
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–United States maritime border and lies approximately 60 mi (97 km) west of Pennsylvania. Cleveland is the most populous city on Lake Erie, the second-most populous city in Ohio, and the 54th-most populous city in the U.S. with a population of 372,624 in 2020. The city anchors the Cleveland metropolitan area, the 33rd-largest in the U.S. at 2.18 million residents, as well as the larger Cleveland–Akron–Canton combined statistical area with 3.63 million residents.

Oneonta is a city in Blount County, Alabama, United States. At the 2020 census, the population was 6,938. The city is the county seat of Blount County. Oneonta is home to the Covered Bridge Festival.

Lima is a city in and the county seat of Allen County, Ohio, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 35,579. It is located in northwest Ohio along Interstate 75, approximately 72 miles (116 km) north of Dayton, 78 miles (126 km) southwest of Toledo, and 63 mi (101 km) southeast of Fort Wayne, Indiana.
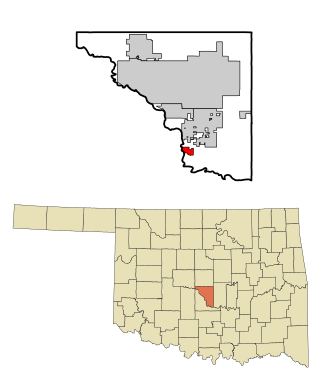
Lexington is a city in Cleveland County, Oklahoma, United States. The city population was 2,010 at the 2020 census, a 6.6% decrease from 2010.

Cleveland is the county seat of, and largest city in, Bradley County, Tennessee. The population was 47,356 at the 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Cleveland metropolitan area, Tennessee, which is included in the Chattanooga–Cleveland–Dalton, TN–GA–AL Combined Statistical Area.

Purcell is a city in and the county seat of McClain County, Oklahoma, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city population was 6,651, a 13% increase from 2010.

Weirton is a city in Hancock and Brooke counties in the U.S. state of West Virginia. Located along the Ohio River in the state's Northern Panhandle, the city's population was 19,163 as of the 2020 census, making it the seventh most populous city in the state.

The United States Public Health Service is a collection of agencies of the Department of Health and Human Services concerned with public health, containing nine out of the department's twelve operating divisions. The Assistant Secretary for Health oversees the PHS. The Public Health Service Commissioned Corps (PHSCC) is the federal uniformed service of the PHS, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States.
The NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital is a nonprofit academic medical center in New York City. It is the primary teaching hospital for Weill Cornell Medicine and Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. The hospital includes seven campuses located throughout the New York metropolitan area. The hospital's two flagship medical centers, Columbia University Irving Medical Center and Weill Cornell Medical Center, are located on opposite sides of Upper Manhattan.

Cleveland Clinic is an American nonprofit academic medical center based in Cleveland, Ohio. Owned and operated by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, an Ohio nonprofit corporation, Cleveland Clinic was founded in 1921 by a group of faculty and alumni from the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine. The Clinic runs a 170-acre (69-hectare) main campus in Cleveland, as well as 14 affiliated hospitals, 20 family health centers in Northeast Ohio, 5 affiliated hospitals in Florida, and cancer center in Nevada. International operations include the Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi hospital in the United Arab Emirates and Cleveland Clinic Canada, which has two executive health and sports medicine clinics in Toronto. Another hospital campus in the United Kingdom, Cleveland Clinic London, opened to outpatients in 2021 and fully opened in 2022. Tomislav Mihaljevic is the president and CEO.

University Circle is a district in the neighborhood of University on the East Side of Cleveland, Ohio. It is home to the Cleveland Museum of Art, Severance Hall, the Cleveland Institute of Art, the Cleveland Cinematheque, Case Western Reserve University, the Cleveland Institute of Music, the Museum of Contemporary Art Cleveland, the Cleveland Botanical Garden, historic Lake View Cemetery, the Cleveland Museum of Natural History, and University Hospitals/Case Medical Center.

Grady Memorial Hospital is the public hospital for the city of Atlanta. The hospital is ranked as the tenth largest public hospital in the United States and is a Level I trauma center.

Mary Burnett Talbert was an American orator, activist, suffragist and reformer. In 2005, Talbert was inducted into the National Women's Hall of Fame.
Medical centers in the United States are conglomerations of health care facilities including hospitals and research facilities that also either include or are closely affiliated with a medical school.
George Armstrong Garretson enlisted as private in the Union Army during the Civil War and later graduated from the U.S. Military Academy at West Point, New York. He returned to duty for the Spanish–American War as a Brigadier-general of U.S. Volunteers. In civilian life he held many prominent positions including President of The Bank of Commerce. National Association ; First Vice-President, The Guardian Savings & Trust Company; Trustee, Western Reserve University; Director, The Cleveland Electric Railway Co.; Director and Chairman of Board, The Great Lakes Towing Company; Treasurer, The Montreal Mining Company; Director, The Citizens Savings & Trust Company; Director. The Wheeling & Lake Erie R. R. Co.; Director, The Cleveland Stone Company; Treasurer, Cleveland Subdivision Ohio Branch, American National Red Cross, all of Cleveland, Ohio.

Lake View Cemetery is a privately owned, nonprofit garden cemetery located in the cities of Cleveland, Cleveland Heights, and East Cleveland in the U.S. state of Ohio. Founded in 1869, the cemetery was favored by wealthy families during the Gilded Age, and today the cemetery is known for its numerous lavish funerary monuments and mausoleums. The extensive early monument building at Lake View helped give rise to the Little Italy neighborhood, but over-expansion nearly bankrupted the burial ground in 1888. Financial recovery only began in 1893, and took several years. Lake View grew and modernized significantly from 1896 to 1915 under the leadership of president Henry R. Hatch. The cemetery's cautious management allowed it to avoid retrenchment and financial problems during the Great Depression.

NewYork-Presbyterian Queens, stylized as NewYork-Presbyterian/Queens (NYP/Q or NYP/Queens), is a not-for-profit acute care and teaching hospital affiliated with Weill Cornell Medicine in the Flushing neighborhood of Queens in New York City. Formerly operating as Booth Memorial Hospital and New York Hospital Queens (NYHQ), it is located on the northeast corner of Main Street and Booth Memorial Avenue.
Booth Memorial Hospital is the name of any of the hospitals affiliated with The Salvation Army (TSA); the latter was "founded by William Booth in 1878." The first of these "opened Booth Memorial in Manhattan in 1914 and its center in Flushing in 1957." Salvation Army Booth Memorial Hospital is a longer name used for some of them.

Mount Sinai West, opened in 1871 as Roosevelt Hospital, is affiliated with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Mount Sinai Health System.















