Related Research Articles

Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) is a hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy of the peripheral nervous system characterized by progressive loss of muscle tissue and touch sensation across various parts of the body. This disease is the most commonly inherited neurological disorder, affecting about one in 2,500 people. It is named after those who classically described it: the Frenchman Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893), his pupil Pierre Marie (1853–1940), and the Briton Howard Henry Tooth (1856–1925).

X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation, see zygosity. Females with one copy of the mutated gene are carriers.
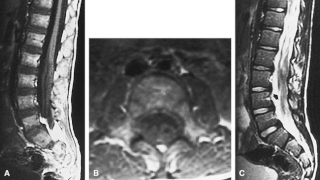
Dejerine–Sottas disease, also known as, Dejerine–Sottas syndrome, hereditary motor and sensory polyneuropathy type III, and Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 3, is a hereditary neurological disorder characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves, demyelination, and resulting progressive muscle wasting and somatosensory loss. The condition is caused by mutations in various genes and currently has no known cure.

Myelin protein zero is a single membrane glycoprotein which in humans is encoded by the MPZ gene. P0 is a major structural component of the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Myelin protein zero is expressed by Schwann cells and accounts for over 50% of all proteins in the peripheral nervous system, making it the most common protein expressed in the PNS. Mutations in myelin protein zero can cause myelin deficiency and are associated with neuropathies like Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and Dejerine–Sottas disease.
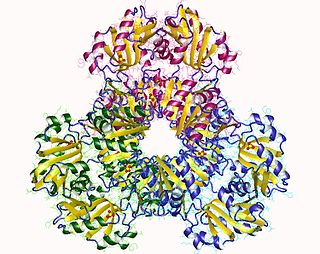
Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase is an enzyme that converts ribose 5-phosphate into phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP). It is classified under EC 2.7.6.1.

Gap junction beta-1 protein (GJB1), also known as connexin 32 (Cx32), is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the GJB1 gene. Gap junction beta-1 protein is a member of the gap junction connexin family of proteins that regulates and controls the transfer of communication signals across cell membranes, primarily in the liver and peripheral nervous system. However, the protein is expressed in multiple organs, including in oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system.

Glycine—tRNA ligase also known as glycyl–tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GARS1 gene.

Peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22), also called Growth arrest-specific protein 3 (GAS-3), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PMP22 gene. Mutations in PMP22 cause changes in the expression of peripheral myelin protein 22 which can result in several neuropathies.

Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LITAF gene.

Ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein 1 is a type of protein that in humans is encoded by the GDAP1 gene.

Periaxin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRX gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 2 also known as phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase or phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate phosphatase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR2 gene.

SH3 domain and tetratricopeptide repeats-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SH3TC2 gene. It is believed to be expressed in the Schwann cells that wrap the myelin sheath around nerves.

Myotubularin-related protein 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SBF2 gene.

Neurofilament light polypeptide, also known as neurofilament light chain, abbreviated to NF-L or Nfl and with the HGNC name NEFL is a member of the intermediate filament protein family. This protein family consists of over 50 human proteins divided into 5 major classes, the Class I and II keratins, Class III vimentin, GFAP, desmin and the others, the Class IV neurofilaments and the Class V nuclear lamins. There are four major neurofilament subunits, NF-L, NF-M, NF-H and α-internexin. These form heteropolymers which assemble to produce 10 nm neurofilaments which are only expressed in neurons where they are major structural proteins, particularly concentrated in large projection axons. Axons are particularly sensitive to mechanical and metabolic compromise and as a result axonal degeneration is a significant problem in many neurological disorders. The detection of neurofilament subunits in CSF and blood has therefore become widely used as a biomarker of ongoing axonal compromise. The NF-L protein is encoded by the NEFL gene. Neurofilament light chain is a biomarker that can be measured with immunoassays in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma and reflects axonal damage in a wide variety of neurological disorders. It is a useful marker for disease monitoring in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and more recently Huntington's disease. It is also promising marker for follow-up of patients with brain tumors. Higher levels of blood or CSF NF-L have been associated with increased mortality, as would be expected as release of this protein reflects ongoing axonal loss. Recent work performed as a collaboration between EnCor Biotechnology Inc. and the University of Florida showed that the NF-L antibodies employed in the most widely used NF-L assays are specific for cleaved forms of NF-L generated by proteolysis induced by cell death. Methods used in different studies for NfL measurement are sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), electrochemiluminescence, and high-sensitive single molecule array (SIMOA).

Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies (HMSN) is a name sometimes given to a group of different neuropathies which are all characterized by their impact upon both afferent and efferent neural communication. HMSN are characterised by atypical neural development and degradation of neural tissue. The two common forms of HMSN are either hypertrophic demyelinated nerves or complete atrophy of neural tissue. Hypertrophic condition causes neural stiffness and a demyelination of nerves in the peripheral nervous system, and atrophy causes the breakdown of axons and neural cell bodies. In these disorders, a patient experiences progressive muscle atrophy and sensory neuropathy of the extremities.

Neurofilament, heavy polypeptide (NEFH) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NEFH gene.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, X-linked 3 (dominant) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CMTX3 gene.
X-linked Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease is a group of genetic disorders and a type of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease characterized by sensory loss associated with muscle weakness and atrophy alongside many other symptoms.
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, X-linked 2 (recessive)" . Retrieved 2014-02-23.
- ↑ "CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH DISEASE, X-LINKED RECESSIVE, 2; CMTX2". Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Retrieved 2024-10-17.