
The United Mexican States is a federal republic composed of 32 federal entities: 31 states and Mexico City, an autonomous entity. According to the Constitution of 1917, the states of the federation are free and sovereign in all matters concerning their internal affairs. Each state has its own congress and constitution.

The State of Mexico, officially just Mexico, is one of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Commonly known as Edomex to distinguish it from the name of the whole country, it is the most populous, as well as the second most densely populated, state in the country.

Guadalupe Victoria, born José Miguel Ramón Adaucto Fernández y Félix, was a Mexican general and politician who fought for independence against the Spanish Empire in the Mexican War of Independence and after the adoption of the Constitution of 1824, was elected as the first president of the United Mexican States. He was a deputy in the Mexican Chamber of Deputies for Durango and a member of the Supreme Executive Power following the downfall of the First Mexican Empire, which was followed by the 1824 Constitution and his presidency. He later served as Governor of Puebla.

José Venustiano Carranza de la Garza, known as Venustiano Carranza, was a Mexican land owner and politician who served as President of Mexico from 1917 until his assassination in 1920, during the Mexican Revolution. He was previously Mexico's de facto head of state as Primer Jefe of the Constitutionalist faction from 1914 to 1917, and previously served as a senator and governor for Coahuila. He played the leading role in drafting the Constitution of 1917 and maintained Mexican neutrality in World War I.

Quintana Roo is a state in southeast Mexico established out of the Quintana Roo Territory in 1974 with seven municipalities, which has since grown into eleven municipalities. According to the 2020 Mexican census, it has the twenty-fourth largest population of all states with 1,857,985 inhabitants and is the 19th largest by land area spanning 44,705.2 square kilometres (17,260.8 sq mi).

Municipalities are the second-level administrative divisions of Mexico, where the first-level administrative division is the state. They should not be confused with cities or towns that may share the same name as they are distinct entities and do not share geographical boundaries. As of March 2024, there are 2,476 municipalities in Mexico, excluding the 16 boroughs of Mexico City.
Nueva Vizcaya was the first province in the north of New Spain to be explored and settled by the Spanish. It consisted mostly of the area which is today the states of Chihuahua and Durango and the southwest of Coahuila in Mexico as well as parts of Texas in the United States.

The governor of Baja California represents the executive branch of the government of the state of Baja California, Mexico, per the state's constitution. The official title is "Free and Sovereign State of Baja California", and the position is democratically elected for a period of 6 years, and is not re-electable. From 1953 to 2019, the governor's term began November 1 of the year of the election and finishes October 31, six years later. To coincide with the federal elections, the law was changed, decreeing there would be an election in 2019, another in 2021, and yet another in 2024 before reverting to a six-year term.
Events in the year 2002 in Mexico.

The governor of Morelos, which was created with the state of Mexico in 1869.
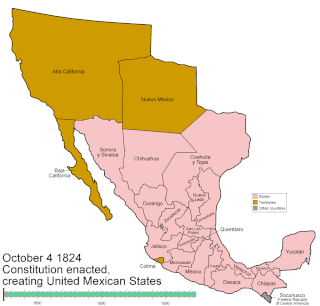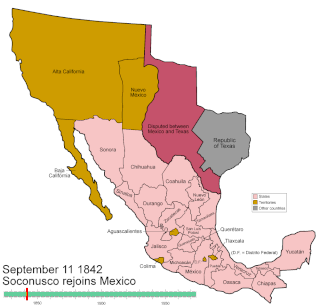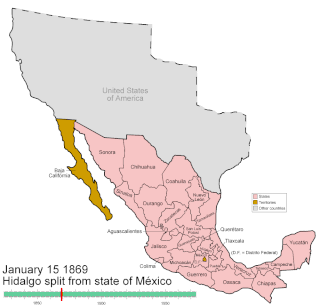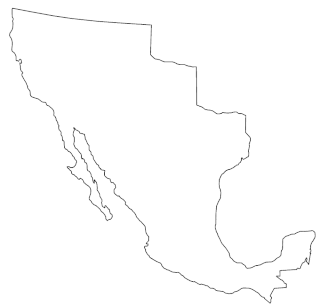
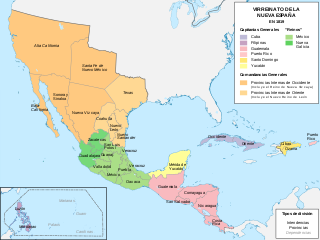
Mexico has experienced many changes in territorial organization during its history as an independent state. The territorial boundaries of Mexico were affected by presidential and imperial decrees. One such decree was the Law of Bases for the Convocation of the Constituent Congress to the Constitutive Act of the Mexican Federation, which determined the national land area as the result of integration of the jurisdictions that corresponded to New Spain, the Captaincy General of Yucatán, the Captaincy General of Guatemala and the autonomous Kingdoms of East and West. The decree resulted in the independence from Spain.

Mexico uses four time zones:

Chihuahua, officially the Estado Libre y Soberano de Chihuahua, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is located in the northwestern part of Mexico and is bordered by the states of Sonora to the west, Sinaloa to the southwest, Durango to the south, and Coahuila to the east. To the north and northeast, it shares an extensive border with the U.S. adjacent to the U.S. states of New Mexico and Texas. The state was named after its capital city, Chihuahua City; the largest city is Ciudad Juárez. In 1864 the city of Chihuahua was declared capital of Mexico by Benito Juarez during the Reform War and French intervention. The city of Parral was the largest producer of silver in the world in 1640. During the Mexican War of Independence, Miguel Hidalgo was executed on July 30, 1811, in Chihuahua city.

The Constitution of Apatzingán, formally Decreto Constitucional para la Libertad de la América Mexicana, was promulgated on 22 October 1814 by the Congress of Anahuac gathered in the city of Apatzingán because of the persecution of the troops of Félix María Calleja. The constitution was valid for insurgent forces in the territories that it controlled during the Mexican War of Independence.
Events in the year 1973 in Mexico.
The Jiménez Territory was a federal territory of Mexico that existed between 1914 and 1917. It was created by the decree of 17 June 1914 issued by the Congress of the United Mexican States that amended articles 43 and 44 of the Constitution of 1857, with the districts of Arteaga, Andrés del Río, Mina, Jiménez, and its capital, Hidalgo del Parral, from the state of Chihuahua; the decree also created the territories of Bravo and Morelos.

The Morelos Territory was a federal territory of Mexico that existed between 1914 and 1917. It was created by the decree of 17 June 1914 issued by the Congress of the United Mexican States which amended articles 43 and 44 of the Constitution of 1857, with the territory the same as the state of Morelos; the decree also created the territories Bravo and Jiménez.













