
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.

Ethanol is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula C2H6O. Its formula can be also written as CH3−CH2−OH or C2H5OH. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, and the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks.
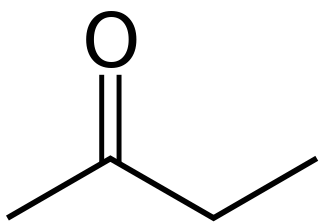
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.
Ethane is an organic chemical compound with chemical formula C
2H
6. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petrochemical by-product of petroleum refining. Its chief use is as feedstock for ethylene production.

In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile.

Lipid peroxidation is the chain of reactions of oxidative degradation of lipids. It is the process in which free radicals "steal" electrons from the lipids in cell membranes, resulting in cell damage. This process proceeds by a free radical chain reaction mechanism. It most often affects polyunsaturated fatty acids, because they contain multiple double bonds in between which lie methylene bridges (-CH2-) that possess especially reactive hydrogen atoms. As with any radical reaction, the reaction consists of three major steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. The chemical products of this oxidation are known as lipid peroxides or lipid oxidation products (LOPs).
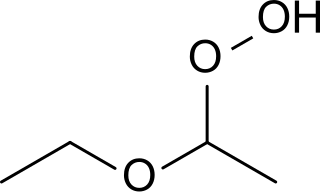
Diethyl ether hydroperoxide is the organic compound with the formula C2H5OCH(OOH)CH3. It is a colorless, distillable liquid. Diethyl ether hydroperoxide and its condensation products are blamed for the explosive organic peroxides that slowly form upon exposure of diethyl ether to ambient air and temperature conditions.

In chemistry, photocatalysis is the acceleration of a photoreaction in the presence of a photocatalyst, the excited state of which "repeatedly interacts with the reaction partners forming reaction intermediates and regenerates itself after each cycle of such interactions." In many cases, the catalyst is a solid that upon irradiation with UV- or visible light generates electron–hole pairs that generate free radicals.

tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.
Autoxidation refers to oxidations brought about by reactions with oxygen at normal temperatures, without the intervention of flame or electric spark. The term is usually used to describe the gradual degradation of organic compounds in air at ambient temperatures. Many common phenomena can be attributed to autoxidation, such as food going rancid, the 'drying' of varnishes and paints, and the perishing of rubber. It is also an important concept in both industrial chemistry and biology. Autoxidation is therefore a fairly broad term and can encompass examples of photooxygenation and catalytic oxidation.

Hydroperoxides or peroxols are compounds containing the hydroperoxide functional group (ROOH). If the R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds.

3-Methylbutanoic acid, also known as β-methylbutyric acid or more commonly isovaleric acid, is a branched-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula (CH3)2CHCH2CO2H. It is classified as a short-chain fatty acid. Like other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, it has an unpleasant odor. The compound occurs naturally and can be found in many foods, such as cheese, soy milk, and apple juice.

In polymer chemistry photo-oxidation is the degradation of a polymer surface due to the combined action of light and oxygen. It is the most significant factor in the weathering of plastics. Photo-oxidation causes the polymer chains to break, resulting in the material becoming increasingly brittle. This leads to mechanical failure and, at an advanced stage, the formation of microplastics. In textiles the process is called phototendering.
tert-Butyl hydroperoxide (tBuOOH) is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)3COOH. It is one of the most widely used hydroperoxides in a variety of oxidation processes, for example the Halcon process. It is normally supplied as a 69–70% aqueous solution. Compared to hydrogen peroxide and organic peracids, tert-butyl hydroperoxide is less reactive and more soluble in organic solvents. Overall, it is renowned for the convenient handling properties of its solutions. Its solutions in organic solvents are highly stable.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements.
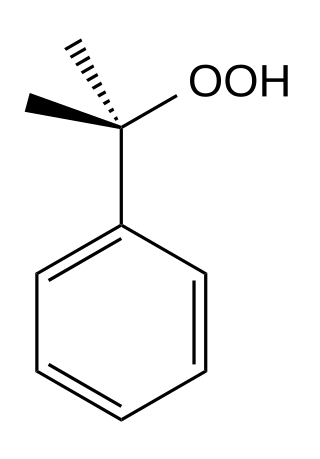
Cumene hydroperoxide is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CMe2OOH (Me = CH3). An oily liquid, it is classified as an organic hydroperoxide. Products of decomposition of cumene hydroperoxide are methylstyrene, acetophenone, and cumyl alcohol. Its formula is C6H5C(CH3)2OOH.
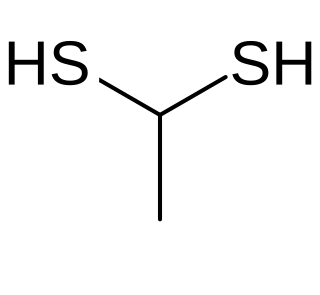
Ethane-1,1-dithiol is an organosulfur compound with formula CH3CH(SH)2. It is a colourless smelly liquid that is added to or found in some foods. The compound is an example of a geminal dithiol.
Radical theory is an obsolete scientific theory in chemistry describing the structure of organic compounds. The theory was pioneered by Justus von Liebig, Friedrich Wöhler and Auguste Laurent around 1830 and is not related to the modern understanding of free radicals. In this theory, organic compounds were thought to exist as combinations of radicals that could be exchanged in chemical reactions just as chemical elements could be interchanged in inorganic compounds.

Photogeochemistry merges photochemistry and geochemistry into the study of light-induced chemical reactions that occur or may occur among natural components of Earth's surface. The first comprehensive review on the subject was published in 2017 by the chemist and soil scientist Timothy A Doane, but the term photogeochemistry appeared a few years earlier as a keyword in studies that described the role of light-induced mineral transformations in shaping the biogeochemistry of Earth; this indeed describes the core of photogeochemical study, although other facets may be admitted into the definition.

Transition metal isocyanide complexes are coordination compounds containing isocyanide ligands. Because isocyanides are relatively basic, but also good pi-acceptors, a wide range of complexes are known. Some isocyanide complexes are used in medical imaging.

















