
Beginning on August 7, 1961, a series of social psychology experiments were conducted by Yale University psychologist Stanley Milgram, who intended to measure the willingness of study participants to obey an authority figure who instructed them to perform acts conflicting with their personal conscience. Participants were led to believe that they were assisting an unrelated experiment, in which they had to administer electric shocks to a "learner". These sham or fake electric shocks gradually increased to levels that would have been fatal had they been real.
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values. People display this bias when they select information that supports their views, ignoring contrary information, or when they interpret ambiguous evidence as supporting their existing attitudes. The effect is strongest for desired outcomes, for emotionally charged issues, and for deeply entrenched beliefs. Confirmation bias is insuperable for most people, but they can manage it, for example, by education and training in critical thinking skills.
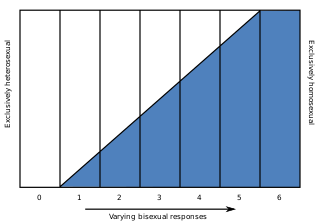
The Kinsey scale, also called the Heterosexual–Homosexual Rating Scale, is used in research to describe a person's sexual orientation based on one's experience or response at a given time. The scale typically ranges from 0, meaning exclusively heterosexual, to a 6, meaning exclusively homosexual. In both the male and female volumes of the Kinsey Reports, an additional grade, listed as "X", indicated "no socio-sexual contacts or reactions" (asexuality). The reports were first published in Sexual Behavior in the Human Male (1948) by Alfred Kinsey, Wardell Pomeroy, and others, and were also prominent in the complementary work Sexual Behavior in the Human Female (1953).

The Stanford prison experiment (SPE) was a psychological experiment conducted in August 1971. It was a two-week simulation of a prison environment that examined the effects of situational variables on participants' reactions and behaviors. Stanford University psychology professor Philip Zimbardo led the research team who administered the study.

Brainstorming is a creativity technique in which a group of people interact to suggest ideas spontaneously in response to a prompt. Stress is typically placed on the volume and variety of ideas, including ideas that may seem outlandish or "off-the-wall". Ideas are noted down during the activity, but not assessed or critiqued until later. The absence of criticism and assessment is intended to avoid inhibiting participants in their idea production. The term was popularized by advertising executive Alex Faickney Osborn in the classic work Applied Imagination (1953).
The availability heuristic, also known as availability bias, is a mental shortcut that relies on immediate examples that come to a given person's mind when evaluating a specific topic, concept, method, or decision. This heuristic, operating on the notion that, if something can be recalled, it must be important, or at least more important than alternative solutions not as readily recalled, is inherently biased toward recently acquired information.
Serial-position effect is the tendency of a person to recall the first and last items in a series best, and the middle items worst. The term was coined by Hermann Ebbinghaus through studies he performed on himself, and refers to the finding that recall accuracy varies as a function of an item's position within a study list. When asked to recall a list of items in any order, people tend to begin recall with the end of the list, recalling those items best. Among earlier list items, the first few items are recalled more frequently than the middle items.

A scavenger hunt is a game in which the organizers prepare a list defining specific items, which the participants seek to gather or complete all items on the list, usually without purchasing them. Usually participants work in small teams, although the rules may allow individuals to participate. The goal is to be the first to complete the list or to complete the most items on that list. In variations of the game, players take photographs of listed items or be challenged to complete the tasks on the list in the most creative manner. A treasure hunt is another name for the game, but it may involve following a series of clues to find objects or a single prize in a particular order.
Random assignment or random placement is an experimental technique for assigning human participants or animal subjects to different groups in an experiment using randomization, such as by a chance procedure or a random number generator. This ensures that each participant or subject has an equal chance of being placed in any group. Random assignment of participants helps to ensure that any differences between and within the groups are not systematic at the outset of the experiment. Thus, any differences between groups recorded at the end of the experiment can be more confidently attributed to the experimental procedures or treatment.

Participant Media, LLC was an American independent film and television production company founded in 2004 by Jeffrey Skoll, dedicated to entertainment intended to spur social change. The company finances and co-produces film and television content, as well as digital entertainment through its subsidiary SoulPancake, which the company acquired in 2016.
The 2002 Russian census was the first census of the Russian Federation since the dissolution of the Soviet Union, carried out on October 9 through October 16, 2002. It was carried out by the Russian Federal Service of State Statistics (Rosstat).
The World Open Pairs Championship is a contract bridge competition initiated in 1962 and held as part of the World Bridge Series Championships every four years. Open to all pairs without any quota restrictions on nationality, the championship is widely regarded as the most prestigious pairs competition in contract bridge. In its present form, the competition lasts eight days.
The World Mixed Pairs Championship is a bridge championship for mixed-gender pairs held every four years as part of the World Bridge Championships.
Free recall is a common task in the psychological study of memory. In this task, participants study a list of items on each trial, and then are prompted to recall the items in any order. Items are usually presented one at a time for a short duration, and can be any of a number of nameable materials, although traditionally, words from a larger set are chosen. The recall period typically lasts a few minutes, and can involve spoken or written recall. The standard test involves the recall period starting immediately after the final list item; this can be referred to as immediate free recall (IFR) to distinguish it from delayed free recall (DFR). In delayed free recall, there is a short distraction period between the final list item and the start of the recall period. Both IFR and DFR have been used to test certain effects that appear during recall tests, such as the primacy effect and recency effect.
The World Women Pairs Championship is a bridge championship held every four years as part of the World Bridge Championships. It is restricted to women pairs only.
The World Senior Pairs Championship is one of the competitions held as part of the quadrennial World Bridge Championships, inaugurated at the 8th rendition of the meet in 1990.

Sport is a form of physical activity or game. Often competitive and organized, sports use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills. They also provide enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Many sports exist, with different participant numbers, some are done by a single person with others being done by hundreds. Most sports take place either in teams or competing as individuals. Some sports allow a "tie" or "draw", in which there is no single winner; others provide tie-breaking methods to ensure one winner. A number of contests may be arranged in a tournament format, producing a champion. Many sports leagues make an annual champion by arranging games in a regular sports season, followed in some cases by playoffs.

Introductory diving, also known as introductory scuba experience, trial diving and resort diving are dives where people without diver training or certification can experience scuba diving under the guidance of a recreational diving instructor. Introductory diving is an opportunity for interested people to find out by practical experience at a relatively low cost if they would be interested in greater involvement in scuba diving. For scuba instructors and diving schools is it an opportunity to acquire new customers. An introductory diving experience is much less time-consuming and costly than the completion of autonomous diver training, but has little lasting value, as it is an experience program only, for which no certification is issued. Introductory scuba diving experiences are intended to introduce people to recreational diving, and increase the potential client base of dive shops to include people who do not have the time or inclination to complete an entry level certification program.







