
The Pandya dynasty, also referred to as the Pandyas of Madurai, was an ancient Tamil dynasty of South India, and among the four great kingdoms of Tamilakam, the other three being the Pallavas, the Cholas and the Cheras. Existing since at least the 4th to 3rd centuries BCE, the dynasty passed through two periods of imperial dominance, the 6th to 10th centuries CE, and under the 'Later Pandyas'. Under Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan I and Maravarman Kulasekara Pandyan I, the Pandyas ruled extensive territories including regions of present-day South India and northern Sri Lanka through vassal states subject to Madurai. Pandya dynasty is the longest ruling dynasty in the world.

The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The Pallavas played a crucial role in shaping in particular southern Indian history and heritage. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahana Empire, whom they had formerly served as feudatories.

Kanchipuram also known as Kanjeevaram, is a stand alone city corporation, satellite nodal city of Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu in the Tondaimandalam region, 72 km (45 mi) from Chennai – the capital of Tamil Nadu. Known as the City of Thousand Temples, Kanchipuram is known for its temple architectures, 1000-pillared halls, huge temple towers and silk saris. Kanchipuram serves as one of the most important inland tourist destinations in India. Kanchipuram has become a centre of attraction for foreign tourists as well. The city covers an area of 36.14 km2 (13.95 sq mi) and an estimated population of 232,816 in 2011. It is the administrative headquarters of Kanchipuram District. Kanchipuram is well-connected by road and rail.
Pulakeshi II popularly known as Immaḍi Pulakeśi, was the greatest Chalukyan Emperor who reigned from Vatapi. During his reign, the Chalukya empire expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in peninsular India.

Vishnuvardhana was a king of the Hoysala Empire in what is today the state of Karnataka, India. He ascended the Hoysala throne after the death of his elder brother Veera Ballala I in c.1108. Originally a follower of Jainism and known as Bitti Deva, he came under the influence of the Hindu philosopher Ramanuja, converted to Hindu Vaishnavism and took the name "Vishnuvardhana". His queen Shanthala however remained a Jain. This was the transition period from Jainism to Hinduism. Vishnuvardhana took the first steps in creating an independent Hoysala Empire in South India through a series of battles against his overlord, the Western Chalukya King Vikramaditya VI, and the Chola Empire to the south. He recovered parts of Gangavadi province from the hegemony of the Cholas in the battle of Talakad, and parts of Nolambavdi. According to historian Coelho, the Hoysalas gained the dignity of a kingdom due to the efforts of Vishnuvardhana, whose rule was packed with "glorious" military campaigns. According to historians Sen, Chopra et al., and Sastri, Vishnuvardhana was a "great soldier" and an "ambitious monarch".

Vijayalaya Chola founded the Imperial Chola Empire. He ruled over the region to the north of the river Kaveri. He is one of the descendants of the famous Sangam age Chola king, Karikala Chola. Vijayalaya was succeeded by his son Aditya Chola I who laid the foundation of the Imperial Chola Empire.

Karikala, often referred to as Karikala the Great, was a Tamil Emperor of the Early Cholas of the Chola dynasty who ruled ancient Tamilakam from Uraiyur. He is credited with the construction of the flood banks of the river Kaveri and conquest of Tamilakam, Andhra and Sri Lanka. He is recognised as the greatest of the Early Cholas. In Thiruvalangadu plates of Rajendra Chola I, Medieval Tamil Cholas listed Karikala Chola as one of their ancestors.

Kulothunga II was a Chola Emperor from 1133 CE to 1150 CE. He succeeded Vikrama Chola to the throne in 1135 CE. Vikrama Chola made Kulothunga his heir apparent and coregent in 1133 CE, so the inscriptions of Kulothunga II count his reign from 1133 CE. According to historians Nilakanta Sastri and T.N Subramanian, Kulottunga Chola II was not the son of Vikrama Chola and they have suggested that there was a break in the line of succession.
Vikramaditya I was the third son and followed his father, Pulakeshi II on to the Chalukya throne. He restored order in the fractured empire and made the Pallavas retreat from the capital Vatapi.
Vinayaditya ruled the Chalukya kingdom from 681 to 696 AD. He was the son of Vikramaditya I and the successor of the chalukya kingdom. Similar to his forefathers, he took up titles such as "Shri-Prithivi-Vallabha", "Satyasraya", "Yuddhamalla" and "Rajasraya". He carried campaigns against the Pallavas, Kalabhras, Haihayas, Vilas, Cholas, Pandyas, Gangas and many more. He levied tribute from the kings of Kavera, Parasika (Iran), Sinhala (Ceylon). He acquired the banner called Palidhvaja by defeating the Lord of the entire Uttarapatha.

