
USS Montpelier (CL-57) was one of 27 United States Navy Cleveland-class light cruisers completed during or shortly after World War II. She was the second US Navy ship to be named for the city of Montpelier, Vermont. Montpelier was commissioned in September 1942 and saw service in several campaigns in the Pacific. Like almost all her sister ships, she was decommissioned shortly after the end of the war, and never saw active service again. Montpelier was scrapped in the early 1960s.

The bombing of Rabaul in November 1943 was an air attack conducted by the Allies of World War II upon a cruiser force at the major Japanese base of Rabaul. In response to the Allied invasion of Bougainville, the Japanese had brought a strong cruiser force down to Rabaul from Truk, their major naval base in the Caroline Islands about 800 miles north of Rabaul in preparation for a night engagement against the Allied supply and support shipping. Allied carrier- and land-based planes attacked the Japanese ships, airfields, and port facilities on the island of New Britain to protect the Allied amphibious invasion of Bougainville. As a result of the Rabaul raids, the Japanese naval forces could no longer threaten the landings. The success of the raid began to change the strongly held belief that carrier-based air forces could not challenge land-based air forces.
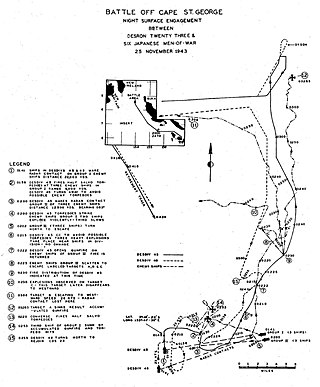
The Battle of Cape St. George was a naval battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II fought on 25 November 1943, between Cape St. George, New Ireland, and Buka Island. It was the last engagement of surface ships in the Solomon Islands campaign. During the engagement, a force of five US Navy destroyers led by Captain Arleigh Burke intercepted a similar sized Japanese force that was withdrawing from Buka towards Rabaul, having landed reinforcements on the island. In the ensuing fight, three Japanese destroyers were sunk and one was damaged, with no losses amongst the US forces.

USS Charles Ausburne (DD-570), a Fletcher-class destroyer, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for Charles L. Ausburne, a sailor in World War I who was posthumously awarded the Navy Cross.

USS Spence (DD-512), a Fletcher-class destroyer, was laid down on 18 May 1942 by the Bath Iron Works, Bath, Maine; launched on 27 October 1942; sponsored by Mrs. Eben Learned; and commissioned on 8 January 1943. The ship was named for Robert T. Spence, superintendent of the construction of USS Ontario (1813), and captain of USS Cyane (1815).

USS Converse (DD-509), a Fletcher-class destroyer, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for George A. Converse (1844–1909).

The Bougainville campaign was a series of land and naval battles of the Pacific campaign of World War II between Allied forces and the Empire of Japan, named after the island of Bougainville. It was part of Operation Cartwheel, the Allied grand strategy in the South Pacific.

Frans Kaisiepo Airport is an airport on Biak island, in Papua, Indonesia. It is also known as Mokmer Airport. The airport is named after Frans Kaisiepo (1921–1979), the fourth Governor of Papua. The airport has seven aircraft parking slots, of which two are capable of handling wide-body aircraft, and a small terminal without jet bridges. The airport's only runway is 3,571m long, designated as 11/29.
Buka Airport is an airport serving Buka Island in the Autonomous Region of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea.

The Landings at Cape Torokina, also known as Operation Cherryblossom, took place at the beginning of the Bougainville campaign in World War II. The amphibious landings were carried out by elements of the United States Marine Corps in November 1943 on Bougainville Island in the South Pacific, as part of Allied efforts to advance towards the main Japanese base around Rabaul under Operation Cartwheel. Coming in the wake of Allied successes at Guadalcanal and in the central Solomons, the landings were intended to secure a beachhead with the purpose of establishing several bases from which to project air and naval power closer towards Rabaul, in an effort to neutralize the large Japanese force that had been established there.

Fenton Airfield was a World War II military airfield in the Northern Territory of Australia located at Tipperary Station in what is now the locality of Douglas-Daly and named after flight lieutenant Clyde Fenton.

Buin is a town on Bougainville Island, and the capital of the South Bougainville District, in the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, in eastern Papua New Guinea. The island is in the northern Solomon Islands Archipelago of the Melanesia region, in the South Pacific Ocean.
The Bonis Peninsula is a narrow peninsula located on Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea, at the north of the island. The Buka Passage separates the peninsula from Buka Island.
This is a list of Imperial Japanese Navy bases and facilities

Between 9 March and 5 April 1942 during World War II, forces of the Empire of Japan occupied the islands of Buka and Bougainville in the South Pacific. At that time Buka and Bougainville were part of the Australian-administered Territory of New Guinea. A platoon of Australian commandos from the 1st Independent Company was located at Buka Airfield when the Japanese landed but did not contest the invasion.

Buka Passage is a narrow strait that separates Buka Island from the northern part of Bougainville Island, within the Autonomous Region of Bougainville of northeastern Papua New Guinea.

Captain Eikichi Kato was a senior officer in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Kato was the senior officer of the Imperial Japanese Navy forces on the Bonis Peninsula and Buka Island during the latter stages of World War II.

Kahili Airfield, also known as Buin Airfield, was an airfield located near Buin, Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea.
Aropa Airport is an airport in Kieta, Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea.

The Japanese occupation of the Solomon Islands was the period in the history of Solomon Islands between 1942 and 1945 when Imperial Japanese forces occupied Solomon Islands during World War II.















