The molecular formula C6H6 (molar mass: 78.114 [1] )
- Benzene
- Benzvalene
- Bicyclopropenyl
- 1,2,3-Cyclohexatriene
- Dewar benzene
- Fulvene
- Prismane
- [3]Radialene
- 3-Methylidenepent-1-en-4-yne
- Hexadiyne
- Hexadienyne
Historical and hypothetical compounds:
The molecular formula C6H6 (molar mass: 78.114 [1] )
Historical and hypothetical compounds:
Benzol may refer to:

In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.
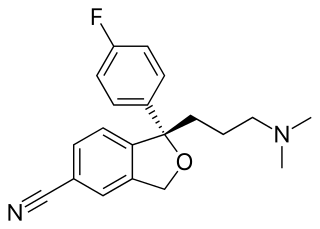
The skeletal formula, or line-angle formula or shorthand formula, of an organic compound is a type of molecular structural formula that serves as a shorthand representation of a molecule's bonding and some details of its molecular geometry. A skeletal formula shows the skeletal structure or skeleton of a molecule, which is composed of the skeletal atoms that make up the molecule. It is represented in two dimensions, as on a piece of paper. It employs certain conventions to represent carbon and hydrogen atoms, which are the most common in organic chemistry.

Cyclooctadecanonaene or [18]annulene is an organic compound with chemical formula C
18H
18. It belongs to the class of highly conjugated compounds known as annulenes and is aromatic. The usual isomer that [18]annulene refers to is the most stable one, containing six interior hydrogens and twelve exterior ones, with the nine formal double bonds in the cis,trans,trans,cis,trans,trans,cis,trans,trans configuration. It is reported to be a red-brown crystalline solid.

In organic chemistry, dimethoxybenzene is an organic compound which is derived from benzene by substituting two methoxy groups. Dimethoxybenzene comes in three structural isomers:

Trichlorobenzene (TCB) may refer to any of three isomeric chlorinated derivatives of benzene with the molecular formula C6H3Cl3. Trichlorobenzenes are man-made chemical compounds that occur in three different forms. Even though the forms have the same molecular weight and molecular formulae, they are structurally different by the positions of the chlorine atoms attached to the benzene ring. 1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene and 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene are colorless solids, but 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene is a colorless oil. The isomers may also have different chemical and toxicological properties.
The molecular formula C6H6O2 (molar mass: 110.1 g/mol) may refer to:
Dioxin may refer to:
The hexynes are a subgroup from the group of alkynes. It consists of several isomeric compounds having the formula C6H10.
The molecular formula C10H14 may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H10 may refer to:
The molecular formula C9H12 may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H4Cl2 (molar mass: 147.00 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H4 may refer to:

Tetrahydroxybenzenes or Benzenetetrols are a group of organic compounds which are tetrahydroxy derivatives of benzene. Tetrahydroxybenzene comes in three isomers:
The molecular formula C9H6O6 may refer to:

The C4-benzenes are a class of organic aromatic compounds which contain a benzene ring and four other carbon atoms. There are three tetramethylbenzenes, six dimethylethylbenzenes, three diethylbenzenes, three isopropylmethylbenzenes, three n-propylmethylbenzenes and four butylbenzenes. The saturated compounds have formula C10H14 and molecular weight 134.22 g/mol. C4-benzenes are found in petroleum. Petrol (gasoline) can contain 5-8% C4-benzenes.
The molecular formula C6H4N2S may refer to:

1,2,3-Cyclohexatriene is an unstable chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. It is an unusual isomer of benzene in which the three double bonds are cumulated.