The molecular formula C4H4O2 may refer to:
- Cyclobutanediones
- Cycloprop-2-ene carboxylic acid
- Diketene
- Dioxins
- 2-Furanone
- Methyl propiolate
- Tetrolic acid
The molecular formula C4H4O2 may refer to:
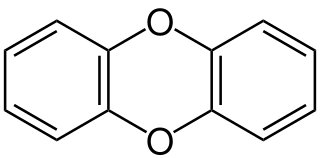
Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, also dibenzodioxin or dibenzo-p-dioxin (dibenzo-para-dioxin), is a polycyclic heterocyclic organic compound in which two benzene rings are connected by a 1,4-dioxin ring. Its molecular formula is C12H8O2. The two oxygen atoms occupy opposite (para-) positions in the six-membered dioxin ring.
C2H4O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H8O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C3H6O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H6O4 (molar mass: 118.09 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H8O3 may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H8O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H12O2 (Molar mass: 116.15 g/mol) may refer to:

1,4-Dioxin (also referred as dioxin or p-dioxin) is a heterocyclic, organic, non-aromatic compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. There is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin, 1,2-dioxin (or o-dioxin). 1,2-Dioxin is very unstable due to its peroxide-like characteristics.

1,2-Dioxin is a heterocyclic, organic, antiaromatic compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. It is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin (or p-dioxin).
Dioxin may refer to a number of different substances. Most notably:
The molecular formula C22H24N2O10 (molar mass: 476.438 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C10H6O8 may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H4O4 may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H4O5 may refer to:

Benzenedicarboxylic acid is a group of chemical compounds which are dicarboxylic derivatives of benzene. Benzenedicarboxylic acid comes in three isomers:

2,4,5-Trichlorophenol (TCP) is an organochloride with the molecular formula C6H3Cl3O. It has been used as a fungicide and herbicide. Precursor chemical used in the production of 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) and hexachlorophene involves the intermediate production of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol (TCP) and the formation of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD, commonly referred to simply as dioxin) as an unwanted by-product. In the course of purifying the hexachlorophene, still bottom wastes were created with concentrated levels of TCP and dioxin.
The molecular formula C3H6OS2 may refer to:
1,2-Cyclobutanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)2(CO)2. It is one of two isomers of cyclobutanedione, the other being 1,3-cyclobutanedione. It is prone to polymerization. It is prepared by desilylation of 1,2-bis(trimethylsiloxy)cyclobutene.
Cyclobutanedione may refer to: