UC San Diego Health is the academic health system of the University of California, San Diego in San Diego, California. It is the only academic health system serving San Diego and has one of three adult Level I trauma centers in the region. In operation since 1966, it comprises three major hospitals: UC San Diego Medical Center in Hillcrest, Jacobs Medical Center in La Jolla, and UC San Diego Health East Campus Medical Center in East County. The La Jolla campus also includes the Moores Cancer Center, Shiley Eye Institute, Sulpizio Cardiovascular Center, and Koman Family Outpatient Pavilion, and the health system also includes several outpatient sites located throughout San Diego County. UC San Diego Health works closely with the university's School of Medicine and Skaggs School of Pharmacy to provide training to medical and pharmacy students and advanced clinical care to patients.

Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory status, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug. The entire process—from concept through preclinical testing in the laboratory to clinical trial development, including Phase I–III trials—to approved vaccine or drug typically takes more than a decade.

The Children's Tumor Foundation (CTF) is a 501(c)(3) foundation dedicated to improving the health and well-being of individuals and families affected by NF, a group of genetic conditions known as neurofibromatosis or schwannomatosis. Their four-part mission includes propelling drug research and development through a series of strategic investments, strengthening patient support, increasing public awareness of NF and establishing best practices in clinical care for affected individuals. The Foundation is incorporated in all 50 states with active chapters and affiliates in 37 states. CTF is the largest private funder of all forms of NF research.

The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) is a unique pan-European non-profit clinical cancer research organisation established in 1962 operating as an international association under Belgium law. It develops, conducts, coordinates and stimulates high-quality translational and clinical trial research to improve the survival and quality of life of cancer patients. This is achieved through the development of new drugs and other innovative approaches, and the testing of more effective therapeutic strategies, using currently approved drugs, surgery and/or radiotherapy in clinical trials conducted under the auspices of a vast network of clinical cancer researchers supported by 220 staff members based in Brussels. The EORTC has the expertise to conduct large and complex trials especially specific populations such as the older patient and rare tumours.
Clinical research is a branch of medical research that involves people and aims to determine the effectiveness (efficacy) and safety of medications, devices, diagnostic products, and treatment regimens intended for improving human health. These research procedures are designed for the prevention, treatment, diagnosis or understanding of disease symptoms.

The mission of the Multiple Myeloma Research Consortium (MMRC) is to champion collaboration with and integration across academia and industry and to focus on speed and innovation to bring the most promising multiple myeloma treatments to patients faster. It was founded by Kathy Giusti, a myeloma patient and founder and chief executive officer of the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation (MMRF).
Milatuzumab is an anti-CD74 humanized monoclonal antibody for the treatment of multiple myeloma non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Translational research is research aimed at translating (converting) results in basic research into results that directly benefit humans. The term is used in science and technology, especially in biology and medical science. As such, translational research forms a subset of applied research.
The Translational Centre for Regenerative Medicine (TRM) is a central scientific institution of the University of Leipzig. It focusses on the development of diagnostic and therapeutic concepts in the field of regenerative medicine and their implementation into a clinical setting.

Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors are a class of medical drugs that are mainly used to treat advanced cancers. They function by inhibiting one or more of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes, which are part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This signal pathway regulates cellular functions such as growth and survival. It is strictly regulated in healthy cells, but is always active in many cancer cells, allowing the cancer cells to better survive and multiply. PI3K inhibitors block the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and thus slow down cancer growth. They are examples of a targeted therapy. While PI3K inhibitors are an effective treatment, they can have very severe side effects and are therefore only used if other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Critical Path Institute (C-Path) is a non-profit organization created to improve the drug development process; its consortia include more than 1,600 scientists from government regulatory and research agencies, academia, patient organizations, and bio-pharmaceutical companies.
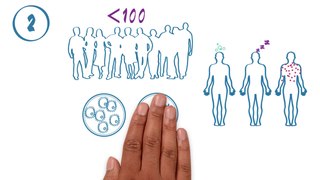
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for drug safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays.
Gilles Salles is a French haematologist who joined the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York in 2020 after a career as a French University Professor & Medical Doctor in Lyon University Hospitals (France). He is specialized in hematologic malignancies, in particular non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphomas.

Copanlisib, sold under the brand name Aliqopa, is a medication used for the treatment of adults experiencing relapsed follicular lymphoma who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.
Polatuzumab vedotin, sold under the brand name Polivy, is a CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate medication used for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (cancer). It was developed by the Genentech subsidiary of Roche.

Venetoclax, sold under the brand names Venclexta and Venclyxto, is a medication used to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), or acute myeloid leukemia (AML).

Cancer Breakthroughs 2020, also known as Cancer Moonshot 2020 is a coalition with the goal of finding vaccine-based immunotherapies against cancer. By pooling the resources of multinational pharmaceutical, biotechnology companies, academic centers and oncologists, it intends to create access to over 60 novel and approved agents under exploration in the war against cancer and is expected to enable rapid testing of novel immunotherapy combination protocols. The initiative is being managed by a consortium of companies called The National Immunotherapy Coalition.
David G. Maloney is an oncologist and researcher at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the University of Washington who specializes in developing targeted immunotherapies for the treatment of blood cancers.
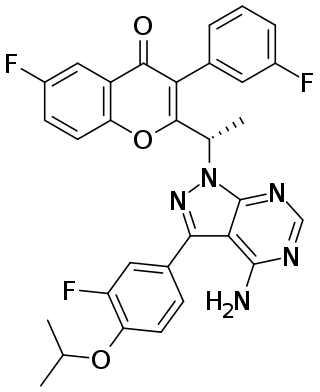
Umbralisib, sold under the brand name Ukoniq, is an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) and follicular lymphoma (FL). It is taken by mouth.

COVID-19 drug development is the research process to develop preventative therapeutic prescription drugs that would alleviate the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). From early 2020 through 2021, several hundred drug companies, biotechnology firms, university research groups, and health organizations were developing therapeutic candidates for COVID-19 disease in various stages of preclinical or clinical research, with 419 potential COVID-19 drugs in clinical trials, as of April 2021.










