Related Research Articles

Air Canada Flight 143 was a Canadian scheduled domestic passenger flight between Montreal and Edmonton that ran out of fuel on July 23, 1983, at an altitude of 41,000 feet (12,000 m), midway through the flight. The crew was able to glide the Boeing 767 aircraft safely to an emergency landing at a former Royal Canadian Air Force base in Gimli, Manitoba, that had been turned into a motor racing track. This unusual aviation incident earned the aircraft the nickname "Gimli Glider".

The Cessna L-19/O-1 Bird Dog is a liaison and observation aircraft. It was the first all-metal fixed-wing aircraft ordered for and by the United States Army following the Army Air Forces' separation from it in 1947. The Bird Dog had a lengthy career in the U.S. military, as well as in other countries.

The Royal Canadian Air Cadets is a Canadian national youth program for young individuals aged 12 to 19. Under the authority of the National Defence Act, the program is administered by the Canadian Forces (CF) and funded through the Department of National Defence (DND). Additional support is provided by the civilian Air Cadet League of Canada (ACL). Together with the Royal Canadian Sea Cadets and Royal Canadian Army Cadets, it forms the "largest federally funded youth program in the country". Cadets are not members of the military and are not obliged to join the Canadian Forces.

Debert is an unincorporated farming community in Nova Scotia, Canada. Located in the central-western part of Colchester County, it is approximately 20 km (12 mi) west of Truro.

The Cadet Instructors Cadre (CIC) Branch consists of approximately 7,500 Canadian Forces (CF) officers whose primary duty is the safety, supervision, administration and training of Royal Canadian Sea, Army, and Air Cadets. The Branch is the largest single group within the Canadian Forces reserve force subcomponent Cadet Organizations Administration and Training Service (COATS) and is the largest officer branch in the Canadian Forces. The COATS subcomponent of the Reserve Force employs members from all branches and occupations of the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force of the Canadian Forces.

The Grob G 115 is a general aviation fixed-wing aircraft, primarily used for flight training. It is built in Germany by Grob Aircraft. The E variant with a 3-blade variable pitch propeller is in service with the Finnish Air Force, the Royal Navy and Army Air Corps for Flying Grading and in the Royal Air Force as part of No. 6 Flying Training School which provides flying to both University Air Squadrons and Air Experience Flights to Cadets from the Air Training Corps and Combined Cadet Force.

Alan Derek Piggott was one of Britain's best known glider pilots and instructors. He had over 5,000 hours on over 153 types of powered aircraft and over 5,000 hours on over 184 types of glider. He was honoured for his work on the instruction and safety of glider pilots. In 1961 he became the first person to make an officially authenticated take-off and flight in a man-powered aircraft. He also worked as a stunt pilot in several feature films.

Canadian Forces Base Comox, commonly referred to as CFB Comox or 19 Wing is a Canadian Forces Base located 2.5 nautical miles north northeast of Comox, British Columbia. It is primarily operated as an air force base by the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and is one of two bases in the country using the CP-140 Aurora anti-submarine/maritime patrol and surveillance aircraft. Its primary RCAF lodger unit is 19 Wing, commonly referred to as 19 Wing Comox.

Debert Airport is located near Debert, Nova Scotia, Canada and has three runways.

The Roland-Désourdy Airport is located 3.4 nautical miles west-southwest of Bromont, Quebec, Canada.
The officer ranks of the Royal Air Force, as they are today, were introduced in 1919. Prior to that Army ranks were used.

Military gliders have been used by the militaries of various countries for carrying troops and heavy equipment to a combat zone, mainly during the Second World War. These engineless aircraft were towed into the air and most of the way to their target by military transport planes, e.g., C-47 Skytrain or Dakota, or bombers relegated to secondary activities, e.g., Short Stirling. Most military gliders do not soar, although there were attempts to build military sailplanes as well, such as the DFS 228.

The TG-10 is the military designation for the Blanik, Super Blaník and Blanik L-33 Solo Czechoslovakian sailplanes used for basic flight training at the United States Air Force Academy. The Academy maintained an inventory of 21 TG-10s, in these three variants, until 2012. The aircraft were flown by cadets and officers of the 94th Flying Training Squadron, 306th Flying Training Group, Nineteenth Air Force, Air Education and Training Command.

The Grob G109 is a light aircraft developed by Grob Aircraft AG of Mindelheim Mattsies in Germany. It first flew in 1980 the G109B followed in 1984. It is a two-seat self-launching motor glider in which the pilot and passenger or student sit side by side, with good visibility provided by large windows.

The Schweizer SGS 2-33 is an American two-seat, high-wing, strut-braced, training glider that was built by Schweizer Aircraft of Elmira, New York.
The Air Cadet Gliding Program is a youth gliding program operated by the Canadian Forces (CF) and the Air Cadet League of Canada for the benefit of the Royal Canadian Air Cadets.

During World War II civilian flying schools, under government contract, provided a considerable part of the flying training effort undertaken by the United States Army Air Forces.
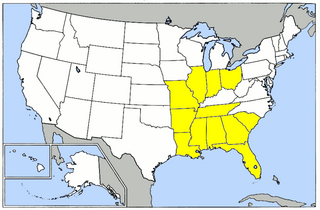
Army Air Forces Eastern Flying Training Command (EFTC) was a unit of the United States Army Air Forces. It was assigned to the Army Air Forces Training Command, stationed at Maxwell Field, Alabama. It was inactivated on 15 December 1945.

Markham Airport or Toronto/Markham Airport,, is a private aerodrome operating 2.6 nautical miles north of Markham, Ontario, Canada near Toronto.

No.2 Flying Training School is a Flying Training School (FTS) of the Royal Air Force (RAF). It is part of No. 22 (Training) Group that delivers glider flying training to the Royal Air Force Air Cadets. Its headquarters is located at RAF Syerston in Nottinghamshire and gliding takes places from several sites throughout the UK using the Grob Viking T1. The RAF Central Gliding School is also under its command.
References
- 1 2 Royal Canadian Air Cadets: Gliding Volume 1 General Information of Air Cadet Glider Pilots, page 3-21. Department of National Defence, November 1975. CCP 1242 (A)(1)