Related Research Articles

The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organisation created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957, aiming to foster economic integration among its member states. It was subsequently renamed the European Community (EC) upon becoming integrated into the first pillar of the newly formed European Union (EU) in 1993. In the popular language, the singular European Community was sometimes inaccurately used in the wider sense of the plural European Communities, in spite of the latter designation covering all the three constituent entities of the first pillar. The EEC was also known as the European Common Market (ECM) in the English-speaking countries, and sometimes referred to as the European Community even before it was officially renamed as such in 1993. In 2009, the EC formally ceased to exist and its institutions were directly absorbed by the EU. This made the Union the formal successor institution of the Community.

The Treaty of Rome, or EEC Treaty, brought about the creation of the European Economic Community (EEC), the best known of the European Communities (EC). The treaty was signed on 25 March 1957 by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and West Germany, and it came into force on 1 January 1958. Originally the "Treaty establishing the European Economic Community", and now continuing under the name "Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union", it remains one of the two most important treaties in what is now the European Union (EU).

The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community, and the European Economic Community (EEC), the last of which was renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993 by the Maastricht Treaty establishing the European Union. The European Union was established at that time more as a concept rather than an entity, while the Communities remained the actual subjects of international law impersonating the rather abstract Union, becoming at the same time its first pillar. In popular language, however, the singular European Community was sometimes used interchangeably with the plural phrase, in the sense of referring to all three entities.

Eurostat is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to the institutions of the European Union (EU) and to promote the harmonisation of statistical methods across its member states and candidates for accession as well as EFTA countries. The organisations in the different countries that cooperate with Eurostat are summarised under the concept of the European Statistical System.
The Merger Treaty, also known as the Treaty of Brussels, was a European treaty which unified the executive institutions of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) and the European Economic Community (EEC). The treaty was signed in Brussels on 8 April 1965 and came into force on 1 July 1967. It set out that the Commission of the European Communities should replace the High Authority of the ECSC, the Commission of the EEC and the Commission of Euratom, and that the Council of the European Communities should replace the Special Council of Ministers of the ECSC, the Council of the EEC and the Council of Euratom. Although each Community remained legally independent, they shared common institutions and were together known as the European Communities. This treaty is regarded by some as the real beginning of the modern European Union.

The presence of the logo on commercial products indicates that the manufacturer or importer affirms the goods' conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is not a quality indicator or a certification mark. The CE marking is required for goods sold in the European Economic Area (EEA); goods sold elsewhere may also carry the mark.

Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006, amended on 16 December 2008 by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008. REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Its 849 pages took seven years to pass, and it has been described as the most complex legislation in the Union's history and the most important in 20 years. It is the strictest law to date regulating chemical substances and will affect industries throughout the world. REACH entered into force on 1 June 2007, with a phased implementation over the next decade. The regulation also established the European Chemicals Agency, which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of REACH.

The Dangerous Substances Directive was one of the main European Union laws concerning chemical safety, until its full replacement by the new regulation CLP Regulation (2008), starting in 2016. It was made under Article 100 of the Treaty of Rome. By agreement, it is also applicable in the EEA, and compliance with the directive will ensure compliance with the relevant Swiss laws. The Directive ceased to be in force on 31 May 2015 and was repealed by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006.
The European Centre for the Development of Professional Training (Cedefop) is an agency of the European Union. The Agency was established in 1975. Cedefop is headquartered and located in Thessaloniki Region, Greece, and has a Brussels office. Cedefop is the acronym of its French title, Centre Européen pour le Développement de la Formation Professionnelle (C.E.DE.FO.P.). Cedefop supports the development of European professional education policies and contributes to their implementation.
The Undertakings for Collective Investment in Transferable Securities Directive is a EU directive that allows collective investment schemes to operate freely throughout the EU on the basis of a single authorisation from one member state. EU member states are entitled to have additional regulatory requirements for the benefit of investors.
The freedom of movement for workers is a policy chapter of the acquis communautaire of the European Union. The free movement of workers means that nationals of any member state of the European Union can take up an employment in another member state on the same conditions as the nationals of that particular member state. In particular, no discrimination based on nationality is allowed. It is part of the free movement of persons and one of the four economic freedoms: free movement of goods, services, labour and capital. Article 45 TFEU states that:
- Freedom of movement for workers shall be secured within the Community.
- Such freedom of movement shall entail the abolition of any discrimination based on nationality between workers of the Member States as regards employment, remuneration and other conditions of work and employment.
- It shall entail the right, subject to limitations justified on grounds of public policy, public security or public health:
- The provisions of this article shall not apply to employment in the public service.
Intrastat is the system for collecting information and producing statistics on the trade in goods between countries of the European Union (EU). It began operation on 1 January 1993, when it replaced customs declarations as the source of trade statistics within the EU. The requirements of Intrastat are similar in all member states of the EU, although there are important exceptions.
Government procurement or public procurement is undertaken by the public authorities of the European Union (EU) and its member states in order to award contracts for public works and for the purchase of goods and services in accordance with principles derived from the Treaties of the European Union. Such procurement represents 13.6% of EU GDP as of March 2023, and has been the subject of increasing European regulation since the 1970s because of its importance to the European single market.
Council Regulation (EEC) No 2658/87 of 23 July 1987, creates the goods nomenclature called the Combined Nomenclature, or in abbreviated form 'CN', established to meet, at one and the same time, the requirements both of the Common Customs Tariff and of the external trade statistics of the European Union. It is closely related to the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States.

The Statistical Classification of Economic Activities in the European Community, commonly referred to as NACE, is the industry standard classification system used in the European Union. The current version is revision 2 and was established by Regulation (EC) No 1893/2006. It is the European implementation of the UN classification ISIC, revision 4.
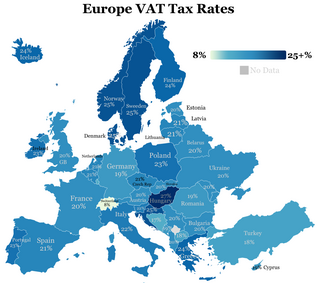
The European Union value-added tax is a value added tax on goods and services within the European Union (EU). The EU's institutions do not collect the tax, but EU member states are each required to adopt in national legislation a value added tax that complies with the EU VAT code. Different rates of VAT apply in different EU member states, ranging from 17% in Luxembourg to 27% in Hungary. The total VAT collected by member states is used as part of the calculation to determine what each state contributes to the EU's budget.

The Dangerous Preparations Directive was a European Union directive in the field of occupational safety and health and consumer protection that came into force in 30 July 1999. It complemented the Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) and replaced a previous Dangerous Preparations Directive (88/379/EEC). The European Court of Justice had ruled in 1985 that Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) applies only to pure substances, not preparations. It was repealed on 1 June 2015, as part of the European Union's adoption of Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals, as part of CLP Regulation.
A statistical business register (SBR) plays a central part in a system of official economic statistics at a national statistics office.
References
- ↑ "Business Register System 95 (URS 95)" (PDF). KombiFiD Unternehmensregister EN. D Statis.
- ↑ "Regulation (EC) No 177/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 February 2008 establishing a common framework for business registers for statistical purposes and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 2186/93". European Commission.