XFS is a high-performance 64-bit journaling file system created by Silicon Graphics, Inc (SGI) in 1993. It was the default file system in SGI's IRIX operating system starting with its version 5.3. XFS was ported to the Linux kernel in 2001; as of June 2014, XFS is supported by most Linux distributions; Red Hat Enterprise Linux uses it as its default file system.
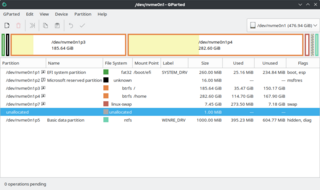
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk after a partitioning scheme is chosen for the new disk before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
A boot sector is the sector of a persistent data storage device which contains machine code to be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and then executed by a computer system's built-in firmware.

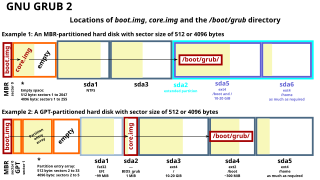
GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Free Software Foundation's Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular operating system's partitions.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.

A bootloader, also spelled as boot loader or called bootstrap loader, is a computer program that is responsible for booting a computer. If it also provides an interactive menu with multiple boot choices then it's often called a boot manager.

Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a specification for the firmware architecture of a computing platform. When a computer is powered on, the UEFI-implementation is typically the first that runs, before starting the operating system. Examples include AMI Aptio, Phoenix SecureCore, TianoCore EDK II, InsydeH2O.

vmlinux is a statically linked executable file that contains the Linux kernel in one of the object file formats supported by Linux, which includes Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) and Common Object File Format (COFF). The vmlinux file might be required for kernel debugging, symbol table generation or other operations, but must be made bootable before being used as an operating system kernel by adding a multiboot header, bootsector and setup routines.

The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of partition tables of a physical computer storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using universally unique identifiers (UUIDs), which are also known as globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). Forming a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard, it is nevertheless also used for some BIOSs, because of the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables, which use 32 bits for logical block addressing (LBA) of traditional 512-byte disk sectors.
loadlin is a Linux boot loader that runs under 16-bit real-mode DOS. It allows the Linux system to load and replace the running DOS without altering existing DOS system files.
The SPARC Improved bootLOader (SILO) is the bootloader used by the SPARC port of the Linux operating system; it can also be used for Solaris as a replacement for the standard Solaris boot loader.

The EFIsystem partition or ESP is a partition on a data storage device that is used by computers that have the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). When a computer is booted, UEFI firmware loads files stored on the ESP to start operating systems and various utilities.

The Windows Boot Manager (BOOTMGR) is the bootloader provided by Microsoft for Windows NT versions starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It is the first program launched by the BIOS or UEFI of the computer and is responsible for loading the rest of Windows. It replaced the NTLDR present in older versions of Windows.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of available bootloaders.
The Linux booting process involves multiple stages and is in many ways similar to the BSD and other Unix-style boot processes, from which it derives. Although the Linux booting process depends very much on the computer architecture, those architectures share similar stages and software components, including system startup, bootloader execution, loading and startup of a Linux kernel image, and execution of various startup scripts and daemons. Those are grouped into 4 steps: system startup, bootloader stage, kernel stage, and init process.
The BIOS boot partition is a partition on a data storage device that GNU GRUB uses on legacy BIOS-based personal computers in order to boot an operating system, when the actual boot device contains a GUID Partition Table (GPT). Such a layout is sometimes referred to as BIOS/GPT boot.

EasyBCD is a program developed by NeoSmart Technologies to configure and tweak the Boot Configuration Data (BCD), a boot database first introduced in Windows Vista and used in all subsequent Windows releases. EasyBCD can be used to set up multi-boot environments for computers on which some versions of Windows, Linux, BSD and Mac OS X can be simultaneously installed; EasyBCD can also be used for adding entries to bootable tools and utilities, as well as modifying and controlling the behavior of the Windows boot menu. EasyBCD 2.3 introduced additional support for creating and managing entries for UEFI-based Windows entries in the boot menu. As of June 20, 2011 with the release of EasyBCD 2.1, it is no longer free for use in commercial environments which require the purchase of a paid license, however it remains free for home and non-profit use without limitations.
A master boot record (MBR) is a type of boot sector in the first block of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.

rEFInd is a boot manager for UEFI and EFI-based machines. It can be used to boot multiple operating systems that are installed on a single non-volatile device. It also provides a way to launch UEFI applications.











