIB was the Soviet Union portion of the Alaska-Siberian air road receiving Lend-Lease aircraft from the Northwest Staging Route. Aircraft manufactured in the United States were flown over this route for World War II combat service on the Eastern Front.

HMS Thorn (N11) was a T-class submarine of the Royal Navy. She was laid down by Cammell Laird & Co Limited, Birkenhead and launched in March 1941.
The Hartley Bay Indian Band is also known as the Gitga'at First Nation or the Hartley Bay First Nation. The members of the Gitga'at First nation are often referred to as Gitka'a'ata. The population of Gitk’a’ata peoples living in Hartley Bay ranges from approximately 130-200 people. There are also about 400-500 Gitk’a’ata peoples living in Prince Rupert, British Columbia, Canada, a neighboring territory. The Gitk’a’ata people have lived in Hartley Bay for hundreds of years, if not always. Some notable things regarding the Gitga'at First Nation are their economy, geography, government, sports involvement, COVID-19 regulations, and relations.

Fimbulheimen is a mountain range in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It stretches from Jutulstraumen by 1° west of Carsten Borchgrevink Ice at 18° east, about 200 km from the ice edge. Fimbulheimen is thus between Maudheim Plateau and Sør-Rondane.
Sidi Azeiz Airfield, or Sidi Azeis is an abandoned World War II military airfield in the eastern desert of Libya. It was located near the Egypt–Libya border near Jabbanat Sidi, about 100 km east of Tobruk. German Coordinates are given as 31°40′00″N24°54′00″E
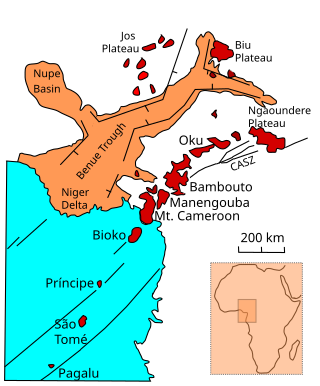
The Oku Volcanic Field or Oku Massif is a group of volcanoes based on a swell in the Cameroon Volcanic Line, located in the Oku region of the Western High Plateau of Cameroon. The Mount Oku stratovolcano rises to 3,011 m above sea level.

The Bambouto massif or Bamboutos Mountains is a group of volcanoes based on a swell in the Cameroon Volcanic Line, located in the Western High Plateau of Cameroon, merging in the north with the Oku Volcanic Field.

The wildlife of the Central African Republic is in the vast natural habitat in the Central African Republic (CAR) located between the Congo Basin's rain forests and large savannas, where the human density was smaller than 0.5 per km2 prior to 1850. The forest area of 22.755 million, considered one of the richest storehouses of wildlife spread over national parks, hunting reserves and community hunting areas, experienced an alarming loss of wildlife because of greed for ivory and bushmeat exploitation by hunters – mostly Arab slavers from across the borders of the Central African Republic with Chad and Sudan.

Ranuli Ice Piedmont is the glacier extending 7 nautical miles in south-southeast to north-northwest direction and 3 nautical miles in west-southwest to east-northeast direction on the east side of Sentinel Range in Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It is draining the east slopes of Barnes Ridge to flow into Rutford Ice Stream to the east-northeast, Young Glacier to the north, and Ellen Glacier to the south.
The Baiyang River, also known under a Mongolian name transcribed in Chinese as Namuguolei, is a river in Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region of China. It flows through the region's Tacheng Prefecture and the Urho District of Karamay City. The river's total length is estimated at 170 kilometres (110 mi), and the average annual flow at 109 million cubic metres (88,000 acre⋅ft). The river's basin occupies 16,400 square kilometres (6,300 sq mi),
The Moore Islands, also known as the Moore Group, are a group of small islands in the North Coast region of British Columbia, Canada. They are located in Hecate Strait to the west of Aristazabal Island.
Varlamov Glacier is a glacier on Beethoven Peninsula, Alexander Island, flowing northwest into the head of Brahms Inlet. It was named by the USSR Academy of Sciences in 1987 after Alexander Egorovich Varlamov (1801-48), the Russian composer.

The Kotto River is a tributary of the Oubangui River in the Central African Republic.











