In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons.
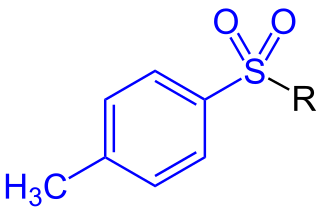
In organic chemistry, a toluenesulfonyl group (tosyl group, abbreviated Ts or Tos) is a univalent functional group with the chemical formula −SO2−C6H4−CH3. It consists of a tolyl group, −C6H4−CH3, joined to a sulfonyl group, −SO2−, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, CH3C6H4SO2Cl (abbreviated TsCl), which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid, CH3C6H4SO2OH (abbreviated TsOH). The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl without a prefix refers to the p-toluenesulfonyl group.

In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfonate is a salt, anion or ester of a sulfonic acid. Its formula is R−S(=O)2−O−, containing the functional group −S(=O)2−O−, where R is typically an organyl group, amino group or a halogen atom. Sulfonates are the conjugate bases of sulfonic acids. Sulfonates are generally stable in water, non-oxidizing, and colorless. Many useful compounds and even some biochemicals feature sulfonates.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfonyl group can refer either to a functional group found primarily in sulfones, or to a substituent obtained from a sulfonic acid by the removal of the hydroxyl group, similarly to acyl groups. Sulfonyl groups can be written as having the general formula R−S(=O)2−R′, where there are two double bonds between the sulfur and oxygen.

In organic chemistry, a sulfone is a organosulfur compound containing a sulfonyl functional group attached to two carbon atoms. The central hexavalent sulfur atom is double-bonded to each of two oxygen atoms and has a single bond to each of two carbon atoms, usually in two separate hydrocarbon substituents.
The Fries rearrangement, named for the German chemist Karl Theophil Fries, is a rearrangement reaction of a phenolic ester to a hydroxy aryl ketone by catalysis of Lewis acids.
Hydrazides in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds with the formula R−NR1−NR2R3 where R is acyl, sulfonyl, phosphoryl, phosphonyl and similar groups, R1, R2, R3 and R' are any groups. Unlike hydrazine and alkylhydrazines, hydrazides are nonbasic owing to the inductive influence of the acyl, sulfonyl, or phosphoryl substituent.
In inorganic chemistry, sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula RSO2X, where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides > chlorides > bromides > iodides, all four types being well known. The sulfonyl chlorides and fluorides are of dominant importance in this series.

TosMIC (toluenesulfonylmethyl isocyanide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2CH2NC. The molecule contains both sulfonyl and isocyanide groups. It is a colourless solid that, unlike many isocyanides, is odorless. It is prepared by dehydration of the related formamide derivative. It is used in the Van Leusen reaction which is used to convert ketones to nitriles or in the preparation of oxazoles and imidazoles. The versatility of TosMIC in organic synthesis has been documented. It is a fairly strong carbon acid, with an estimated pKa of 14 (compared to 29 for methyl tolyl sulfone), the isocyano group acting as an electron acceptor of strength comparable to an ester group.

In chemistry, the haloform reaction is a chemical reaction in which a haloform is produced by the exhaustive halogenation of an acetyl group, in the presence of a base. The reaction can be used to transform acetyl groups into carboxyl groups or to produce chloroform, bromoform, or iodoform. Note that fluoroform can't be prepared in this way.
4-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (p-toluenesulfonyl chloride, toluene-p-sulfonyl chloride) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2Cl. This white, malodorous solid is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Abbreviated TsCl or TosCl, it is a derivative of toluene and contains a sulfonyl chloride (−SO2Cl) functional group.

Imidazole-1-sulfonyl azide is an organic azide compound that can be used as an alternative organic synthesis reagent to trifluoromethanesulfonyl azide. It is an explosive colorless liquid, but some of its organic-soluble salts can be safely handled and stored as a solid.

Benzenesulfonic acid (conjugate base benzenesulfonate) is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H6O3S. It is the simplest aromatic sulfonic acid. It forms white deliquescent sheet crystals or a white waxy solid that is soluble in water and ethanol, slightly soluble in benzene and insoluble in nonpolar solvents like diethyl ether. It is often stored in the form of alkali metal salts. Its aqueous solution is strongly acidic.
Desulfonylation reactions are chemical reactions leading to the removal of a sulfonyl group from organic compounds. As the sulfonyl functional group is electron-withdrawing, methods for cleaving the sulfur–carbon bonds of sulfones are typically reductive in nature. Olefination or replacement with hydrogen may be accomplished using reductive desulfonylation methods.
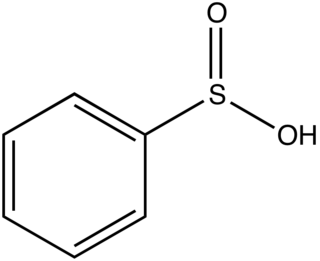
Phenylsulfinic acid is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SO2H. It is a colorless or white crystalline solid that is usually stored in the form of its sodium salt. In aqueous solution it is strongly acidic and is easily oxidized in air. Phenylsulfinic acid and its esters are chiral.

Sulfinyl halide have the general formula R−S(O)−X, where X is a halogen. They are intermediate in oxidation level between sulfenyl halides, R−S−X, and sulfonyl halides, R−SO2−X. The best known examples are sulfinyl chlorides, thermolabile, moisture-sensitive compounds, which are useful intermediates for preparation of other sufinyl derivatives such as sulfinamides, sulfinates, sulfoxides, and thiosulfinates. Unlike the sulfur atom in sulfonyl halides and sulfenyl halides, the sulfur atom in sulfinyl halides is chiral, as shown for methanesulfinyl chloride.

In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group is an organosulfur group with the structure R−S(=O)2−NR2. It consists of a sulfonyl group connected to an amine group. Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group.
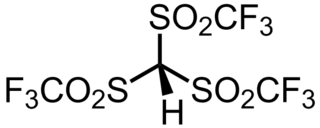
Triflidic acid (IUPAC name: tris[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]methane, abbreviated formula: Tf3CH) is an organic superacid. It is one of the strongest known carbon acids and is among the strongest Brønsted acids in general, with an acidity exceeded only by the carborane acids. Notably, triflidic acid is estimated to have an acidity 104 times that of triflic acid (pKaaq ~ –14), as measured by its acid dissociation constant. It was first prepared in 1987 by Seppelt and Turowsky by the following route:
(1) Tf2CH2 + 2CH3MgBr → Tf2C(MgBr)2 + 2CH4
(2) Tf2C(MgBr)2 + TfF → Tf3C(MgBr) + MgBrF
(3) Tf3C(MgBr) + H2SO4 → Tf3CH + MgBrHSO4















