
The Bristol group was a group of British warships that were sent to the "Total Exclusion Zone" as reinforcements late in the Falklands War. The majority sailed from the UK on 10 May 1982. The group consisted of:
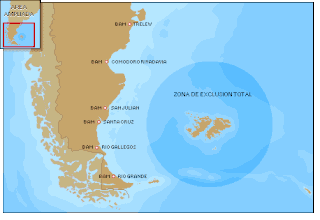
The Total Exclusion Zone (TEZ) was an area declared by the United Kingdom on 30 April 1982 covering a circle of radius 200 nautical miles from the centre of the Falkland Islands. During the Falklands War any sea vessel or aircraft from any country entering the zone may have been fired upon without further warning.

The Falklands War, also known as the Falklands Conflict, Falklands Crisis, Malvinas War, South Atlantic Conflict, and the Guerra del Atlántico Sur, was a ten-week war between Argentina and the United Kingdom over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands, and its territorial dependency, the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. It began on Friday, 2 April 1982, when Argentina invaded and occupied the Falkland Islands in an attempt to establish the sovereignty it had claimed over them. On 5 April, the British government dispatched a naval task force to engage the Argentine Navy and Air Force before making an amphibious assault on the islands. The conflict lasted 74 days and ended with the Argentine surrender on 14 June 1982, returning the islands to British control. In total, 649 Argentine military personnel, 255 British military personnel, and three Falkland Islanders died during the hostilities.
- HMS Bristol (D23), Type 82
- HMS Cardiff (D108), Type 42 joined group en route having started in Gibraltar

HMS Bristol (D23) is a Type 82 destroyer, the only vessel of her class to be built for the Royal Navy. Originally intended as the first of a class of large destroyers to escort the CVA-01 aircraft carriers projected to come into service in the early 1970s, Bristol turned out to be a unique ship: the rest of the class were cancelled with the CVA-01 carriers in the 1966 Strategic Defence Review. Following a long career which included the Falklands War, she was converted into a training ship in 1987 and continues to serve in that role. HMS Bristol is named after the English city of Bristol.

HMS Cardiff was a British Type 42 destroyer and the third ship of the Royal Navy to be named in honour of the Welsh capital city of Cardiff.
- HMS Active (F171), Type 21 frigate
- HMS Andromeda (F57), Leander class
- HMS Avenger (F185), Type 21 frigate
- HMS Minerva (F45), Leander class
- HMS Penelope (F127), Leander class

HMS Active was a Type 21-class frigate of the Royal Navy. Built by Vosper Thornycroft, Southampton, England, she was completed with Exocet launchers in 'B' position, the first of the class to be so fitted.

HMS Andromeda was a Leander-class frigate of the Royal Navy. She was built at HM Dockyard Portsmouth, the last ship to be built there. She was launched on 24 May 1967 and commissioned into the Royal Navy on 2 December 1968. She took part in the Falklands War and was sold to India in 1995, for use as a training ship, being renamed INS Krishna. She was finally decommissioned in May 2012.

HMS Avenger was a Type 21 frigate of the Royal Navy. Built by Yarrow Shipbuilders Ltd, Glasgow, Scotland, she was completed with Exocet launchers in 'B' position.
- RFA Bayleaf [ citation needed ], support tanker
- RFA Olna, fleet tanker [1] [2]

RFA Bayleaf (A109) was a Leaf-class support tanker of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary.

RFA Olna (A123) was the third and final of the three Ol-class "fast fleet tanker" of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary. Olna saw service in the Falklands War.
The group reached the task force around 26 May. [3]











