Related Research Articles
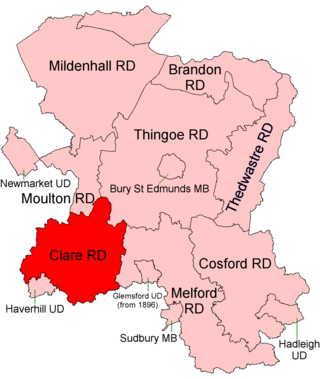
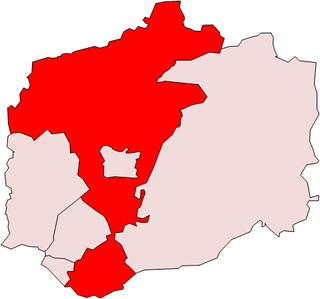
Clare Rural District was a rural district in the county of West Suffolk, England. It was created by the Local Government Act 1894, comprising those parishes in the Risbridge rural sanitary district which were in Suffolk.

Melford Rural District was a rural district in the county of West Suffolk, England. It was created in 1894, under the Local Government Act 1894 from that part of the Sudbury rural sanitary district in West Suffolk. It was named after Long Melford and administered from Sudbury. Shortly after its creation, in 1896, the parish of Glemsford was made a separate urban district.
Gloucester was, from 1894 to 1974, a rural district in the administrative county of Gloucestershire, England. The district did not include the City of Gloucester, which was a separate county borough. In 1935, Gloucester RD was more than doubled in size.
Melton was a rural district in Leicestershire, England from 1894 to 1935.

Melbourn Rural District was a rural district in Cambridgeshire, England, from 1894 to 1934.
Halstead was a rural district in Essex, England from 1894 to 1974. It was created by the Local Government Act 1894 as a successor to the Halstead rural sanitary district.
Belchamp was a rural district in Essex in England. It was formed under the Local Government Act 1894 from that part of the Sudbury rural sanitary district which was in Essex.
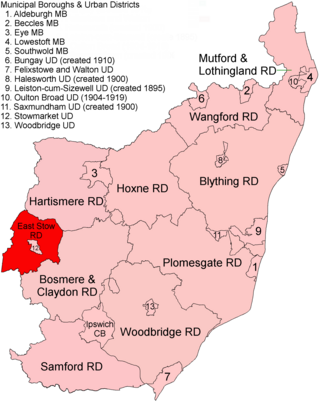
East Stow was a rural district in East Suffolk, England from 1894 to 1934.
Gnosall was a rural district in Staffordshire, England from 1894 to 1934. It was formed under the Local Government Act 1894 from that part of the Newport Rural Sanitary District which was in Staffordshire.
Stansted was a rural district in Essex, England from 1894 to 1934.
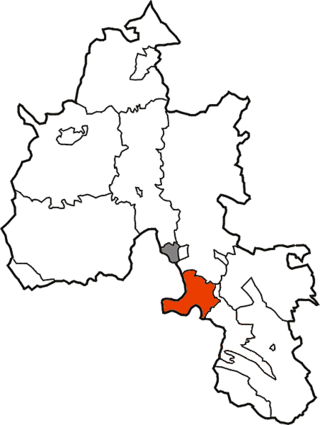
Culham was a rural district in Oxfordshire, England, from 1894 to 1932. It was formed under the Local Government Act 1894 from the part of the Abingdon Rural Sanitary District in the administrative county of Oxfordshire. The remainder of the sanitary district, in the administrative county of Berkshire, became Abingdon Rural District. The rural district council continued to be based at Abingdon, holding meetings in the workhouse of the poor law union.
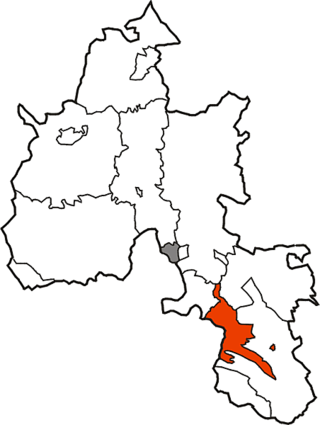
Crowmarsh was a rural district in Oxfordshire, England from 1894 to 1932.
Cannock was a rural district in Staffordshire, England, from 1894 to 1974.

Helions Bumpstead is a village and civil parish in the Braintree district, in Essex, England, located near Haverhill and the meeting-point of the Essex, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire borders. It is 2 miles from Steeple Bumpstead. Helions Bumpstead has "the greens"; Pale Green, Wiggens Green, and Drapers Green. There are four roads into and out of the village; they are Mill Road, Water Lane, Sages End Road and Camps Road. The centre of the village is marked by the crossroads and village green. There is also a meadow with a pond in the centre of the village. In 2011 the parish had a population of 439.
Epping was, from 1894 to 1955, a rural district in the administrative county of Essex, England.

Marston Sicca was, from 1894 to 1931, a rural district in the administrative county of Gloucestershire, England. The district formed part of a salient of Gloucestershire nearly surrounded by Warwickshire and Worcestershire. In 1931 the boundaries of the three counties were adjusted. The rural district was abolished and its area transferred to Warwickshire.

Campden was, from 1894 to 1935, a rural district in the administrative county of Gloucestershire, England. The district lay on the north-eastern boundary of Gloucestershire, and consisted of three separate areas nearly surrounded by the counties of Warwickshire and Worcestershire. The county and district boundaries were simplified in 1931 and the district was abolished in 1935.
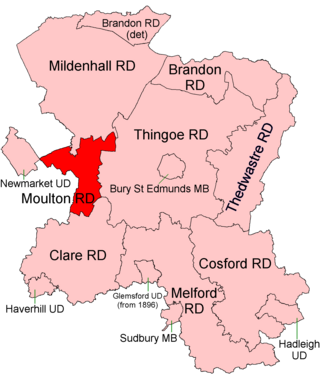
Moulton was a rural district in Suffolk, England from 1894 to 1935. It covered the area to the east of the town of Newmarket.
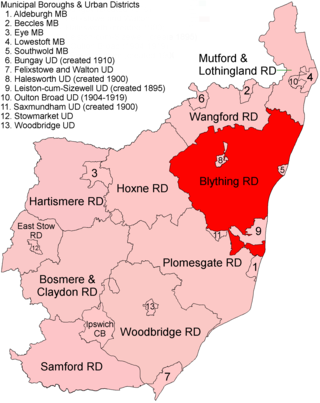
Blything Rural District was a rural district within the administrative county of East Suffolk between 1894 and 1934.

Cotton Hall is a Grade II listed stately home in the village of Kedington, Suffolk, England. It is located on the banks of the River Stour and is one of the ancient notable manor houses in the parish. From 1742 it was the residence of the Bowyer family of Suffolk. The present building is a timber-frame and plaster structure estimated to be built between the 15th and 17th centuries. It was heavily restored in the 20th century.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Youngs, Frederic A Jr. (1979). Guide to the Local Administrative Units of England, Vol.I: Southern England. London: Royal Historical Society. p. 602. ISBN 0-901050-67-9.
- ↑ "Steeple Bumpstead". Kelly's Directory of Essex. 1914. p. 590. Retrieved 12 April 2009.