The molecular formula C2H6O2 (molar mass: 62.07 g/mol, exact mass: 62.03678 u) may refer to:
- Ethylene glycol (ethane-1,2-diol)
- Ethyl hydroperoxide
- Methoxymethanol
- Dimethyl peroxide
The molecular formula C2H6O2 (molar mass: 62.07 g/mol, exact mass: 62.03678 u) may refer to:
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance which is the number of moles in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.
In organic chemistry, an alkyl substituent is an alkane missing one hydrogen. The term alkyl is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions. An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of CnH2n+1. A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloalkane by removal of a hydrogen atom from a ring and has the general formula CnH2n-1. Typically an alkyl is a part of a larger molecule. In structural formulae, the symbol R is used to designate a generic (unspecified) alkyl group. The smallest alkyl group is methyl, with the formula CH3.
C2H2 may mean:
The molecular formula C2H6O (molar mass: 46.07 g/mol, exact mass: 46.04186 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H6OS (molar mass: 78.13 g/mol, exact mass: 78.01394 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H6S (molar mass: 62.13 g/mol, exact mass: 62.01902 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula CH2O3 (molar mass: 62.02 g/mol, exact mass: 62.0004 u) may refer to:
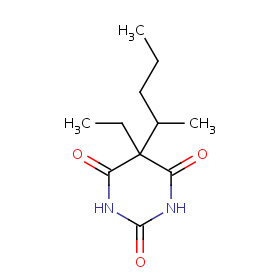
The molecular formula C11H18N2O3 (molar mass: 226.27 g/mol) may be referred as:
The molecular formula C27H42O3 (molar mass: 414.62 g/mol, exact mass: 414.313395 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C26H43NO5 (molar mass: 449.62 g/mol, exact mass: 449.3141 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H18BrNO2 (molar mass: 288.18 g/mol, exact mass: 287.0521 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C10H7Cl (molar mass: 162.62 g/mol, exact mass: 162.0236 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C30H62 (molar mass: 422.81 g/mol, exact mass: 422.4852 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C62H111N11O12 (molar mass: 1202.611 g/mol, exact mass: 1201.841 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula H2N2O2 (molar mass: 62.03 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H3FO (molar mass: 62.04 g/mol, exact mass: 62.0179 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula CH2OS (molar mass: 62.09 g/mol, exact mass: 61.9826 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C24H46O4 (molar mass: 398.62 g/mol, exact mass: 398.3396 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C25H42N7O17P3S (molar mass: 837.62 g/mol) may refer to: