
Broth microdilution is a method used to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to antibiotics. It is the most commonly used method to perform this test in the United States [1] and Europe. [2]

Broth microdilution is a method used to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to antibiotics. It is the most commonly used method to perform this test in the United States [1] and Europe. [2]
During testing, multiple microtiter plates are filled with a certain broth, according to the needs of target bacteria. [3] Varying concentrations of the antibiotics and the bacteria to be tested are then added to the plate. The plate is then placed into a non-CO2 incubator and incubated at thirty-seven degrees Celsius for sixteen to twenty hours. Following the allotted time, the plate is removed and checked for bacterial growth. If the broth became cloudy or a layer of cells formed at the bottom, then bacterial growth has occurred. The results of the broth microdilution method are reported in Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC), or the lowest concentration of antibiotics that stopped bacterial expansion. [1]
The broth microdilution method can be used to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to multiple antibiotics at once. [4] Broth microdilution is also highly accurate. The accuracy of its results are comparable to agar dilution, the gold standard of susceptibility testing. Other advantages include the commercial availability of plates, the ease of testing and storing the plates, and the ability for the results of some tests to be read by machines. [1]

An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.

A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as research tools in molecular biology.

Ureaplasma urealyticum is a bacterium belonging to the genus Ureaplasma and the family Mycoplasmataceae in the order Mycoplasmatales. This family consists of the genera Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma. Its type strain is T960. There are two known biovars of this species; T960 and 27. These strains of bacteria are commonly found as commensals in the urogenital tracts of human beings, but overgrowth can lead to infections that cause the patient discomfort. Unlike most bacteria, Ureaplasma urealyticum lacks a cell wall making it unique in physiology and medical treatment.

A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or fungemia, which in severe cases may result in sepsis. By culturing the blood, microbes can be identified and tested for resistance to antimicrobial drugs, which allows clinicians to provide an effective treatment.

A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss Physcomitrella patens. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells.

Antibiotic sensitivity testing or antibiotic susceptibility testing is the measurement of the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. It is used because bacteria may have resistance to some antibiotics. Sensitivity testing results can allow a clinician to change the choice of antibiotics from empiric therapy, which is when an antibiotic is selected based on clinical suspicion about the site of an infection and common causative bacteria, to directed therapy, in which the choice of antibiotic is based on knowledge of the organism and its sensitivities.

Subacute bacterial endocarditis, abbreviated SBE, is a type of endocarditis. Subacute bacterial endocarditis can be considered a form of type III hypersensitivity.
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible in vitro growth of bacteria or fungi. MIC testing is performed in both diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories.

The disk diffusion test is a culture-based microbiology assay used in diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. In diagnostic labs, the assay is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria isolated from a patient's infection to clinically approved antibiotics. This allows physicians to prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic treatment. In drug discovery labs, especially bioprospecting labs, the assay is used to screen biological material and drug candidates for antibacterial activity. When bioprospecting, the assay can be performed with paired strains of bacteria to achieve dereplication and provisionally identify antibacterial mechanism of action.
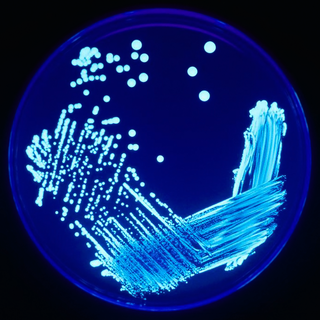
In microbiology, streaking is a technique used to isolate a pure strain from a single species of microorganism, often bacteria. Samples can then be taken from the resulting colonies and a microbiological culture can be grown on a new plate so that the organism can be identified, studied, or tested.
The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) is the lowest concentration of an antibacterial agent required to kill a particular bacterium. It can be determined from broth dilution minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) tests by subculturing to agar plates that do not contain the test agent. The MBC is identified by determining the lowest concentration of antibacterial agent that reduces the viability of the initial bacterial inoculum by ≥99.9%. The MBC is complementary to the MIC; whereas the MIC test demonstrates the lowest level of antimicrobial agent that inhibits growth, the MBC demonstrates the lowest level of antimicrobial agent that results in microbial death. This means that even if a particular MIC shows inhibition, plating the bacteria onto agar might still result in organism proliferation because the antimicrobial did not cause death. Antibacterial agents are usually regarded as bactericidal if the MBC is no more than four times the MIC. Because the MBC test uses colony-forming units as a proxy measure of bacterial viability, it can be confounded by antibacterial agents which cause aggregation of bacterial cells. Examples of antibacterial agents which do this include flavonoids and peptides.

Cefoxitin is a second-generation cephamycin antibiotic developed by Merck & Co., Inc. from Cephamycin C in the year following its discovery, 1972. It was synthesized in order to create an antibiotic with a broader spectrum. It is often grouped with the second-generation cephalosporins. Cefoxitin requires a prescription and as of 2010 is sold under the brand name Mefoxin by Bioniche Pharma, LLC. The generic version of cefoxitin is known as cefoxitin sodium.

Etest is a way of determining antimicrobial sensitivity by placing a strip impregnated with antimicrobials onto an agar plate. A strain of bacterium or fungus will not grow near a concentration of antibiotic or antifungal if it is sensitive. For some microbial and antimicrobial combinations, the results can be used to determine a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Etest is a proprietary system manufactured by bioMérieux. It is a laboratory test used in healthcare settings to help guide physicians by indicating what concentration of antimicrobial could successfully be used to treat patients' infections.

Nutrient agar is a general-purpose solid medium supporting growth of a wide range of non-fastidious organisms. It typically contains (mass/volume):

Mueller Hinton agar is a type of growth medium used in microbiology to culture bacterial isolates and test their susceptibility to antibiotics. This medium was first developed in 1941 by John Howard Mueller and Jane Hinton, who were microbiologists working at Harvard University. However, Mueller Hinton agar is made up of a couple of components, including beef extract, acid hydrolysate of casein, and starch, as well as agar to solidify the mixture. The composition of Mueller Hinton agar can vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended use, but the medium is generally nutrient-rich and free of inhibitors that could interfere with bacterial growth.
Virtual colony count (VCC) is a kinetic, 96-well microbiological assay originally developed to measure the activity of defensins. It has since been applied to other antimicrobial peptides including LL-37. It utilizes a method of enumerating bacteria called quantitative growth kinetics, which compares the time taken for a bacterial batch culture to reach a threshold optical density with that of a series of calibration curves. The name VCC has also been used to describe the application of quantitative growth kinetics to enumerate bacteria in cell culture infection models. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) can be done on 96-well plates by diluting the antimicrobial agent at varying concentrations in broth inoculated with bacteria and measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration that results in no growth. However, these methods cannot be used to study some membrane-active antimicrobial peptides, which are inhibited by the broth itself. The virtual colony count procedure takes advantage of this fact by first exposing bacterial cells to the active antimicrobial agent in a low-salt buffer for two hours, then simultaneously inhibiting antimicrobial activity and inducing exponential growth by adding broth. The growth kinetics of surviving cells can then be monitored using a temperature-controlled plate reader. The time taken for each growth curve to reach a threshold change in optical density is then converted into virtual survival values, which serve as a measure of antimicrobial activity.
Agar dilution is one of two methods used by researchers to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotics. It is the dilution method most frequently used to test the effectiveness of new antibiotics when a few antibiotics are tested against a large panel of different bacteria.
Diagnostic microbiology is the study of microbial identification. Since the discovery of the germ theory of disease, scientists have been finding ways to harvest specific organisms. Using methods such as differential media or genome sequencing, physicians and scientists can observe novel functions in organisms for more effective and accurate diagnosis of organisms. Methods used in diagnostic microbiology are often used to take advantage of a particular difference in organisms and attain information about what species it can be identified as, which is often through a reference of previous studies. New studies provide information that others can reference so that scientists can attain a basic understanding of the organism they are examining.
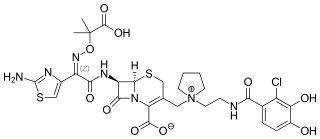
Cefiderocol, sold under the brand name Fetroja among others, is an antibiotic used to treat complicated urinary tract infections when no other options are available. It is indicated for the treatment of multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is given by injection into a vein.
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is a scientific committee for defining guidelines to interpret antimicrobial resistance. It was formed in 1997 and is jointly organized by ESCMID, ECDC and other European laboratories.