Related Research Articles
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a penile erection with sufficient rigidity and duration for satisfactory sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in males and can cause psychological distress due to its impact on self-image and sexual relationships.
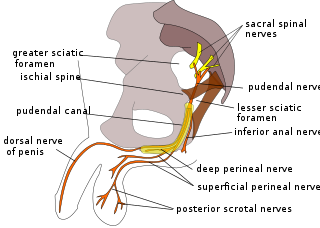
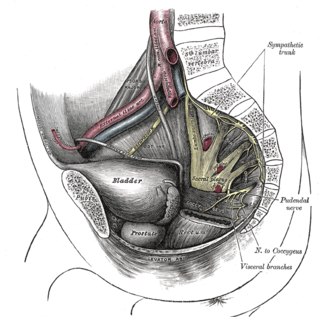
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a mixed nerve and also conveys sympathetic autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter.

Urination is the release of urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Urine is released from the urethra through the penis or vulva in placental mammals and through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, pissing, and euphemistically going number one. The process of urination is under voluntary control in healthy humans and other animals, but may occur as a reflex in infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury. It is normal for adult humans to urinate up to seven times during the day.

The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

Tetraplegia, also known as quadriplegia, is defined as the dysfunction or loss of motor and/or sensory function in the cervical area of the spinal cord. A loss of motor function can present as either weakness or paralysis leading to partial or total loss of function in the arms, legs, trunk, and pelvis. The paralysis may be flaccid or spastic. A loss of sensory function can present as an impairment or complete inability to sense light touch, pressure, heat, pinprick/pain, and proprioception. In these types of spinal cord injury, it is common to have a loss of both sensation and motor control.

The cauda equina is a bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consisting of the second through fifth lumbar nerve pairs, the first through fifth sacral nerve pairs, and the coccygeal nerve, all of which arise from the lumbar enlargement and the conus medullaris of the spinal cord. The cauda equina occupies the lumbar cistern, a subarachnoid space inferior to the conus medullaris. The nerves that compose the cauda equina innervate the pelvic organs and lower limbs to include motor innervation of the hips, knees, ankles, feet, internal anal sphincter and external anal sphincter. In addition, the cauda equina extends to sensory innervation of the perineum and, partially, parasympathetic innervation of the bladder.

Retrograde ejaculation occurs when semen which would be ejaculated via the urethra is redirected to the urinary bladder. Normally, the sphincter of the bladder contracts before ejaculation, inhibiting urination and preventing a reflux of semen into the bladder. The semen is forced to exit via the urethra, the path of least resistance. When the bladder sphincter does not function properly, retrograde ejaculation may occur. It can also be induced deliberately by a male as a primitive form of male birth control or as part of certain alternative medicine practices. The retrograde-ejaculated semen is excreted from the bladder during the next urination.

The bulbospongiosus muscles are a subgroup of the superficial muscles of the perineum. They have a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, these muscles cover the bulb of the penis, while in females, they cover the vestibular bulbs.
The anal wink, anal reflex, perineal reflex, or anocutaneous reflex is the reflexive contraction of the external anal sphincter upon stroking of the skin around the anus.

Onuf's nucleus is a distinct group of neurons located in the ventral part of the anterior horn of the sacral region of the human spinal cord involved in the maintenance of micturition and defecatory continence, as well as muscular contraction during orgasm. It contains motor neurons, and is the origin of the pudendal nerve. The sacral region of the spinal cord is the fourth segment of vertebrae in the spinal cord which consists of the vertebrae 26-30. While working in New York City in 1899, Bronislaw Onuf-Onufrowicz discovered this group of unique cells and originally identified it as “Group X.” “Group X” was considered distinct by Onufrowicz because the cells were different in size from the surrounding neurons in the anterolateral group, suggesting that they were independent.

The external anal sphincter is an oval tube of skeletal muscle fibers. Distally, it is adherent to the skin surrounding the margin of the anus. It exhibits a resting state of tonical contraction and also contracts during the bulbospongiosus reflex.

The internal anal sphincter, IAS, or sphincter ani internus is a ring of smooth muscle that surrounds about 2.5–4.0 cm of the anal canal. It is about 5 mm thick, and is formed by an aggregation of the smooth (involuntary) circular muscle fibers of the rectum. It terminates distally about 6 mm from the anal orifice.