Mayurasharma or Mayuravarma, a native of Talagunda, was the founder of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi, the earliest native kingdom to rule over what is today the modern state of Karnataka, India. Before the rise of the Kadambas, the centres of power ruling the land were outside the Karnataka region; thus the Kadambas' ascent to power as an independent geo-political entity, with Kannada, the language of the soil as a major regional language, is a landmark event in the history of modern Karnataka with Mayurasharma as an important historical figure. The earliest Kannada language inscriptions are attributed to the Kadambas of Banavasi.
Narasimhavarman II, popularly known as Rajasimha and as Rajamalla, was a Pallava monarch who reigned from 695 CE to 728 CE. He is credited with the construction of the Shore Temple Complex, the Isvara and Mukunda Temples in Mamallapuram, the Talagirisvara Temple in Panamalai and the Kailasanathar Temple in Kanchi. He is further credited with the construction of a Buddhist Vihara at Nagipattinam, which is commonly known as ‘China-pagoda'.

Kallidaikurichi Aiyah Nilakanta Sastri was an Indian historian who wrote on South Indian history. Many of his books form the standard reference works on the subject. Sastri was acclaimed for his scholarship and mastery of sources and was a recipient of the third highest Indian civilian honour, the Padma Bhushan.
Maravarman Rajasimha I, also known as Pallavabhanjana,(Tamil:முதலாம் இராசசிம்மன்) was a Pandya king of early medieval south India. He was the son and successor of Ko Chadaiyan Ranadhira. He remembered for his important successes against the Pallavas and in the Kongu country.
Arikesari Maravarman, also known as Parankusa,(Tamil: அரிகேசரி மாறவர்மன்) was a Pandya king of early medieval south India.
Diwan Bahadur Sakkottai Krishnaswamy Aiyangar was an Indian historian, academician and Dravidologist. He chaired the Department of Indian History and Archaeology at the University of Madras from 1914 to 1929.

Thiru Parameswara Vinnagaram or Vaikunta Perumal Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to the God Vishnu, located in Kanchipuram in the Southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Constructed in the Dravidian style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Nalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th through the 9th centuries CE. It is one among the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to the God Vishnu, who is worshipped as Vaikuntanathan and his consort, the Goddess Lakshmi as Sri Vaikundavalli. The temple is considered the second oldest extant temple in Kanchipuram after the Kailasanathar temple.
Tondaiman Ilandiraiyan or Ilamtiraiyan was a ruler of Kanchipuram and a contemporary of the Early Chola king, Karikala. He is traditionally regarded as the founder of the Pallava dynasty. Ilandiraiyan is referred to in the literature of the Sangam period and is the hero of some of the poems in the Pathupattu. He was a poet himself and four of his songs are extant even today. He ruled from Tondaimandalam and was known as 'Tondaman'. According to historian S. Krishnaswami Aiyengar, the Pallavas were natives of Tondaimandalam and the name Pallava is identical with the word Tondaiyar.
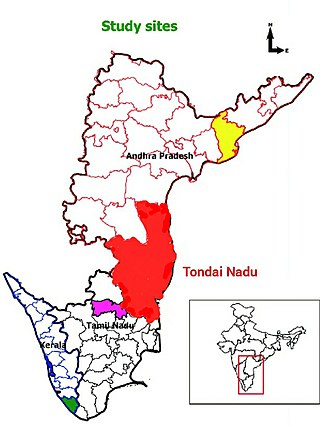
Toṇḍaimaṇḍalam, also known as Toṇḍai Nāḍu, is a historical region located in the northernmost part of Tamil Nadu and southernmost part of Andhra Pradesh. The region comprises the districts which formed a part of the legendary kingdom of Athondai Chakravarti. The boundaries of Tondaimandalam are ambiguous – between the river basins of Penna River and Ponnaiyar River. During the reign of Rajaraja I, this region was called as Jayankonda Cholamandalam.










