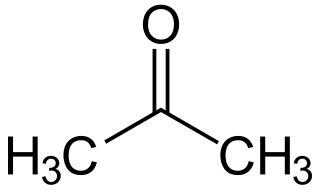
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.
The Robinson annulation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry for ring formation. It was discovered by Robert Robinson in 1935 as a method to create a six membered ring by forming three new carbon–carbon bonds. The method uses a ketone and a methyl vinyl ketone to form an α,β-unsaturated ketone in a cyclohexane ring by a Michael addition followed by an aldol condensation. This procedure is one of the key methods to form fused ring systems.
In organic chemistry, hydrocyanation is a process for conversion of alkenes to nitriles. The reaction involves the addition of hydrogen cyanide and requires a catalyst. This conversion is conducted on an industrial scale for the production of precursors to nylon.
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation.
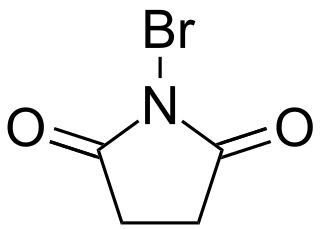
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent used in radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry. NBS can be a convenient source of Br•, the bromine radical.

Palladium(II) acetate is a chemical compound of palladium described by the formula [Pd(O2CCH3)2]n, abbreviated [Pd(OAc)2]n. It is more reactive than the analogous platinum compound. Depending on the value of n, the compound is soluble in many organic solvents and is commonly used as a catalyst for organic reactions.
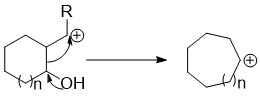
Ring expansion and ring contraction reactions expand or contract rings, usually in organic chemistry. The term usually refers to reactions involve making and breaking C-C bonds, Diverse mechanisms lead to these kinds of reactions.

The Danishefsky Taxol total synthesis in organic chemistry is an important third Taxol synthesis published by the group of Samuel Danishefsky in 1996 two years after the first two efforts described in the Holton Taxol total synthesis and the Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis. Combined they provide a good insight in the application of organic chemistry in total synthesis.
The Ramberg–Bäcklund reaction is an organic reaction converting an α-halo sulfone into an alkene in presence of a base with extrusion of sulfur dioxide. The reaction is named after the two Swedish chemists Ludwig Ramberg and Birger Bäcklund. The carbanion formed by deprotonation gives an unstable episulfone that decomposes with elimination of sulfur dioxide. This elimination step is considered to be a concerted cheletropic extrusion.

Schwartz's reagent is the common name for the organozirconium compound with the formula (C5H5)2ZrHCl, sometimes called zirconocene hydrochloride or zirconocene chloride hydride, and is named after Jeffrey Schwartz, a chemistry professor at Princeton University. This metallocene is used in organic synthesis for various transformations of alkenes and alkynes.
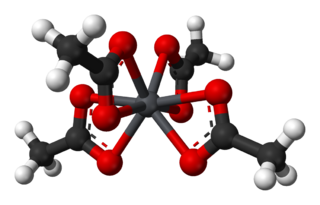
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is an metalorganic compound with chemical formula Pb(C2H3O2)4. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar, organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis.
The Wulff–Dötz reaction (also known as the Dötz reaction or the benzannulation reaction of the Fischer carbene complexes) is the chemical reaction of an aromatic or vinylic alkoxy pentacarbonyl chromium carbene complex with an alkyne and carbon monoxide to give a Cr(CO)3-coordinated substituted phenol. Several reviews have been published. It is named after the German chemist Karl Heinz Dötz (b. 1943) and the American chemist William D. Wulff (b. 1949) at Michigan State University. The reaction was first discovered by Karl Dötz and was extensively developed by his group and W. Wulff's group. They subsequently share the name of the reaction.

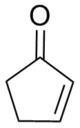
Cyclohexenone is an organic compound which is a versatile intermediate used in the synthesis of a variety of chemical products such as pharmaceuticals and fragrances. It is colorless liquid, but commercial samples are often yellow.
Selenoxide elimination is a method for the chemical synthesis of alkenes from selenoxides. It is most commonly used to synthesize α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds from the corresponding saturated analogues. It is mechanistically related to the Cope reaction.
The Saegusa–Ito oxidation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry. It was discovered in 1978 by Takeo Saegusa and Yoshihiko Ito as a method to introduce α-β unsaturation in carbonyl compounds. The reaction as originally reported involved formation of a silyl enol ether followed by treatment with palladium(II) acetate and benzoquinone to yield the corresponding enone. The original publication noted its utility for regeneration of unsaturation following 1,4-addition with nucleophiles such as organocuprates.
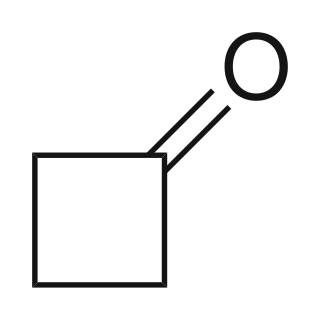
Cyclobutanone is an organic compound with molecular formula (CH2)3CO. It is a four-membered cyclic ketone (cycloalkanone). It is a colorless volatile liquid at room temperature. Since cyclopropanone is highly sensitive, cyclobutanone is the smallest easily handled cyclic ketone.
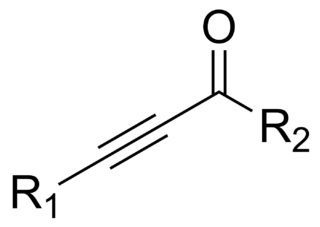
In organic chemistry, an ynone is an organic compound containing a ketone functional group and a C≡C triple bond. Many ynones are α,β-ynones, where the carbonyl and alkyne groups are conjugated. Capillin is a naturally occurring example. Some ynones are not conjugated.

α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds are organic compounds with the general structure (O=CR)−Cα=Cβ−R. Such compounds include enones and enals, but also carboxylic acids and the corresponding esters and amides. In these compounds, the carbonyl group is conjugated with an alkene. Unlike the case for carbonyls without a flanking alkene group, α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are susceptible to attack by nucleophiles at the β-carbon. This pattern of reactivity is called vinylogous. Examples of unsaturated carbonyls are acrolein (propenal), mesityl oxide, acrylic acid, and maleic acid. Unsaturated carbonyls can be prepared in the laboratory in an aldol reaction and in the Perkin reaction.
In organic chemistry, methylenation is a chemical reaction that inserts a methylene group into a chemical compound: