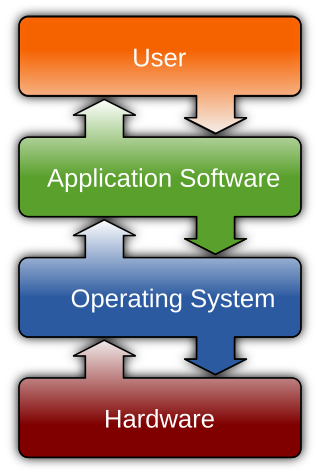
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.

Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real-world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the acronyms DAS,DAQ, or DAU, typically convert analog waveforms into digital values for processing. The components of data acquisition systems include:

Home automation or domotics is building automation for a home. A home automation system will monitor and/or control home attributes such as lighting, climate, entertainment systems, and appliances. It may also include home security such as access control and alarm systems.

Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench (LabVIEW) is a system-design platform and development environment for a visual programming language developed by National Instruments.
A gateway is a piece of networking hardware or software used in telecommunications networks that allows data to flow from one discrete network to another. Gateways are distinct from routers or switches in that they communicate using more than one protocol to connect multiple networks and can operate at any of the seven layers of the open systems interconnection model (OSI).

Open-source hardware (OSH) consists of physical artifacts of technology designed and offered by the open-design movement. Both free and open-source software (FOSS) and open-source hardware are created by this open-source culture movement and apply a like concept to a variety of components. It is sometimes, thus, referred to as FOSH. The term usually means that information about the hardware is easily discerned so that others can make it – coupling it closely to the maker movement. Hardware design, in addition to the software that drives the hardware, are all released under free/libre terms. The original sharer gains feedback and potentially improvements on the design from the FOSH community. There is now significant evidence that such sharing can drive a high return on investment for the scientific community.
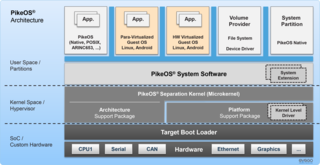
PikeOS is a commercial, hard real-time operating system (RTOS) that offers a separation kernel based hypervisor with multiple logical partition types for many other operating systems (OS), each called a GuestOS, and applications. It enables users to build certifiable smart devices for the Internet of things (IoT) according to the high quality, safety and security standards of different industries. For safety and security, critical real-time applications on controller-based systems without memory management unit (MMU) but with memory protection unit (MPU) PikeOS for MPU is available.

Windows Error Reporting (WER) is a crash reporting technology introduced by Microsoft with Windows XP and included in later Windows versions and Windows Mobile 5.0 and 6.0. Not to be confused with the Dr. Watson debugging tool which left the memory dump on the user's local machine, Windows Error Reporting collects and offers to send post-error debug information using the Internet to Microsoft when an application crashes or stops responding on a user's desktop. No data is sent without the user's consent. When a crash dump reaches the Microsoft server, it is analyzed, and information about a solution is sent back to the user if available. Solutions are served using Windows Error Reporting Responses. Windows Error Reporting runs as a Windows service. Kinshuman Kinshumann is the original architect of WER. WER was also included in the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) hall of fame for its impact on the computing industry.
The Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communications networks. The Internet of things encompasses electronics, communication and computer science engineering. Internet of things has been considered a misnomer because devices do not need to be connected to the public internet, they only need to be connected to a network, and be individually addressable.

Microsoft Azure, often referred to as Azure, is a cloud computing platform run by Microsoft. It offers access, management, and the development of applications and services through global data centers. It also provides a range of capabilities, including software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). Microsoft Azure supports many programming languages, tools, and frameworks, including Microsoft-specific and third-party software and systems.

RhoMobile Suite, based on the Rhodes open source framework, is a set of development tools for creating data-centric, cross-platform, native mobile consumer and enterprise applications. It allows developers to build native mobile apps using web technologies, such as CSS3, HTML5, JavaScript and Ruby. Developers can deploy RhoMobile Suite to write an app once and run it on the most-used operating systems, including iOS, Android, Windows Phone, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, Windows 10 Mobile and Windows Desktop. Developers control how apps behave on different devices. RhoMobile Suite consists of a set of tools for building, testing, debugging, integrating, deploying and managing consumer and enterprise apps. It consists of the products Rhodes, RhoElements, RhoStudio, RhoConnect, and RhoGallery, and includes a built-in Model View Controller pattern, an Object Relational Mapper for data intensive apps, integrated data synchronization, and a broad API set. These mobile development services are offered in the cloud and include hosted build, synchronization and application management.

Linaro is an engineering organization that works on free and open-source software such as the Linux kernel, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), QEMU, power management, graphics and multimedia interfaces for the ARM family of instruction sets and implementations thereof as well as for the Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA). The company provides a collaborative engineering forum for companies to share engineering resources and funding to solve common problems on ARM software. In addition to Linaro's collaborative engineering forum, Linaro also works with companies on a one-to-one basis through its Services division.
Mbed is a development platform and real-time operating system (RTOS) designed for internet-connected devices that utilize 32-bit ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers. These internet-enabled devices are often categorized under the Internet of Things (IoT) umbrella. The Mbed project is a collaborative effort led by Arm Holdings, in partnership with various technology companies and contributors.
SensorUp Inc. is an Internet of Things company based in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. SensorUp led the development of the Open Geospatial Consortium SensorThings API standard specification, an open and unified geospatial framework to interconnect IoT sensing devices, data, and applications over the Web. In 2014, SensorUp received funding supports from Natural Resources Canada's GeoConnections and TecTerra. In 2016, as part of the OGC Internet of Things pilot project SensorUp demonstrated its interoperable OGC SensorThings API platform solution at the Department of Homeland Security. Dr. Reginald Brothers, the Undersecretary of the Homeland Security Science and Technology, was "impressed with the ‘state of the practical’ where these various industry sensors can be integrated today using open standards that remove the stovepipe limitations of one-off technologies. " In March 2016 SensorUp submitted a new open source software project proposal, titled Whiskers, to the Eclipse Foundation. Whiskers will be an open source Javascript client library for the OGC SensorThings API and a light-weight OGC SensorThings API server for IoT gateways.
WebUSB is a JavaScript application programming interface (API) specification for securely providing access to USB devices from web applications.

oneM2M is a global partnership project founded in 2012 and constituted by 8 of the world's leading ICT standards development organizations, notably: ARIB (Japan), ATIS, CCSA (China), ETSI (Europe), TIA (USA), TSDSI (India), TTA (Korea) and TTC (Japan). The goal of the organization is to create a global technical standard for interoperability concerning the architecture, API specifications, security and enrolment solutions for Machine-to-Machine and IoT technologies based on requirements contributed by its members.

Cisco DevNet is Cisco's developer program to help developers and IT professionals who want to write applications and develop integrations with Cisco products, platforms, and APIs. Cisco DevNet includes Cisco's products in software-defined networking, security, cloud, data center, internet of things, collaboration, and open-source software development. The developer.cisco.com site also provides learning and sandbox environments as well as a video series for those trying to learn coding and testing apps.
The industrial internet of things (IIoT) refers to interconnected sensors, instruments, and other devices networked together with computers' industrial applications, including manufacturing and energy management. This connectivity allows for data collection, exchange, and analysis, potentially facilitating improvements in productivity and efficiency as well as other economic benefits. The IIoT is an evolution of a distributed control system (DCS) that allows for a higher degree of automation by using cloud computing to refine and optimize the process controls.
Zerynth is a software implementation of the Python programming language for programming microcontrollers. It targets 32-bit microcontroller platforms and is designed to mix Python with C code. It connects the microcontrollers to the Cloud for developing Internet of Things (IoT) products.
Apache IoTDB is a column-oriented open-source, time-series database (TSDB) management system written in Java. It has both edge and cloud versions, provides an optimized columnar file format for efficient time-series data storage, and TSDB with high ingestion rate, low latency queries and data analysis support. It is specially optimized for time-series oriented operations like aggregations query, downsampling and sub-sequence similarity search. The name IoTDB comes from Internet of Things (IoT) Database, which means it was designed as an IoT-native TSDB that resolves the pain points of the typical IoT scenarios, including massive data generation, high frequency sampling, out-of-order data, specific analytics requirements, high costs of storage and operation & maintenance, low computational power of IoT devices.












