
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that have human occupancy or use as their principal purpose. Etymologically, the term architect derives from the Latin architectus, which derives from the Greek, i.e., chief builder.

Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

In systems engineering and software engineering, requirements analysis focuses on the tasks that determine the needs or conditions to meet the new or altered product or project, taking account of the possibly conflicting requirements of the various stakeholders, analyzing, documenting, validating and managing software or system requirements.

Ventilation is the intentional introduction of outdoor air into a space. Ventilation is mainly used to control indoor air quality by diluting and displacing indoor pollutants; it can also be used to control indoor temperature, humidity, and air motion to benefit thermal comfort, satisfaction with other aspects of the indoor environment, or other objectives.

A basement or cellar is one or more floors of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, car park, and air-conditioning system are located; so also are amenities such as the electrical system and cable television distribution point. In cities with high property prices, such as London, basements are often fitted out to a high standard and used as living space.

Interior design is the art and science of enhancing the interior of a building to achieve a healthier and more aesthetically pleasing environment for the people using the space. An interior designer is someone who plans, researches, coordinates, and manages such enhancement projects. Interior design is a multifaceted profession that includes conceptual development, space planning, site inspections, programming, research, communicating with the stakeholders of a project, construction management, and execution of the design.

A data center or data centre is a building, a dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems.

A vivarium is an area, usually enclosed, for keeping and raising animals or plants for observation or research. Water-based vivaria may have open tops providing they are not connected to other water bodies. An animal enclosure is considered a vivarium only if it provides quality of life through naturalistic components such as ample living space and natural decor that allow and encourage natural behaviours. Often, a portion of the ecosystem for a particular species is simulated on a smaller scale, with controls for environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity and light.
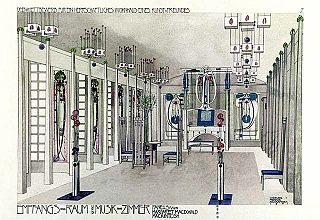
Interior architecture is the design of a building or shelter from inside out, or the design of a new interior for a type of home that can be fixed. It can refer to the initial design and plan used for a building's interior, to that interior's later redesign made to accommodate a changed purpose, or to the significant revision of an original design for the adaptive reuse of the shell of the building concerned. The latter is often part of sustainable architecture practices, whereby resources are conserved by "recycling" a structure through adaptive redesign.
A general contractor, main contractor or prime contractor is responsible for the day-to-day oversight of a construction site, management of vendors and trades, and the communication of information to all involved parties throughout the course of a building project.

The systems architect is an information and communications technology professional. Systems architects define the architecture of a computerized system in order to fulfill certain requirements. Such definitions include: a breakdown of the system into components, the component interactions and interfaces, and the technologies and resources to be used in its design and implementation.

A raised floor provides an elevated structural floor above a solid substrate to create a hidden void for the passage of mechanical and electrical services. Raised floors are widely used in modern office buildings, and in specialized areas such as command centers, Information technology data centers and computer rooms, where there is a requirement to route mechanical services and cables, wiring, and electrical supply. Such flooring can be installed at varying heights from 2 inches (51 mm) to heights above 4 feet (1.2 m) to suit services that may be accommodated beneath. Additional structural support and lighting are often provided when a floor is raised enough for a person to crawl or even walk beneath.
In systems engineering and requirements engineering, a non-functional requirement (NFR) is a requirement that specifies criteria that can be used to judge the operation of a system, rather than specific behaviours. They are contrasted with functional requirements that define specific behavior or functions. The plan for implementing functional requirements is detailed in the system design. The plan for implementing non-functional requirements is detailed in the system architecture, because they are usually architecturally significant requirements.

Noise control or noise mitigation is a set of strategies to reduce noise pollution or to reduce the impact of that noise, whether outdoors or indoors.
(In the automation and engineering environments, the hardware engineer or architect encompasses the electronics engineering and electrical engineering fields, with subspecialities in analog, digital, or electromechanical systems.)

A server room is a room, usually air-conditioned, devoted to the continuous operation of computer servers. An entire building or station devoted to this purpose is a data center.
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
HVAC is a major sub discipline of mechanical engineering. The goal of HVAC design is to balance indoor environmental comfort with other factors such as installation cost, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency. The discipline of HVAC includes a large number of specialized terms and acronyms, many of which are summarized in this glossary.

Office space planning is the process of organizing the workplace layout, furniture and office functions to work effectively together, while using space efficiently. Floor plans should consider the workgroup function, building codes and regulations, lighting, teaming requirements, inter-communication and storage, as well as zoning for employee workstations, task space needs, support rooms and reception areas to make the best use of available space. Optimising office spaces with effective space planning can aid circulation, productivity and improve workplace wellness, as well as the health and safety of occupants.

Learning space or learning setting refers to a physical setting for a learning environment, a place in which teaching and learning occur. The term is commonly used as a more definitive alternative to "classroom," but it may also refer to an indoor or outdoor location, either actual or virtual. Learning spaces are highly diverse in use, configuration, location, and educational institution. They support a variety of pedagogies, including quiet study, passive or active learning, kinesthetic or physical learning, vocational learning, experiential learning, and others. As the design of a learning space impacts the learning process, it is deemed important to design a learning space with the learning process in mind.














