Related Research Articles

Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms. Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called medical oncology.
Fluorouracil, sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. As a cream it is used for actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and skin warts.

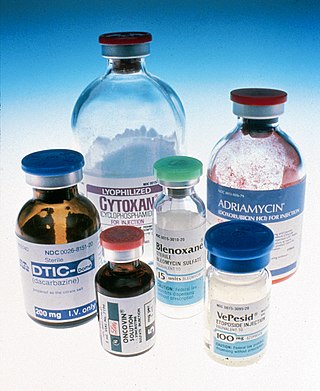
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.
The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.

Capecitabine, sold under the brand name Xeloda among others, is a anticancer medication used to treat breast cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. For breast cancer it is often used together with docetaxel. It is taken by mouth.

Epirubicin is an anthracycline drug used for chemotherapy. It can be used in combination with other medications to treat breast cancer in patients who have had surgery to remove the tumor. It is marketed by Pfizer under the trade name Ellence in the US and Pharmorubicin or Epirubicin Ebewe elsewhere.
FOLFOX is a chemotherapy regimen for treatment of colorectal cancer, made up of the drugs folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin.
CHOP is the acronym for a chemotherapy regimen used in the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. CHOP consists of:
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in cancer therapy have led the term to be used mainly to describe adjuvant cancer treatments. An example of such adjuvant therapy is the additional treatment usually given after surgery where all detectable disease has been removed, but where there remains a statistical risk of relapse due to the presence of undetected disease. If known disease is left behind following surgery, then further treatment is not technically adjuvant.
Post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment (PCCI) describes the cognitive impairment that can result from chemotherapy treatment. Approximately 20 to 30% of people who undergo chemotherapy experience some level of post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment. The phenomenon first came to light because of the large number of breast cancer survivors who complained of changes in memory, fluency, and other cognitive abilities that impeded their ability to function as they had pre-chemotherapy.

Breast cancer chemotherapy refers to the use of cytotoxic drugs (chemotherapy) in the treatment of breast cancer.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is any breast cancer that either lacks or shows low levels of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression and/or gene amplification. Triple-negative is sometimes used as a surrogate term for basal-like.
Hyper-CVAD is a chemotherapy regimen used to treat some forms of leukemia, high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and lymphoblastic leukemia.
Tegafur/uracil is a chemotherapy drug combination used in the treatment of cancer, primarily bowel cancer. It is also called UFT or UFUR.
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) is a common side-effect of many cancer treatments. Nausea and vomiting are two of the most feared cancer treatment-related side effects for cancer patients and their families. In 1983, Coates et al. found that patients receiving chemotherapy ranked nausea and vomiting as the first and second most severe side effects, respectively. Up to 20% of patients receiving highly emetogenic agents in this era postponed, or even refused, potentially curative treatments. Since the 1990s, several novel classes of antiemetics have been developed and commercialized, becoming a nearly universal standard in chemotherapy regimens, and helping to better manage these symptoms in a large portion of patients. Efficient mediation of these unpleasant and sometimes debilitating symptoms results in increased quality of life for the patient, and better overall health of the patient, and, due to better patient tolerance, more effective treatment cycles.
High-dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant (HDC/BMT), also high-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow transplant, was an ineffective treatment regimen for metastatic breast cancer, and later high-risk breast cancer, that was considered promising during the 1980s and 1990s. With an overall idea that more is better, this process involved taking cells from the person's bone marrow to store in a lab, then to give such high doses of chemotherapy drugs that the remaining bone marrow was destroyed, and then to inject the cells taken earlier back into the body as replacement. It was ultimately determined to be no more effective than normal treatment, and to have significantly higher side effects, including treatment-related death.

Min Chiu Li was a Chinese-American oncologist and cancer researcher. Li was the first scientist to use chemotherapy to cure widely metastatic, malignant cancer.
This is a historical timeline of the development and progress of cancer treatments, which includes time of discovery, progress, and approval of the treatments.

Doxifluridine is a second generation nucleoside analog prodrug developed by Roche and used as a cytostatic agent in chemotherapy in several Asian countries including China and South Korea. Doxifluridine is not FDA-approved for use in the USA. It is currently being evaluated in several clinical trials as a stand-alone or combination therapy treatment.
Metronomic therapy is a new type of chemotherapy in which anti-cancer drugs are administered in a lower dose than the maximum tolerated dose repetitively over a long period to treat cancers with fewer side effects. Metronomic therapy is shown to affect both tumor microenvironment and tumor cells to achieve its therapeutic effects. Metronomic therapy is also cost-effective as a lower dose is used compared to conventional chemotherapy. The use of metronomic therapy has been extensively investigated and can be advantageous in selected group of patients. Yet, more clinical trials are necessary to generalize the method.
References
- ↑ Kimmick GG, Cirrincione C, Duggan DB, et al. (2008). "Fifteen-year median follow-up results after neoadjuvant doxorubicin, followed by mastectomy, followed by adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil (CMF) followed by radiation for stage III breast cancer: a phase II trial (CALGB 8944)". Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 113 (3): 479–90. doi:10.1007/s10549-008-9943-2. PMC 4217205 . PMID 18306034.
- ↑ Ferreira Filho AF, Di Leo A, Paesmans M, et al. (2002). "The feasibility of classical cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil (CMF) for pre- and post-menopausal node-positive breast cancer patients in a Belgian multicentric trial: a study of consistency in relative dose intensity (RDI) and cumulative doses across institutions". Annals of Oncology. 13 (3): 416–421. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdf051 . PMID 11996473.
- 1 2 "CMF (cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil)". UK: Breakthrough Breast Cancer. Archived from the original on 2009-01-06. Retrieved 2008-10-13.