The external sphincter muscle of the male urethra, also sphincter urethrae membranaceae, sphincter urethrae externus, surrounds the whole length of the membranous urethra, and is enclosed in the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.

Radical retropubic prostatectomy is a surgical procedure in which the prostate gland is removed through an incision in the abdomen. It is most often used to treat individuals who have early prostate cancer. Radical retropubic prostatectomy can be performed under general, spinal, or epidural anesthesia and requires blood transfusion less than one-fifth of the time. Radical retropubic prostatectomy is associated with complications such as urinary incontinence and impotence, but these outcomes are related to a combination of individual patient anatomy, surgical technique, and the experience and skill of the surgeon.
Nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT) is a spontaneous erection of the penis during sleep or when waking up. Along with nocturnal clitoral tumescence, it is also known as sleep-related erection. Colloquially, the term morning wood, or less commonly, morning glory is also used, although this is more commonly used to refer specifically to an erection beginning during sleep and persisting into the period just after waking. Men without physiological erectile dysfunction or severe depression experience nocturnal penile tumescence, usually three to five times during a period of sleep, typically during rapid eye movement sleep. Nocturnal penile tumescence is believed to contribute to penile health.

In human anatomy, the penis is an external male sex organ that serves as a passage for excretion of urine and ejaculation of semen. The main parts are the root, body, the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the opening, the urinary meatus.

In human male anatomy, the radix or root of the penis is the internal and most proximal portion of the human penis that lies in the perineum. Unlike the pendulous body of the penis, which is suspended from the pubic symphysis, the root is attached to the pubic arch of the pelvis and is not visible externally. It is triradiate in form, consisting of three masses of erectile tissue; the two diverging crura, one on either side, and the median bulb of the penis or urethral bulb. Approximately one third to one half of the penis is embedded in the pelvis and can be felt through the scrotum and in the perineum.

An erection is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is often associated with sexual arousal, sexual attraction or libido, although erections can also be spontaneous. The shape, angle, and direction of an erection vary considerably between humans.

Ejaculation is the discharge of semen through the urethra in men. It is normally linked with orgasm, which involves involuntary contractions of the pelvic floor. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. Ejaculation can occur spontaneously during sleep, and is a normal part of human sexual development. In rare cases, ejaculation occurs because of prostatic disease. Anejaculation is the condition of being unable to ejaculate. Ejaculation is normally intensely pleasurable for men; dysejaculation is an ejaculation that is painful or uncomfortable. Retrograde ejaculation is the backward flow of semen into the bladder rather than out of the urethra.
Hard flaccid syndrome (HFS), also known as hard flaccid (HF), is a chronic painful condition characterized by a semi-rigid penis at the flaccid state, a soft glans at the erect state (cold glans syndrome), pelvic pain, low libido, erectile dysfunction, erectile pain, pain on ejaculation, penile sensory changes (numbness or coldness), lower urinary tract symptoms, contraction of the pelvic floor muscles, and psychological distress. Other complaints include rectal and perineal discomfort, cold hands and feet, and a hollow or detached feeling inside the penile shaft. The majority of HFS patients are in their 20s–30s and symptoms significantly affect one's quality of life.
References
- ↑ Vodušek DB, Deletis V (2002). "Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring of the Sacral Nervous System". Neurophysiology in Neurosurgery, A Modern Intraoperative Approach: 153–165. doi:10.1016/B978-012209036-3/50011-1. ISBN 9780122090363. S2CID 78605592.
- ↑ Jiang XZ, Zhou CK, Guo LH, Chen J, Wang HQ, Zhang DQ, et al. (December 2009). "[Role of bulbocavernosus reflex to stimulation of prostatic urethra in pathologic mechanism of primary premature ejaculation]". Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (in Chinese). 89 (46): 3249–3252. PMID 20193361.
- ↑ Sarica Y, Karacan I (July 1987). "Bulbocavernosus reflex to somatic and visceral nerve stimulation in normal subjects and in diabetics with erectile impotence". The Journal of Urology. 138 (1): 55–58. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(17)42987-9. PMID 3599220.