The molecular formula C5H6O (molar mass: 82.10 g/mol, exact mass: 82.0419 u) may refer to:
- Cyclopentenone, or 2-cyclopentenone
- Methylfuran
- Pyran, or oxine
The molecular formula C5H6O (molar mass: 82.10 g/mol, exact mass: 82.0419 u) may refer to:
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance which is the number of moles in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.
C2H2 may mean:
The molecular formula C2H6O (molar mass: 46.07 g/mol, exact mass: 46.04186 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H10 (molar mass: 58.12 g/mol, exact mass: 58.07825 u) may refer to:
Cyclopentenone prostaglandins are a subset of prostaglandins (PGs) or prostanoids that has 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15-d-Δ12,14-PGJ2), Δ12-PGJ2, and PGJ2 as its most prominent members but also including PGA2, PGA1, and, while not classified as such, other PGs. 15-d-Δ12,14-PGJ2, Δ12-PGJ2, and PGJ2 share a common mono-unsaturated cyclopentenone structure as well as a set of similar biological activities including the ability to suppress inflammation responses and the growth as well as survival of cells, particularly those of cancerous or neurological origin. Consequently, these three cyclopentenone-PGs and the two epoxyisoprostanes are suggested to be models for the development of novel anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer drugs. The cyclopenentone prostaglandins are structurally and functionally related to a subset of isoprostanes viz., two cyclopentenone isoprostanes, 5,6-epoxyisoprostane E2 and 5,6-epoxisoprostane A2.
The molecular formula C5H11NO2S (molar mass: 149.21 g/mol, exact mass: 149.0510 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H10 (molar mass: 82.14 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C9H8O4 (molar mass: 180.15 g/mol, exact mass: 180.0423 u) may refer to:
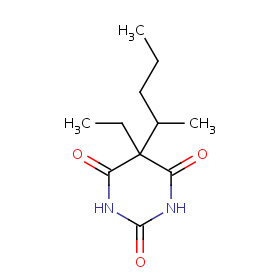
The molecular formula C11H18N2O3 (molar mass: 226.27 g/mol) may be referred as:
The molecular formula C19H18ClN3O (molar mass: 339.82 g/mol, exact mass: 339.1138 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H18BrNO2 (molar mass: 288.18 g/mol, exact mass: 287.0521 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C18H19ClN4 (molar mass: 326.82 g/mol, exact mass: 326.1298 u) may refer to:

2-Methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O. It is a highly flammable, mobile liquid. It is mainly used as a replacement for Tetrahydrofuran (THF) in specialized applications for its better performance, such as to obtain higher reaction temperatures, or easier separations (as, unlike THF, it is not miscible with water). It is derived from sugars via furfural and is occasionally touted as a biofuel.
The molecular formula C16H21ClN4 (molar mass: 304.82 g/mol, exact mass: 304.1455 u) may refer to:
2-Cyclopentenone is a ketone with chemical formula C5H6O and CAS number 930-30-3. It is structurally similar to cyclopentanone, with the additional feature of α-β unsaturation in the ring system. 2-Cyclopentenone contains two functional groups, a ketone and an alkene. It is a colorless liquid.
The molecular formula C16H22ClN3O2 (molar mass: 323.82 g/mol, exact mass: 323.1401 u) may refer to:
Eulim or ilm is a chemistry library written in Ruby under the MIT license. It supports the calculation of molecular mass of compound, balancing chemical equations, efficient handling of states of chemical species and many more things.
The molecular formula C65H82N2O18S2 (molar mass: 1243.49 g/mol) may refer to: