
Beer is one of the oldest alcoholic drinks in the world, the most widely consumed, and the third most popular drink after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grains—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The fermentation of the starch sugars in the wort produces ethanol and carbonation in the beer. Most modern beer is brewed with hops, which add bitterness and other flavours and act as a natural preservative and stabilising agent. Other flavouring agents, such as gruit, herbs, or fruits, may be included or used instead of hops. In commercial brewing, natural carbonation is often replaced with forced carbonation.

Hops are the flowers of the hop plant Humulus lupulus, a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to which, in addition to bitterness, they impart floral, fruity, or citrus flavours and aromas. Hops are also used for various purposes in other beverages and herbal medicine. The hops plants have separate female and male plants, and only female plants are used for commercial production. The hop plant is a vigorous, climbing, herbaceous perennial, usually trained to grow up strings in a field called a hopfield, hop garden, or hop yard when grown commercially. Many different varieties of hops are grown by farmers around the world, with different types used for particular styles of beer.

Pilsner is a type of pale lager. It takes its name from the Bohemian city of Plzeň, where the world's first pale lager was produced in 1842 by Pilsner Urquell Brewery.
The Reinheitsgebot is a series of regulations limiting the ingredients in beer in Germany and the states of the former Holy Roman Empire. The best known version of the law was adopted in Bavaria in 1516, but similar regulations predate the Bavarian order, and modern regulations also significantly differ from the 1516 Bavarian version. Although today, the Reinheitsgebot is mentioned in various texts about the history of beer, historically it was only applied in the duchy of Bavaria and from 1906 in Germany as a whole, and it had little or no effect in other countries or regions.

Gambrinus is a legendary European culture hero celebrated as an icon of beer, brewing, joviality, and joie de vivre. Typical representations in the visual arts depict him as a rotund, bearded duke or king, holding a tankard or mug, and sometimes with a keg nearby.

Beer in Belgium includes pale ales, lambics, Flemish red ales, sour brown ales, strong ales and stouts. In 2018, there were 304 breweries in Belgium, including international companies, such as AB InBev, and traditional breweries, such as Trappist monasteries. On average, Belgians drink 68 litres of beer each year, down from around 200 each year in 1900. Most beers are bought or served in bottles, rather than cans, and almost every beer has its own branded, sometimes uniquely shaped, glass. In 2016, UNESCO inscribed Belgian beer culture on their list of the intangible cultural heritage of humanity.

In brewing, adjuncts are unmalted grains or grain products used in brewing beer which supplement the main mash ingredient. This is often done with the intention of cutting costs, but sometimes also to create an additional feature, such as better foam retention, flavours or nutritional value or additives. Both solid and liquid adjuncts are commonly used.

Gruit is a herb mixture used for bittering and flavouring beer, popular before the extensive use of hops. The terms gruit and grut ale may also refer to the beverage produced using gruit. Historically, gruit is the term used in the historic Low Countries and the Holy Roman Empire. Today, however, gruit is a colloquial term misapplied to a beer seasoned with gruit-like herbs.

Lucky Lager is an American lager with U.S. brewing and distribution rights held by the Pabst Brewing Company. Originally launched in 1934 by San Francisco-based General Brewing Company, Lucky Lager grew to be one of the prominent beers of the Western United States during the 1950s and 1960s. In 2019, Pabst announced that the beer brand would be revived and would be brewed by 21st Amendment Brewery, based in San Leandro.

Beer styles differentiate and categorise beers by colour, flavour, strength, ingredients, production method, recipe, history, or origin.

Beer is one of the oldest human-produced drinks. The first chemically confirmed barley-beer – from the area of Mesopotamia, part of modern-day Iraq – dates back to the 5th millennium BCE. The written history of ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia records the use of beer, and the drink has spread throughout the world; a 3,900-year-old Sumerian poem honouring Ninkasi, the patron goddess of brewing, contains the oldest surviving beer-recipe, describing the production of beer from barley bread, and in China, residue on pottery dating from around 5,000 years ago shows that beer was brewed using barley and other grains.

Jopen is a beer brewery from Haarlem, Netherlands. Jopen's beer is a result of the work of Stichting Haarlems Biergenootschap, which was founded in 1992. The mission of the Biergenootschap is to re-create traditional Haarlem beers and bring them to the commercial market. Two recipes were found in the Haarlem city archives that were used as a foundation for two initial beers. The first one was a recipe from 1407; the recreation of this was named Koyt, a gruit beer.
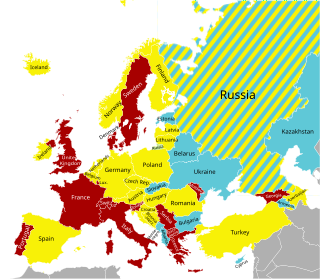
Alcohol preferences in Europe vary from country to country between beer, wine or spirits. These preferences are traditionally associated with certain regions. Hence, the Central European pattern of alcohol consumption is associated with beer-drinking, the Mediterranean pattern with wine-drinking and the Eastern or Northern European pattern with spirit-drinking countries. However, traditional preferences do not necessarily correspond to current drinking habits, as beer has become the most popular alcoholic drink world-wide.

Beer in Slovakia has been produced and consumed at least since the 15th century. Together with the neighbouring Czech Republic, with whom it has a shared and intertwined history, Slovakia has a number of breweries and a rich beer culture.

Gotlandsdricka is a traditional homebrewed alcoholic beverage made on the island of Gotland, Sweden. It is a kind of ale, closely related to the Finnish sahti, and Norwegian Maltøl with a smoky, bitter-sweet, spicy (juniper) flavor. It is similar to gruit.

Ale is a type of beer originating in medieval England, brewed using a warm fermentation method. Historically, the term referred to a drink brewed without hops.
Maashaus is a spacious room taking the whole front part of a ground floor of a multi-storied Gothic or Renaissance town house.

Beer in Egypt has long held a significant role, and its presence in the country is thought to date back to the Predynastic period. In ancient Egypt wine was preferred by the upper class, whereas beer was a staple for working class Egyptians and a central part of their diet. Despite religious restrictions and conflicting views on alcohol after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, the consumption of beer did not cease, and it still remains the most popular alcoholic beverage in the country by far, accounting for 54 percent of all alcohol consumption.

Belgian beer culture includes traditions of craftsmanship for brewing beer and is part of the diet and social life of Belgians. Its cultural value was formally recognised in 2016 when it was added to UNESCO's "Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity" list.

Saint Vincent Beer was a dark lager brewed by monks at Saint Vincent Archabbey in Unity Township, Pennsylvania, United States, between 1856 and 1918. Pope Pius IX granted the monks permission to brew in 1852, ending a dispute with the Roman Catholic Diocese of Pittsburgh. The brewery was located in a log cabin near the Saint Vincent Archabbey Gristmill and a brick building supplemented the cabin in 1868. After production ceased, the monastery used the buildings for storage until they burned down in 1926. The walls were removed from the site in 1995 during the restoration of the gristmill.

















