
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), also known as androstenolone, is an endogenous steroid hormone precursor. It is one of the most abundant circulating steroids in humans. DHEA is produced in the adrenal glands, the gonads, and the brain. It functions as a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the androgen and estrogen sex steroids both in the gonads and in various other tissues. However, DHEA also has a variety of potential biological effects in its own right, binding to an array of nuclear and cell surface receptors, and acting as a neurosteroid and modulator of neurotrophic factor receptors.
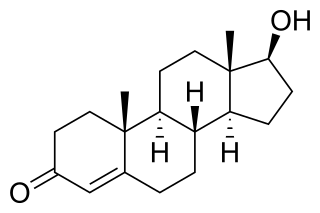
An androgen is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes the embryological development of the primary male sex organs, and the development of male secondary sex characteristics at puberty. Androgens are synthesized in the testes, the ovaries, and the adrenal glands.

Prasterone, also known as dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and sold under the brand names Intrarosa, Diandrone, and Gynodian Depot among others, is a medication as well as over-the-counter dietary supplement which is used to correct DHEA deficiency due to adrenal insufficiency or old age, as a component of menopausal hormone therapy, to treat painful sexual intercourse due to vaginal atrophy, and to prepare the cervix for childbirth, among other uses. It is taken by mouth, by application to the skin, in through the vagina, or by injection into muscle.

Epiandrosterone, or isoandrosterone, also known as 3β-androsterone, 3β-hydroxy-5α-androstan-17-one, or 5α-androstan-3β-ol-17-one, is a steroid hormone with weak androgenic activity. It is a metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It was first isolated in 1931, by Adolf Friedrich Johann Butenandt and Kurt Tscherning. They distilled over 17,000 litres of male urine, from which they got 50 milligrams of crystalline androsterone, which was sufficient to find that the chemical formula was very similar to estrone.
The molecular formula C20H30O2 (molar mass : 302.45 g/mol, exact mass : 302.22458) may refer to:
The molecular formula C19H28O5S (molar mass: 368.488 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C21H30O3 (molar mass: 330.46 g/mol, exact mass: 330.2195 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C27H40O4 (molar mass: 428.60 g/mol, exact mass: 428.2927 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C25H31NO3 (molar mass: 393.52 g/mol, exact mass: 393.2304 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C30H46O3 (molar mass: 454.68 g/mol, exact mass: 454.3447 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C25H36O4 (molar mass: 400.55 g/mol, exact mass: 400.2614 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C23H34O3 (molar mass: 358.51 g/mol, exact mass: 358.2508 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C25H38O3 (molar mass: 386.57 g/mol) may refer to:

3α-Androstanediol glucuronide (3α-ADG) is a metabolite formed from human androgens; compounds involved in the development and maintenance of sexual characteristics. It is formed by the glucuronidation of both dihydrotestosterone and testosterone, and has been proposed as means of measuring androgenic activity.
Androstenolone may refer to:
The molecular formula C27H34O3 (molar mass: 406.56 g/mol, exact mass: 406.2508 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C29H46O3 (molar mass: 442.674 g/mol, exact mass: 442.3447 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C29H38O3 (molar mass: 434.61 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C28H42O3 (molar mass: 426.641 g/mol, exact mass: 426.3134 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C26H38O3 (molar mass: 398.578 g/mol, exact mass: 398.2821 u) may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



