Related Research Articles

Schist is a medium-grade metamorphic rock formed from mudstone or shale. Schist has medium to large, flat, sheet-like grains in a preferred orientation. It is defined by having more than 50% platy and elongated minerals, often finely interleaved with quartz and feldspar. These lamellar minerals include micas, chlorite, talc, hornblende, graphite, and others. Quartz often occurs in drawn-out grains to such an extent that a particular form called quartz schist is produced. Schist is often garnetiferous. Schist forms at a higher temperature and has larger grains than phyllite. Geological foliation with medium to large grained flakes in a preferred sheetlike orientation is called schistosity.

Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock types, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The original rock (protolith) is subjected to heat and pressure, causing profound physical or chemical change. The protolith may be a sedimentary, igneous, or existing metamorphic rock.

A rock is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition and the way in which it is formed. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks and sedimentary rocks. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the crust.

Metamorphism is the change of minerals or geologic texture in pre-existing rocks (protoliths), without the protolith melting into liquid magma. The change occurs primarily due to heat, pressure, and the introduction of chemically active fluids. The chemical components and crystal structures of the minerals making up the rock may change even though the rock remains a solid. Changes at or just beneath Earth's surface due to weathering or diagenesis are not classified as metamorphism. Metamorphism typically occurs between diagenesis, and melting (~850°C).

Amphibolite is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase.

Greywacke or graywacke is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness, dark color, and poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or lithic fragments set in a compact, clay-fine matrix. It is a texturally immature sedimentary rock generally found in Paleozoic strata. The larger grains can be sand- to gravel-sized, and matrix materials generally constitute more than 15% of the rock by volume. The term "greywacke" can be confusing, since it can refer to either the immature aspect of the rock or its fine-grained (clay) component.

The Moine Thrust Belt or Moine Thrust Zone is a linear tectonic feature in the Scottish Highlands which runs from Loch Eriboll on the north coast 190 kilometres (120 mi) south-west to the Sleat peninsula on the Isle of Skye. The thrust belt consists of a series of thrust faults that branch off the Moine Thrust itself. Topographically, the belt marks a change from rugged, terraced mountains with steep sides sculptured from weathered igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks in the west to an extensive landscape of rolling hills over a metamorphic rock base to the east. Mountains within the belt display complexly folded and faulted layers and the width of the main part of the zone varies up to 10 kilometres (6.2 mi), although it is significantly wider on Skye.

A shear zone is a very important structural discontinuity surface in the Earth's crust and upper mantle. It forms as a response to inhomogeneous deformation partitioning strain into planar or curviplanar high-strain zones. Intervening (crustal) blocks stay relatively unaffected by the deformation. Due to the shearing motion of the surrounding more rigid medium, a rotational, non co-axial component can be induced in the shear zone. Because the discontinuity surface usually passes through a wide depth-range, a great variety of different rock types with their characteristic structures are produced.

Mylonite is a fine-grained, compact metamorphic rock produced by dynamic recrystallization of the constituent minerals resulting in a reduction of the grain size of the rock. Mylonites can have many different mineralogical compositions; it is a classification based on the textural appearance of the rock.

In geology, shear is the response of a rock to deformation usually by compressive stress and forms particular textures. Shear can be homogeneous or non-homogeneous, and may be pure shear or simple shear. Study of geological shear is related to the study of structural geology, rock microstructure or rock texture and fault mechanics.
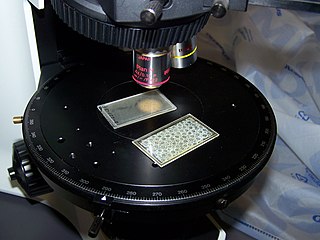
In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section is a laboratory preparation of a rock, mineral, soil, pottery, bones, or even metal sample for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron microprobe. A thin sliver of rock is cut from the sample with a diamond saw and ground optically flat. It is then mounted on a glass slide and then ground smooth using progressively finer abrasive grit until the sample is only 30 μm thick. The method involved using the Michel-Lévy interference colour chart. Typically quartz is used as the gauge to determine thickness as it is one of the most abundant minerals.
A cataclastic rock is a type of fault rock that has been wholly or partly formed by the progressive fracturing and comminution of existing rocks, a process known as cataclasis. Cataclasis involves the granulation, crushing, or milling of the original rock, then rigid-body rotation and translation of mineral grains or aggregates before lithification. Cataclastic rocks are associated with fault zones and impact event breccias.

Tectonites are metamorphic or tectonically deformed rocks whose fabric reflects the history of their deformation, or rocks with fabric that clearly displays coordinated geometric features that indicate continuous solid (ductile) flow during formation. Planar foliation results from a parallel orientation of platey mineral phases such as the phyllosilicates or graphite. Slender prismatic crystals such as amphibole produce a lineation in which these prisms or columnar crystals become aligned. Tectonites are rocks with minerals that have been affected by natural forces of the earth, which allowed their orientations to change. This usually includes recrystallization of minerals, and the foliation formation. Tectonites are studied through structural analysis and allows for the determination of two things:

Cataclasite is a cohesive granular fault rock. Comminution, also known as cataclasis, is an important process in forming cataclasites. They fall into the category of cataclastic rocks which are formed through faulting or fracturing in the upper crust. Cataclasites are distinguished from fault gouge, which is incohesive, and fault breccia, which contains coarser fragments.
The Thiviers-Payzac Unit is a metasedimentary succession of late Neoproterozoic and Cambrian age outcropping in the southern Limousin in France. The unit geologically forms part of the Variscan basement of the northwestern Massif Central.
Oblique foliation, steady state foliation or oblique fabric is a special type of a tectonically produced foliation or fabric, most commonly in quartz-rich layers. The microtectonic structure can be used to determine the shear sense in shear zones and their associated rocks, usually mylonites.

The geology of Massachusetts includes numerous units of volcanic, intrusive igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks formed within the last 1.2 billion years. The oldest formations are gneiss rocks in the Berkshires, which were metamorphosed from older rocks during the Proterozoic Grenville orogeny as the proto-North American continent Laurentia collided against proto-South America. Throughout the Paleozoic, overlapping the rapid diversification of multi-cellular life, a series of six island arcs collided with the Laurentian continental margin. Also termed continental terranes, these sections of continental rock typically formed offshore or onshore of the proto-African continent Gondwana and in many cases had experienced volcanic events and faulting before joining the Laurentian continent. These sequential collisions metamorphosed new rocks from sediments, created uplands and faults and resulted in widespread volcanic activity. Simultaneously, the collisions raised the Appalachian Mountains to the height of the current day Himalayas.
The Bloody Bluff fault is the boundary between the Milford-Dedham zone and the Nashoba zone in eastern Massachusetts. It runs between Westborough, Massachusetts and Lynnfield, Massachusetts. In the south, into Connecticut, the component Lake Char fault is poorly exposed. The Bloody Bluff fault zone is 3.2 kilometers wide in Framingham, Massachusetts and forms the five kilometer wide Burlington mylonite zone to the north. Rocks along the fault have experienced both ductile and brittle deformation.
The Middleton Basin is a small sedimentary basin, in northeastern Massachusetts, containing Late Triassic and Early Jurassic red beds. Estimated to be 5.7 kilometers long and at most half a kilometer wide, it is one of the smallest basins in the state and is closely associated with the Newbury basins.
The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland.
References
- ↑ Goldsmith, Richard (1991). Structural and Metamorphic History of Eastern Massachusetts. USGS. p. H45-H46.
| This Massachusetts state location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |